Abstract
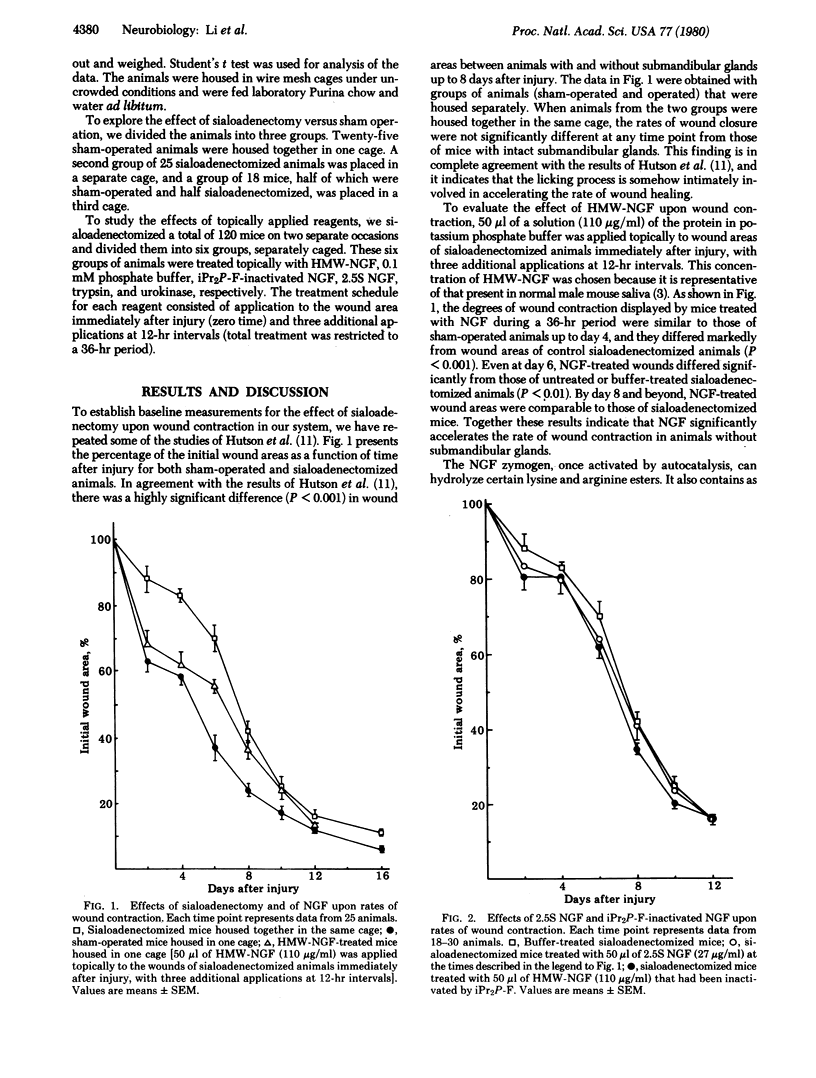
Earlier studies have shown that removal of the submandibular glands of mice retards the rate of contraction of experimentally induced wounds and that communal licking of wounds accelerates contraction in intact animals [Hutson, J. M., Niall, M., Evans, D. & Fowler, R. (1979) Nature (London) 279, 793-795]. In the light of the observation that nerve growth factor (NGF) is secreted in high concentrations in mouse saliva, we have studied the effect of topically applied high molecular weight nerve growth factor (HMW-NGF) upon the rate of wound contraction in sialoadenectomized animals. Results show that HMW-NGF significantly accelerates the rate of wound contraction and that this phenomenon is probably dependent upon the enzymic activity of the protein. Neither diisopropyl fluorophosphate-inactivated NGF nor 2.5S NGF [isolated according to Bocchini, V. & Angeletti, P. U. (1969) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 64, 787-794] displays this biological activity. Thus, it may be that one of the physiological roles of NGF in saliva is to promote wound healing by the licking process.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Shooter E. M., Varon S. Enzymatic activities of mouse nerve growth factor and its subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1383–1388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson J. M., Niall M., Evans D., Fowler R. Effect of salivary glands on wound contraction in mice. Nature. 1979 Jun 28;279(5716):793–795. doi: 10.1038/279793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. A., Saide J. D., Blanchard M. H., Young M. Molecular properties of the nerve growth factor secreted in mouse saliva. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2672–2676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. A., Saide J. D., Blanchard M. H., Young M. Nerve growth factor in mouse serum and saliva: role of the submandibular gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2330–2333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein N. S., Dvorak H. F., Blanchard M. H., Young M. Nerve growth factor: a protease that can activate plasminogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5497–5500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace L. J., Partlow L. M. alpha-Adrenergic regulation of secretion of mouse saliva rich in nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4210–4214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M., Oger J., Blanchard M. H., Asdourian H., Amos H., Arnason B. G. Secretion of a nerve growth factor by primary chick fibroblast cultures. Science. 1975 Jan 31;187(4174):361–362. doi: 10.1126/science.1167427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. Proteolytic activity of nerve growth factor: a case of autocatalytic activation. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 10;18(14):3050–3055. doi: 10.1021/bi00581a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M., Saide J. D., Murphy R. A., Blanchard Nerve growth factor: multiple dissociation products in homogenates of the mouse submandibular gland. Purification and molecular properties of the intact undissociated form of the protein. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1490–1498. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



