Abstract
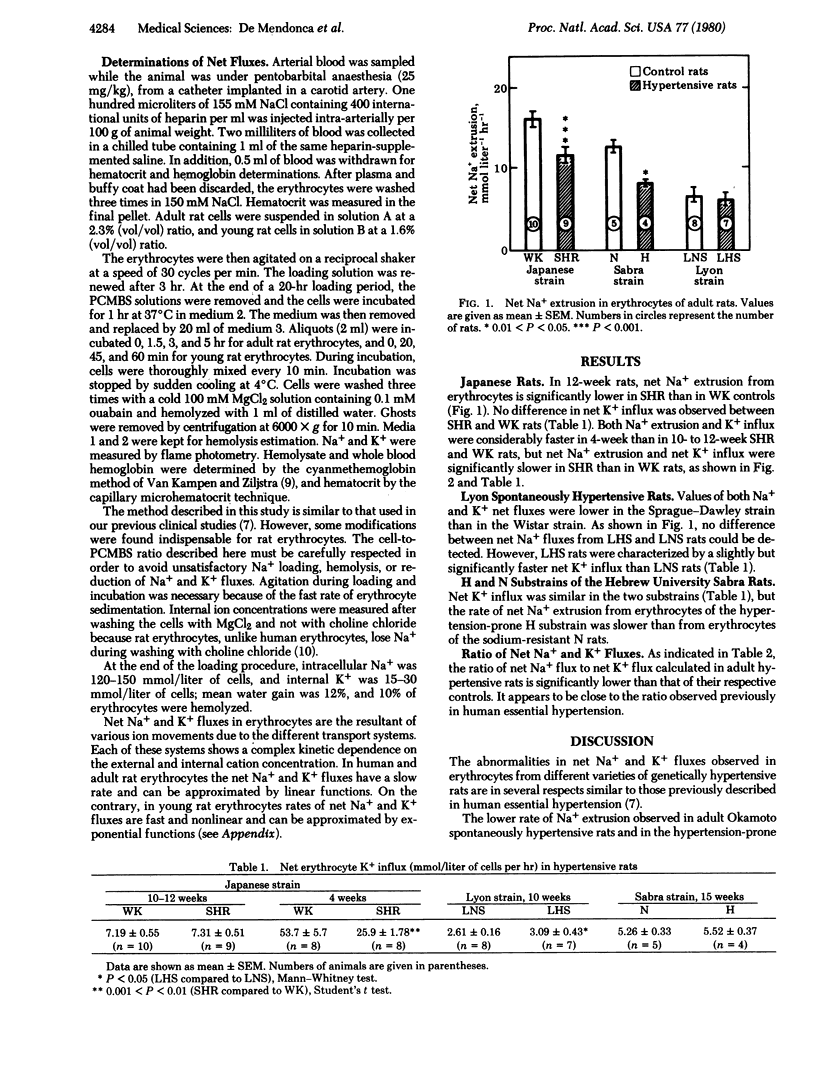
Net Na+ and K+ fluxes were measured in Na+-loaded and K+-depleted erythrocytes of three varieties of genetically hypertensive rats. In Okamoto spontaneously hypertensive rats (4 and 10-12 weeks of age), Na+ extrusion was reduced as compared to normotensive controls (Wistar/Kyoto). Na+ extrusion was also reduced in the hypertension-prone substrain of the Hebrew University Sabra rats as compared to the Na+-resistant substrain. K+ fluxes were similar in both groups. In both Okamoto spontaneously hypertensive rats and the hypertension-prone substrain, hypertension was severe and developed rapidly. In the Lyon spontaneously hypertensive rats, in which the blood pressure elevation is less severe than in other genetically hypertensive rats, erythrocyte net Na+ extrusion was the same as in normotensive controls, but net K+ gain was slightly increased. These erythrocyte abnormalities, observed in three varieties of genetically transmitted hypertension of the rat, are in several aspects similar to those previously described in accelerated and benign human essential hypertension. Erythrocyte Na+ and K+ net flux alterations may thus represent biochemical markers of primary hypertension.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaugé L. A., Ortíz O. Sodium and rubidium fluxes in rat red blood cells. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):533–549. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ishay D., Aviram A., Viskoper R. Increased erythrocytes sodium efflux in genetic hypertensive rats of the Hebrew University strain. Experientia. 1975 Jun 15;31(6):660–662. doi: 10.1007/BF01944615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ishay D., Saliternik R., Welner A. Separation of two strains of rats with inbred dissimilar sensitivity to Doca-salt hypertension. Experientia. 1972 Nov 15;28(11):1321–1322. doi: 10.1007/BF01965321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Sodium ions, calcium ions, blood pressure regulation, and hypertension: a reassessment and a hypothesis. Am J Physiol. 1977 May;232(5):C165–C173. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.232.5.C165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Tellez-Iñon M. T., Hollenberg M. D. Age-related parallel decline in beta-adrenergic receptors, adenylate cyclase and phosphodiesterase activity in rat erythrocyte membranes. Life Sci. 1977 Aug 1;21(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90521-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHL L. K., HEINE M., TASSINARI L. EFFECTS OF CHRONIC EXCESS SALT INGESTION. ROLE OF GENETIC FACTORS IN BOTH DOCA-SALT AND RENAL HYPERTENSION. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:605–617. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. M., Nakashima M., McIndoe R. A., Friedman C. L. Increased erythrocyte permeability to Li and Na in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Experientia. 1976 Apr 15;32(4):476–478. doi: 10.1007/BF01920806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Dagher G., Pernollet M. G., Devynck M. A., Meyer P. Inherited defect in a Na+, K-co-transport system in erythrocytes from essential hypertensive patients. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):281–283. doi: 10.1038/284281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Meyer P. A new test showing abnormal net Na+ and K+ fluxes in erythrocytes of essential hypertensive patients. Lancet. 1979 Feb 17;1(8112):349–353. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92891-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Rega A. F. Cation loading of red blood cells. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):459–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKAMOTO K., AOKI K. Development of a strain of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Jpn Circ J. 1963 Mar;27:282–293. doi: 10.1253/jcj.27.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postnov Y. V., Orlov S. N., Gulak P. V., Shevchenko A. S. Evidence of altered permeability of the erythrocyte membrane for sodium and potassium ions in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1976 Dec;3:169s–172s. doi: 10.1042/cs051169s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMIRK F. H., HALL W. H. Inherited hypertension in rats. Nature. 1958 Sep 13;182(4637):727–728. doi: 10.1038/182727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter H., Selby F. W. Counter-current distribution of red blood cells of slightly different ages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 4;112(1):146–153. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6585(96)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van KAMPEN E., ZIJLSTRA W. G. Standardization of hemoglobinometry. II. The hemiglobincyanide method. Clin Chim Acta. 1961 Jul;6:538–544. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(61)90145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


