Abstract
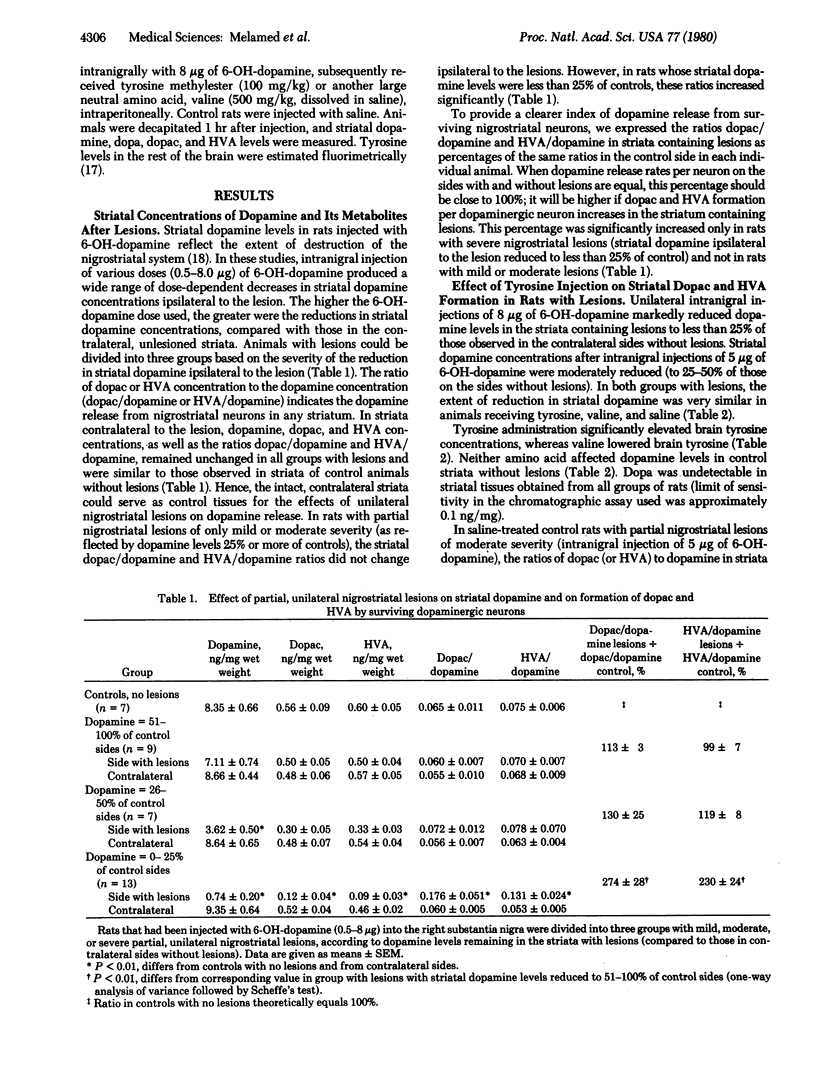
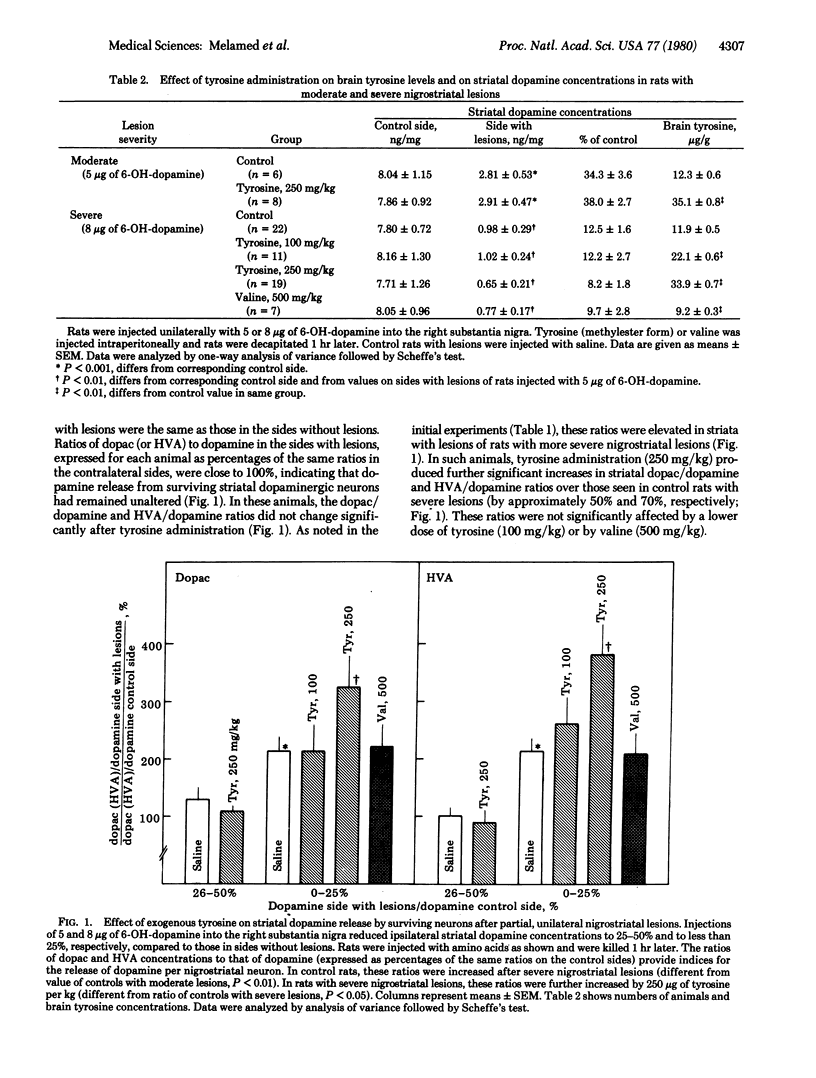
Partial, unilateral nigrostriatal lesions of varying severity were produced in rats by injecting graded doses of 6-hydroxydopamine into the substantia nigra. Formation of the dopamine metabolites dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and homovanillic acid in each surviving nigrostriatal neuron (estimated by the ratios of dihydroxyphenylacetic acid to dopamine and homovanillic acid to dopamine in the striatum) increased significantly when dopamine concentrations in striata containing lesions had been reduced to 25% or less of control values, but remained unchanged in rats with less severe lesions. These findings suggest that, in rats with severe damage of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons, surviving neurons increase their firing rates and accelerate dopamine synthesis and release. In rats that had lesions and enhanced striatal dopamine release, but not in rats with lesser lesions (i.e., which reduced ipsilateral dopamine concentrations by less than 75%), administration of tyrosine (250 mg/kg) caused further significant increases in formation of dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and homovanillic acid. These findings provide further evidence that tyrosine availability can enhance dopamine synthesis in and release from nigrostriatal neurons if the firing rates of these neurons are accelerated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agid Y., Javoy F., Glowinski J. Hyperactivity of remaining dopaminergic neurones after partial destruction of the nigro-striatal dopaminergic system in the rat. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 3;245(144):150–151. doi: 10.1038/newbio245150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer H., Birkmayer W., Hornykiewicz O., Jellinger K., Seitelberger F. Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington. Clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Dec;20(4):415–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer H., Hornykiewicz O. Herabgesetzte Konzentration der Homovanillinsäure im Gehirn von parkinsonkranken Menschen als Ausdruck der Störung des zentralen Dopaminstoffwechsels. Klin Wochenschr. 1965 Jul 1;43(13):711–715. doi: 10.1007/BF01707066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunney B. S., Walters J. R., Roth R. H., Aghajanian G. K. Dopaminergic neurons: effect of antipsychotic drugs and amphetamine on single cell activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Jun;185(3):560–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne D. B. Developments in the pharmacology and therapeutics of parkinsonism. Ann Neurol. 1977 Feb;1(2):111–119. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson A., Lindqvist M. Dependence of 5-HT and catecholamine synthesis on concentrations of precursor amino-acids in rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1978 Jun;303(2):157–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00508062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheramy A., Nieoullon A., Glowinski J. Effects of peripheral and local administration of picrotoxin on the release of newly synthesized 3H-dopamine in the caudate nucleus of the cat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;297(1):31–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00508807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. L., Wurtman R. J. Brain acetylcholine: control by dietary choline. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):561–562. doi: 10.1126/science.1251187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. L., Wurtman R. J. Brain acetylcholine: increase after systemic choline administration. Life Sci. 1975 Apr 1;16(7):1095–1102. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. C., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Decarboxylation to tyramine: a major route of tyrosine metabolism in mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1771–1775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahn S., Calne D. B. Considerations in the management of parkinsonism. Neurology. 1978 Jan;28(1):5–7. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felice L. J., Felice J. D., Kissinger P. T. Determination of catecholamines in rat brain parts by reverse-phase ion-pair liquid chromatography. J Neurochem. 1978 Dec;31(6):1461–1465. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb06573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernstrom J. D., Faller D. V. Neutral amino acids in the brain: changes in response to food ingestion. J Neurochem. 1978 Jun;30(6):1531–1538. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb10489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernstrom J. D., Wurtman R. J. Brain serotonin content: physiological dependence on plasma tryptophan levels. Science. 1971 Jul 9;173(3992):149–152. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3992.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson C. J., Wurtman R. J. Physiological control of brain catechol synthesis by brain tyrosine concentration. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Jun 15;26(12):1137–1142. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson C. J., Wurtman R. J. Physiological control of brain norepinephrine synthesis by brain tyrosine concentration. Life Sci. 1978 Apr 24;22(16):1399–1405. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90633-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTTING G., AXELROD J., PATRICK R. W. Actions of cocaine and tyramine on the uptake and release of H3-norepinephrine in the heart. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Sep;8:246–248. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F. A simple, sensitive method for measuring 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and homovanillic acid in rat brain tissue using high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 27;25(9):775–781. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90522-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornykiewicz O. Dopamine (3-hydroxytyramine) and brain function. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Jun;18(2):925–964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter K. R., Shaw K. M., Laurence D. R., Stern G. M. Sustained levodopa therapy in parkinsonism. Lancet. 1973 Oct 27;2(7835):929–931. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92595-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korf J., Grasdijk L., Westerink B. H. Effects of electrical stimulation of the nigrostriatal pathway of the rat on dopamine metabolism. J Neurochem. 1976 Mar;26(3):579–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb01514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesser R. P., Fahn S., Snider S. R., Cote L. J., Isgreen W. P., Barrett R. E. Analysis of the clinical problems in parkinsonism and the complications of long-term levodopa therapy. Neurology. 1979 Sep;29(9 Pt 1):1253–1260. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.9_part_1.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markovitz D. C., Fernstrom J. D. Diet and uptake of aldomet by the brain: competition with natural large neutral amino acids. Science. 1977 Sep 2;197(4307):1014–1015. doi: 10.1126/science.887937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer E. G., Fibiger H. C., McGeer P. L., Brooke S. Temporal changes in amine synthesizing enzymes of rat extrapyramidal structures after hemitransections or 6-hydroxydopamine administration. Brain Res. 1973 Mar 30;52:289–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90665-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mena I., Cotzias G. C. Protein intake and treatment of Parkinson's disease with levodopa. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jan 23;292(4):181–184. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197501232920404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A., Wurtman R. J. Catecholamines and neurologic diseases (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Aug 7;293(6):274–280. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197508072930605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H. Brain uptake of radiolabeled amino acids, amines, and hexoses after arterial injection. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1629–1639. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racagni G., Bruno F., Cattabeni F., Maggi A., Di Giulio A. M., Parenti M., Groppetti A. Functional interaction between rat substantia nigra and striatum: GABA and dopamine interrelation. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 7;134(2):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinne U. K., Sonninen V., Hyyppä M. Effect of L-dopa on brain monoamines and their metabolites in Parkinson's disease. Life Sci I. 1971 May 15;10(10):549–557. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. H., Murrin L. C., Walters J. R. Central dopaminergic neurons: effects of alterations in impulse flow on the accumulation of dihydroxyphenylacetic acid. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;36(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scally M. C., Ulus I., Wurtman R. J. Brain tyrosine level controls striatal dopamine synthesis in haloperidol-treated rats. J Neural Transm. 1977;41(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF01252960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo C., Javoy F., Agid Y., Glowinski J. Injection of 6-hydroxydopamine in the substantia nigra of the rat. I. Morphological study. Brain Res. 1973 Aug 30;58(2):269–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sved A. F., Fernstrom J. D., Wurtman R. J. Tyrosine administration decreases serum prolactin levels in chronically reserpinized rats. Life Sci. 1979 Oct 8;25(15):1293–1299. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90394-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sved A. F., Fernstrom J. D., Wurtman R. J. Tyrosine administration reduces blood pressure and enhances brain norepinephrine release in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3511–3514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAALKES T. P., UDENFRIEND S. A fluorometric method for the estimation of tyrosine in plasma and tissues. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Nov;50(5):733–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurtman R. J., Larin F., Mostafapour S., Fernstrom J. D. Brain catechol synthesis: control by train tyrosine concentration. Science. 1974 Jul 12;185(4146):183–184. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4146.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



