Abstract
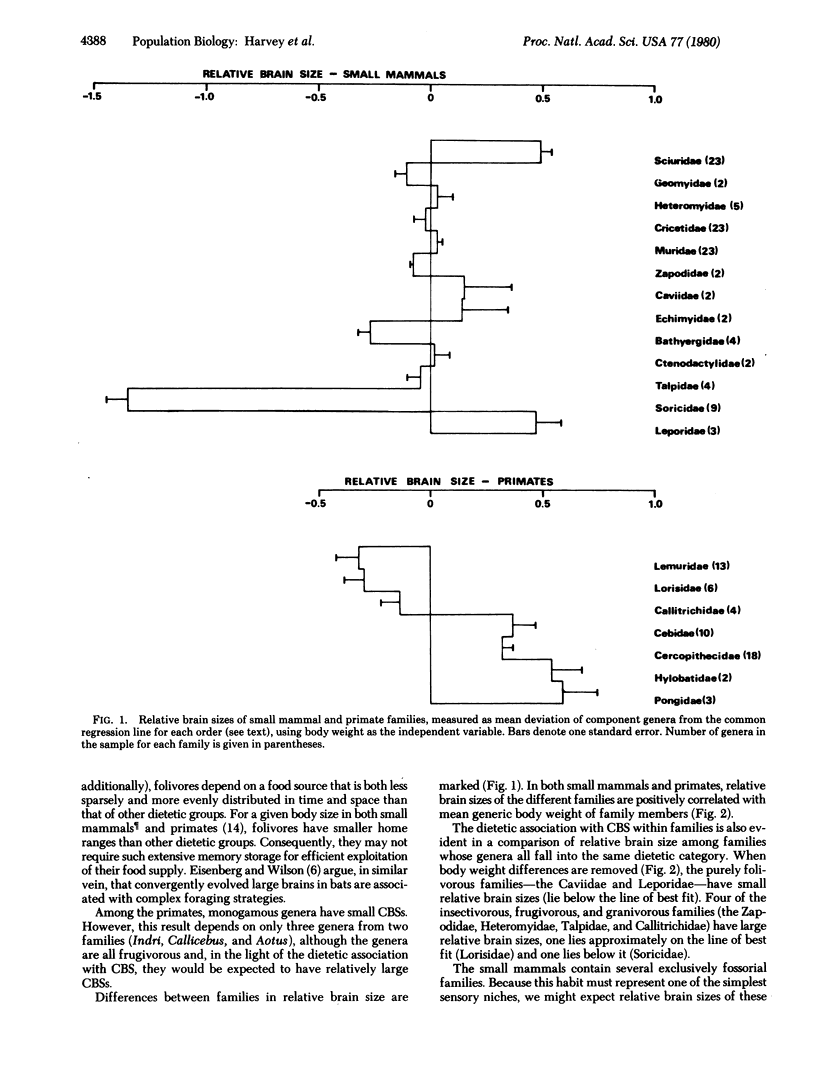
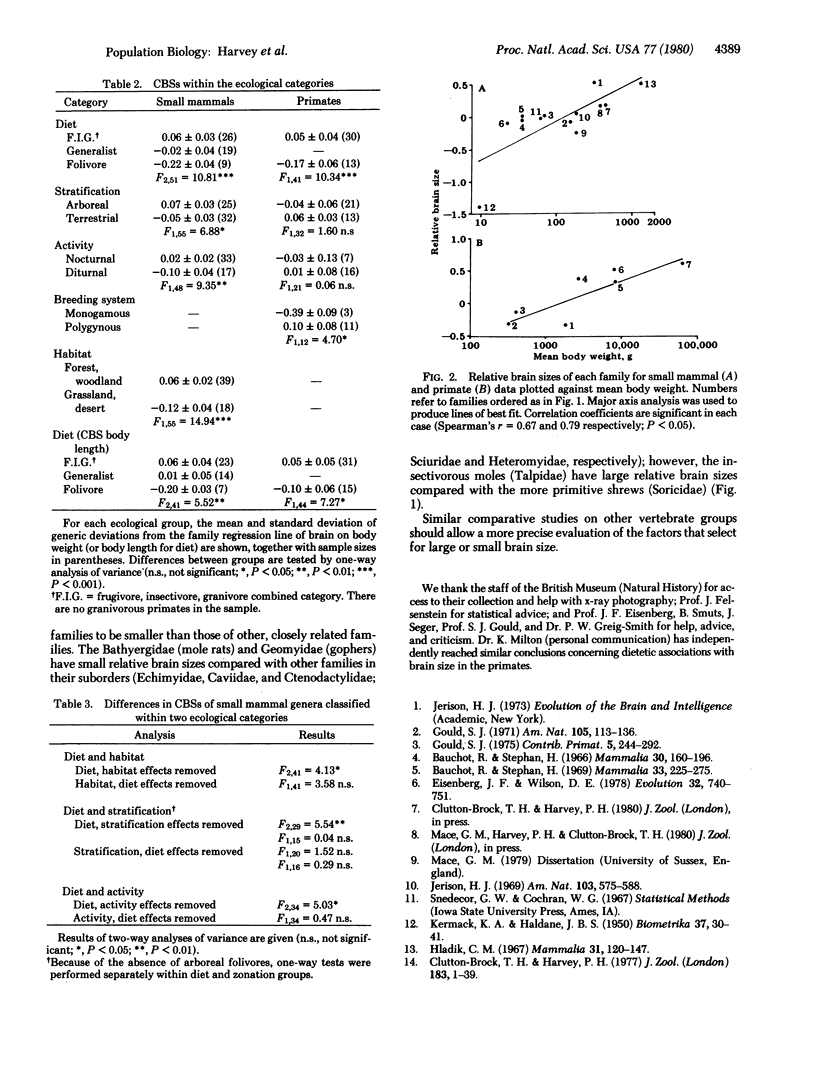
Comparisons of brain-body size relationships within small mammal and primate families reveal intergeneric differences related to diet and foraging strategy. These same associations between relative brain size and ecology are also evident among interfamily comparisons.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gould S. J. Allometry in primates, with emphasis on scaling and the evolution of the brain. Contrib Primatol. 1975;5:244–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERMACK K. A., HALDANE J. B. S. Organic correlation and allometry. Biometrika. 1950 Jun;37(1-2):30–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



