Abstract
Context:
Studies on acute psychosis in patients from India report good outcome. A small proportion of these patients may suffer relapses or other develop major psychiatric disorders later.
Aim:
The aim of this study was to examine the diagnostic stability of acute psychosis in patients from India.
Materials and Methods:
The records of patients who presented with the first episode of acute and transient psychotic disorder (n=57) over 1 year (2004) were analyzed, and the follow-up data at the end of 1 and 2 years were recorded.
Results:
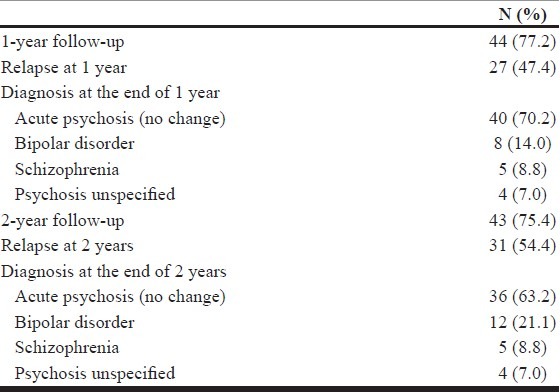
The mean age of the sample was 30.72 years. The mean duration of illness episode was 18.15±17.10 days. The follow-up data were available for 77.2% (n=44) and 75.4% (n=43) of the sample at the end of first and second years. Relapse was recorded in 47.4 and 54.4% at the end of first and second years, respectively.
Conclusion:
The diagnosis changed into other disorders such as bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and unspecified psychosis, while a majority retained the initial diagnosis of acute psychosis. The findings suggest that acute psychosis is a relatively stable condition. A small percentage of these patients may go on to develop schizophrenia or bipolar disorder.
Keywords: Acute psychosis, diagnostic stability, outcome
INTRODUCTION
Acute and transient psychotic disorders (ATPDs) were included as a separate diagnostic category in International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) under the broad category of psychotic disorders (F23). The features that characterize acute psychosis are an acute onset (within 2 weeks), presence of typical syndromes that are either polymorphic or schizophrenic, evidence for associated acute stress and complete recovery in most cases within 2–3 months. International studies have provided enough data for the existence of a nonschizophrenic, nonaffective remitting form of psychosis. It has always been debated on whether ATPDs were related to schizophrenia or to affective disorders. Due to their brief duration and complete remission rates, a proximity to affective disorders has been hypothesized. Jorgensen[1] reported that in 1 year, the diagnostic change occurred in nearly half of the sample and in the rest there was a change in diagnosis to bipolar disorders and schizophrenia.[1] In developing countries, ATPDs have a relatively high diagnostic stability (50–75%) and low rates of relapse.[2,3] This study explored the diagnostic stability of ATPDs in a sample from south India.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We evaluated the records of patients diagnosed with the first episode of ATPDs (F23) according to ICD-10 at the National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), Bangalore, Karnataka, India, in 2004 (for 1 year). Fifty-seven records were identified for that year. The case records contained a detailed evaluation of all admitted patients, including complete history, physical and neurological examinations, mental-status examination, and the basic laboratory examinations. All patients were evaluated independently by two qualified psychiatrists routinely. The records of these patients were reviewed in detail for this study. The course of illness at the end of 1 and 2 years was obtained by reviewing the follow-up data in files. Similarly, the diagnosis at these time points was also recorded.
RESULTS
Demographic parameters and clinical parameters are shown in Table 1. The sample was predominantly composed of females (65%) and a majority hailed from the rural background (63.2%). The mean age of the sample was 30.72±11.75 years. The mean duration of illness was 18.15±17.10 days. The follow-up data were available for 77.2% (n=44) and 75.4% (n=43) of the sample at the end of first and second years. Relapse into another episode was noted in 47.4 and 54.4%, respectively, at the end of 1 and 2 years, respectively. The original diagnosis of ATPD was retained in 70.2 and 63.2% at 1 and 2 years. The diagnostic change in other disorders such as bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and unspecified psychosis is shown in Table 2.
Table 1.
Sociodemographic and clinical parameters
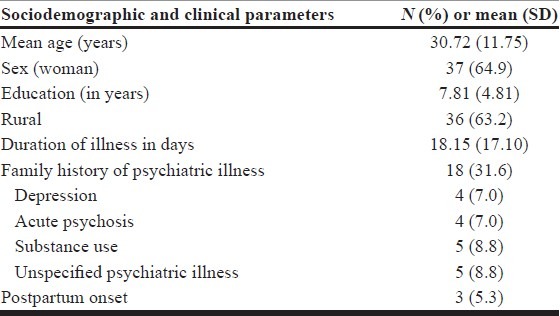
Table 2.
Diagnosis at 1 and 2 years
DISCUSSION
The stability of this diagnostic entity has been questioned since its inclusion in ICD-10. Castagnini et al.[4] reported that about 50% of the cases with ATPD went on to develop ‘schizophrenia and related disorders’ or affective disorders. Similarly, other Western studies also showed lesser diagnostic stability.[1,5] In developing countries, however, ATPD has a relatively high diagnostic stability (50–75%). Sajith et al.[3] reported that 73% retained the original diagnosis of ATPD after 3 years. Similarly, good diagnostic stability was reported by Thangadurai et al.[2] In a 12-year follow-up study of acute psychosis from the Chandigarh DOSMeD cohort, 1 of the 17 cases developed schizophrenia, none developed affective disorders, and a majority retained the initial diagnosis of acute psychosis.[6] In our study also, a majority of the patients retained the original diagnosis, showing a good stability of this disorder overtime.
The relapse rates have ranged between 40 and 70% over varying follow-up periods.[7–9] Marneros et al.[5,10] reported that 75% of their cases with ATPD had a recurrent affective or psychotic episode, 30% developed affective disorders, and a relatively small number developed schizoaffective disorder or schizophrenia. In the study by Jorgensen et al.,[1] of 46 cases followed-up, 15% developed schizophrenia and 28% affective disorders. Our study results also show a similar relapse rate over 1–2 years. Other studies have reported higher rates of schizophrenia in patients initially diagnosed with acute psychosis.[2,11] Although the diagnosis of acute psychosis is stable in many cases, some patients may go on to develop schizophrenia or bipolar disorders over time. It is this group of patients who need to be studied further to identify factors predicting relapse into other disorders. The present study is limited by retrospective design, high attrition rate (nearly 25%), and the lack of standardized instruments for diagnosis. Despite limitations, our report highlights the diagnostic stability of acute psychosis as a separate category of psychotic disorders. It is possible that in these patients recurrent affective and psychotic episodes on follow-up may indicate that ATPD bridges schizophrenia to affective psychoses according to a very broad view of the psychotic spectrum.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None.
REFERENCES
- 1.Jorgensen P, Bennedsen B, Christensen J, Hyllested A. Acute and transient psychotic disorder: a 1-year follow-up study. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1997;96:150–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1997.tb09920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Thangadurai P, Gopalakrishnan R, Kurian S, Jacob KS. Diagnostic stability and status of acute and transient psychotic disorders. Br J Psychiatry. 2006;188:293. doi: 10.1192/bjp.188.3.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sajith SG, Chandrasekaran R, Sadanandan Unni KE, Sahai A. Acute polymorphic psychotic disorder: diagnostic stability over 3 years. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2002;105:104–9. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0447.2002.01080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Castagnini A, Bertelsen A, Berrios GE. Incidence and diagnostic stability of ICD-10 acute and transient psychotic disorders. Compr Psychiatry. 2008;49:255–61. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2007.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Marneros A, Pillmann F, Haring A, Balzuweit S, Bloink R. Features of acute and transient psychotic disorders. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2003;253:167–74. doi: 10.1007/s00406-003-0420-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Susser E, Varma VK, Mattoo SK, Finnerty M, Mojtabai R, Tripathi BM, et al. Long-term course of acute brief psychosis in a developing country setting. Br J Psychiatry. 1998;173:226–30. doi: 10.1192/bjp.173.3.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jager MD, Hintermayr M, Bottlender R, Strauss A, Moller HJ. Course and outcome of first-admitted patients with acute and transient psychotic disorders (ICD-10:F23).Focus on relapses and social adjustment. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2003;253:209–15. doi: 10.1007/s00406-003-0435-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Amin S, Singh SP, Brewin J, Jones PB, Medley I, Harrison G. Diagnostic stability of first-episode psychosis. Comparison of ICD-10 and DSM-III-R systems. Br J Psychiatry. 1999;175:537–43. doi: 10.1192/bjp.175.6.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Singh SP, Burns T, Amin S, Jones PB, Harrison G. Acute and transient psychotic disorders: Precursors, epidemiology, course and outcome. Br J Psychiatry. 2004;185:452–9. doi: 10.1192/bjp.185.6.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Marneros A, Pillmann F. Acute and transient psychoses. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Abe T, Otsuka K, Kato S. Long-term clinical course of patients with acute polymorphic psychotic disorder without symptoms of schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2006;60:452–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.2006.01531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


