Abstract
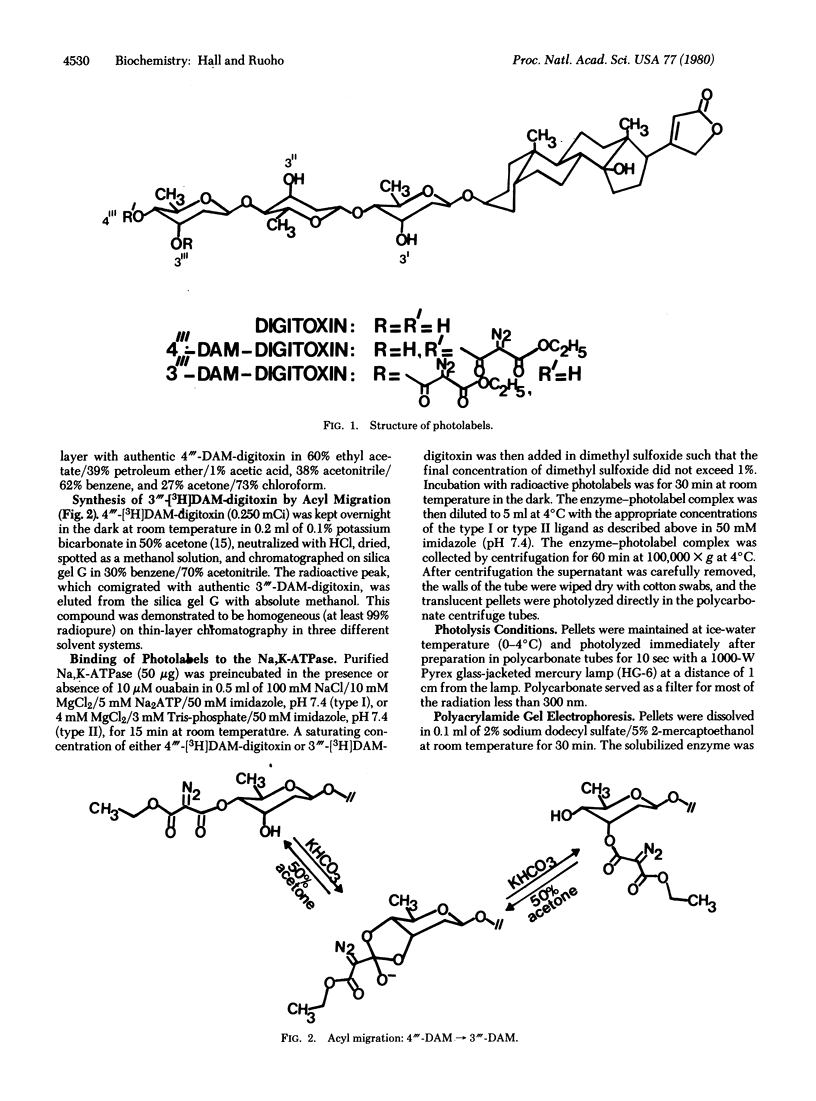
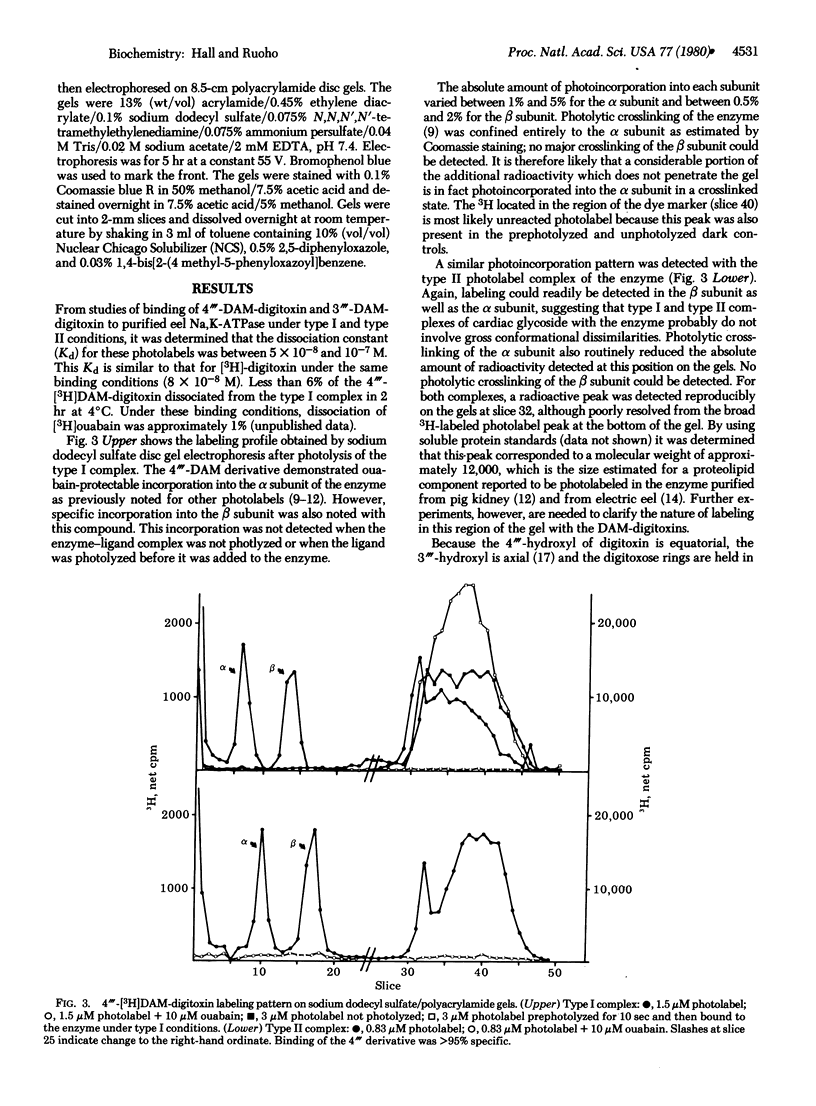
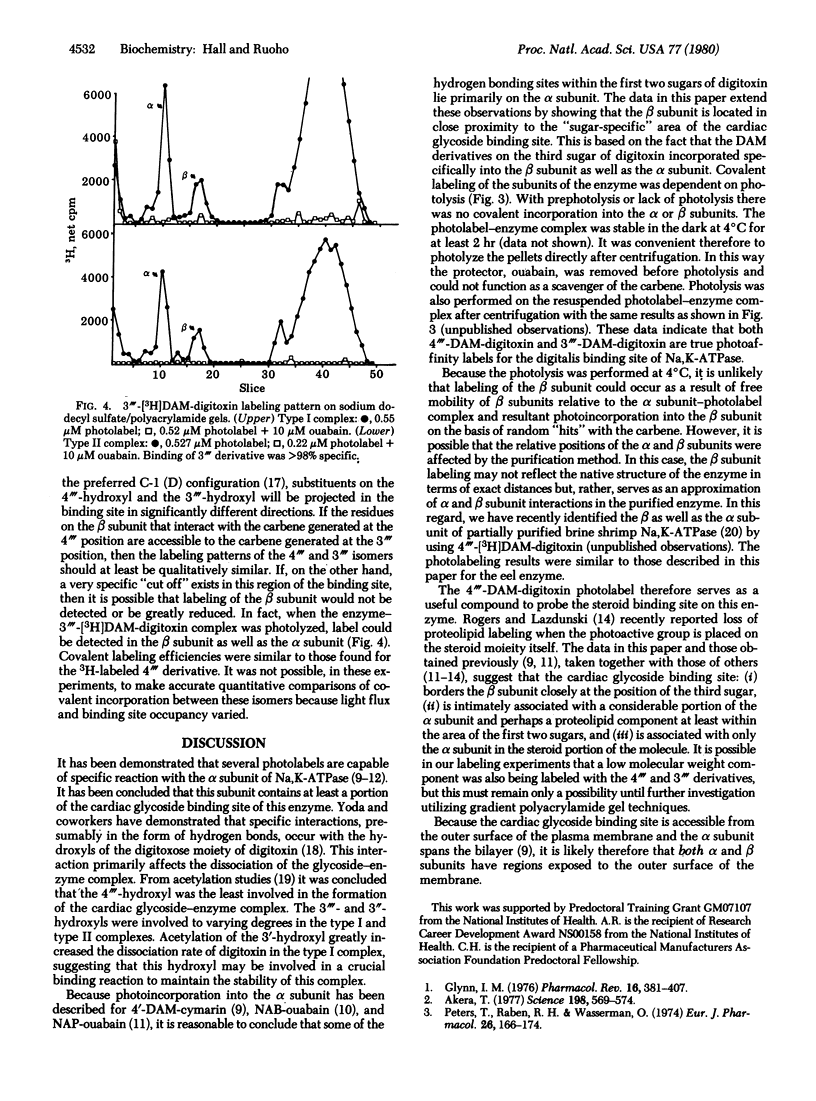
4"'-Diazomalonyldigitoxin and its isomer, 3"'-diazomalonyldigitoxin, have been synthesized at high specific radioactivity and used as photolabels for the Na,K-ATPase (ATP phosphohydrolase, EC 3.6.1.3) purified from Electrophorus electricus. Photoaffinity labeling experiments using both type I and type II complexes of enzyme with both photolabels showed ouabain-protectable labeling of the alpha as well as the beta subunit. These data suggest that, in the purified eel enzyme, the alpha and beta subunits are in intimate contact, at least in the region of the third digitoxose of the "sugar-specific" binding site.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akera T. Membrane adenosinetriphosphatase: a digitalis receptor? Science. 1977 Nov 11;198(4317):569–574. doi: 10.1126/science.144320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill L., Hokin L. E. Biosynthesis and insertion of (Na+ + K+)-adenosine triphosphatase subunits into eel electroplax membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7388–7392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbush B., 3rd, Kaplan J. H., Hoffman J. F. Characterization of a new photoaffinity derivative of ouabain: labeling of the large polypeptide and of a proteolipid component of the Na, K-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 22;17(17):3667–3676. doi: 10.1021/bi00610a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. THE ACTION OF CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES ON ION MOVEMENTS. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Dec;16:381–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings D. F., Reynolds J. A. Molecular weight of (Na+,K+)ATPase from shark rectal gland. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 6;18(5):817–821. doi: 10.1021/bi00572a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegyvary C. Covalent labeling of the digitalis-binding component of plasma membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;11(5):588–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. Properties of the two polypeptides of sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7642–7649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Raben R. H., Wassermann O. Evidence for a dissociation between positive inotropic effect and inhibition of the Na+-K+-ATPase by ouabain, cassaine and their alkylating derivatives. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 May;26(2):166–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L., Ewing R. D., Hootman S. R., Conte F. P. Large scale partial purification and molecular and kinetic properties of the (Na + K)-activated adenosine triphosphatase from Artemia salina nauplii. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4762–4770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L., Ewing R. D., Hootman S. R., Conte F. P. Large scale partial purification and molecular and kinetic properties of the (Na + K)-activated adenosine triphosphatase from Artemia salina nauplii. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4762–4770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. B., Lazdunski M. Photoaffinity labeling of the digitalis receptor in the (sodium + potassium)-activated adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):135–140. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. B., Lazdunski M. Photoaffinity labelling of a small protein component of a purified (Na+-K+)ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 15;98(2):373–376. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoho A., Kyte J. Photoaffinity labeling of the ouabain-binding site on (Na+ plus K+) adenosinetriphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2352–2356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato D., Morita J. Studies on digitalis glycosides. XXX. Digitoxin acetates. (1). Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1969 Jul;17(7):1456–1461. doi: 10.1248/cpb.17.1456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Lindenmayer G. E., Allen J. C. The sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase: pharmacological, physiological and biochemical aspects. Pharmacol Rev. 1975 Mar;27(01):3–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan R. J., Westheimer F. H. A titration method for bovine trypsin. Anal Biochem. 1969 May;29(2):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90314-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoda A. Association and dissociation rate constants of the complexes between various cardiac monoglycosides and Na, K-ATPase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;242(0):598–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb19120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoda A., Yoda S. Structure-activity relationships of cardiotonic steroids for the inhibition of sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase. V. Dissociation rate constants of digitoxin acetates. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;11(5):653–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



