Abstract
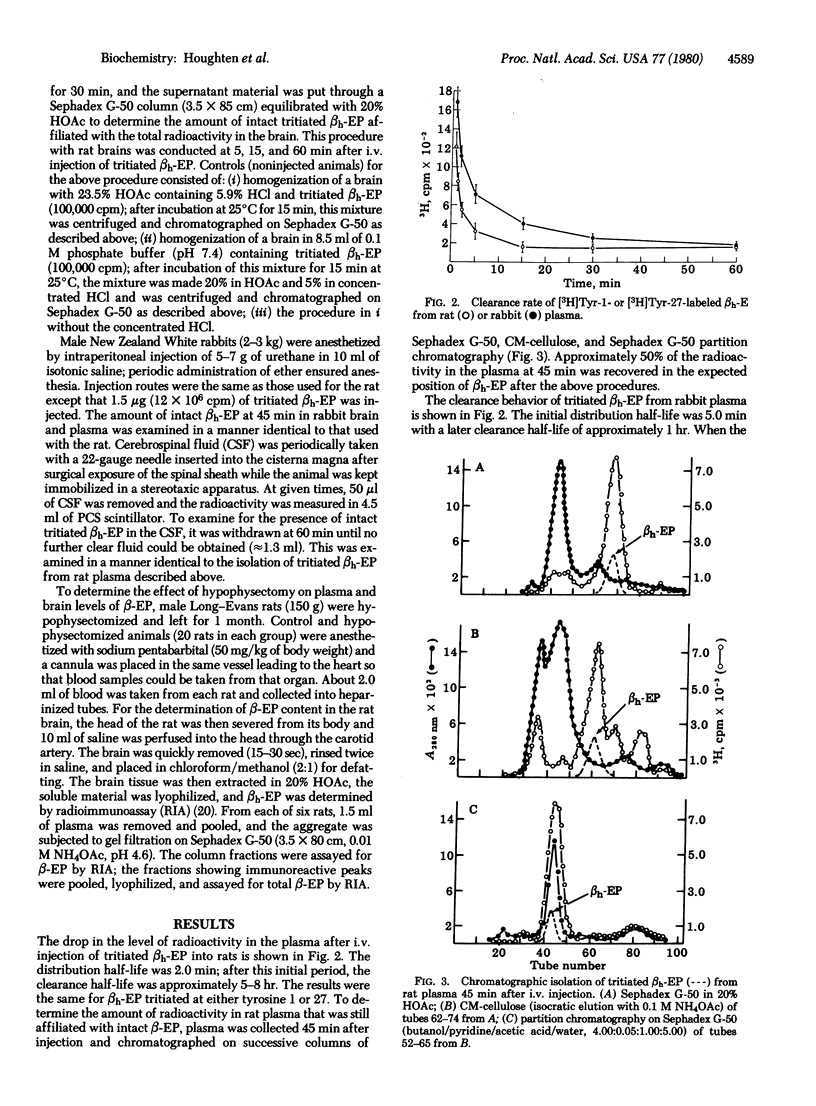
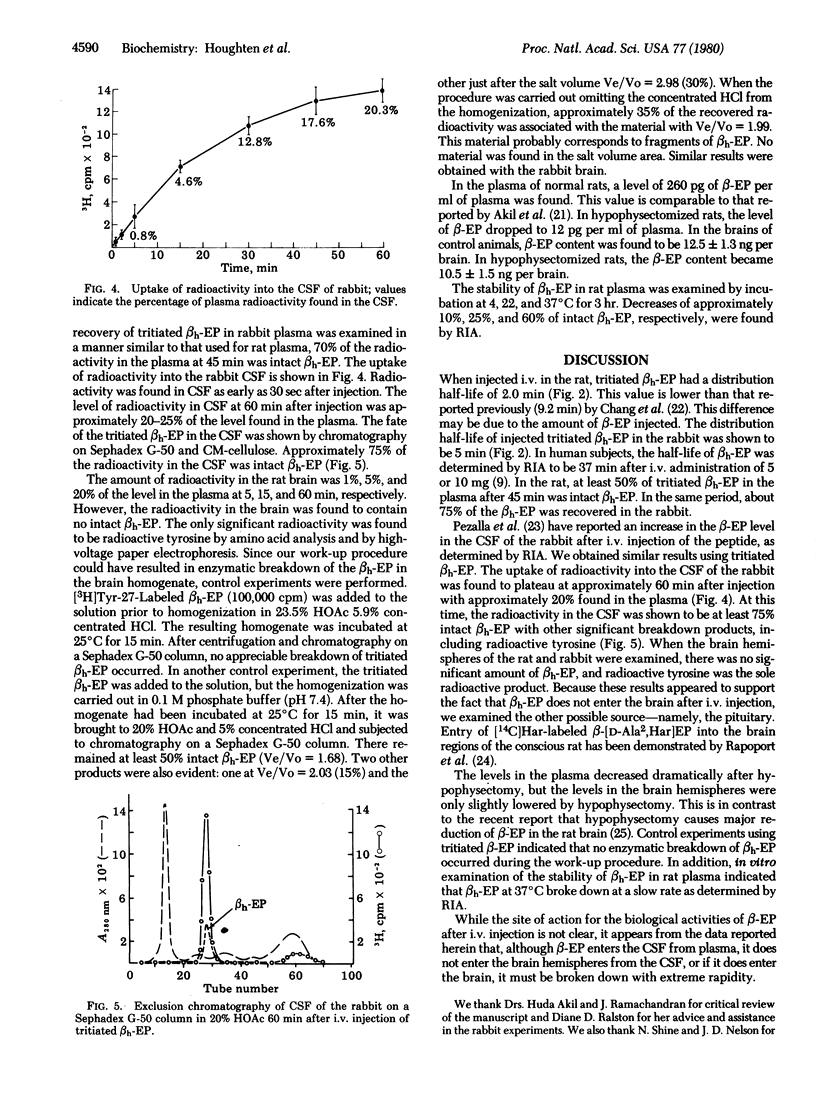
Rabbits and rats were given intravenous injections of tritiated human beta-endorphin. The levels of beta-endorphin were followed by the decrease in radioactivity in the plasma of rats or rabbits and by the increase in radioactivity in the cerebrospinal fluid of the rabbit. The results were identical with the tritium label on either tyrosine-1 or -27. The plasma distribution times were 2 and 5 min in the rat and rabbit, respectively, with a later clearance time of approximately 1-8 hr. In the rat, approximately 50% of the radioactivity in the plasma was found to be intact human beta-endorphin 45 min after injection. Radioactivity appeared in the cerebrospinal fluid of the rabbit within 30 sec after injection and reached a plateau in approximately 60-90 min after injection. Approximately 75% of the radioactivity in the cerebrospinal fluid of the rabbit was intact human beta-endorphin. In the brain hemispheres of the rat and the rabbit, the only significant radiolabeled product was found to be radioactive tyrosine. Moreover, rat plasma levels of beta-endorphin decreased dramatically after hypophysectomy, which only slightly lowered the levels in the brain. It appears that beta-endorphin, upon entry into the plasma, is either not significantly taken up into the brain or is broken down with extreme rapidity upon entry into the brain, although it apparently does enter the cerebrospinal fluid.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akil H., Watson S. J., Barchas J. D., Li C. H. B-ETA-Endorphin immunoreactivity in rat and human blood: radioimmunoassay, comparative levels and physiological alterations. Life Sci. 1979 Apr 30;24(18):1659–1665. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F., Battenberg E., Rossier J., Ling N., Guillemin R. Neurons containing beta-endorphin in rat brain exist separately from those containing enkephalin: immunocytochemical studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1591–1595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin D. H., Hui K. K., Loh H. H., Li C. H. Pharmacologic activity of beta-endorphin in man. Commun Psychopharmacol. 1977;1(5):493–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang W. C., Rao A. J., Li C. H. Rat of disappearance of human beta-lipotropin and beta-endorphin in adult male rats as estimated by radioimmunassay. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1978 Jan;11(1):93–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1978.tb02826.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang W. C., Yeung H. W., Li C. H. Human beta-endorphin. Immunoreactivity of synthetic analogs with various chain lengths. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1979 Mar;13(3):278–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1979.tb01880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley K. M., Kourides I. A., Inturrisi C. E., Kaiko R. F., Zaroulis C. G., Posner J. B., Houde R. W., Li C. H. beta-Endorphin: analgesic and hormonal effects in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5377–5381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosobuchi Y., Li C. H. The analgesic activity of human beta-endorphin in man (1,2,3). Commun Psychopharmacol. 1978;2(1):33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Li C. H. Preparation and properties of tritiated human beta-endorphin with high specific radioactivity. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1978 Nov;12(5):325–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1978.tb02904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline N. S., Li C. H., Lehmann H. E., Lajtha A., Laski E., Cooper T. Beta-endorphin--induced changes in schizophrenic and depressed patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1977 Sep;34(9):1111–1113. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1977.01770210125012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Lydon R. J., Watt A. J. The effects of adrenaline, noradrenaline and isoprenaline on inhibitory alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors in the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jun;39(2):398–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb12903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Yamashiro D., Tseng L. F., Loh H. H. Synthesis and analgesic activity of human beta-endorphin. J Med Chem. 1977 Mar;20(3):325–328. doi: 10.1021/jm00213a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H. beta-Endorphin: a pituitary peptide with potent morphine-like activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Oct;183(2):592–604. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90395-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai Y., Nakao K., Oki S., Imura H., Li C. H. Presence of immunoreactive beta-endorphin in plasma of patients with Nelson's syndrome and Addison's disease. Life Sci. 1978 Dec 4;23(23):2293–2298. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Nakai Y., Oki S., Horii K., Imura H. Presence of immunoreactive beta-endorphin in normal human plasma: a concomitant release of beta-endorphin with adrenocorticotropin after metyrapone administration. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1395–1398. doi: 10.1172/JCI109261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa N., Panerai A. E., Lee S., Forsbach G., Havlicek V., Friesen H. G. beta-Endorphin concentration in the brain of intact and hypophysectomized rats. Life Sci. 1979 Jul 23;25(4):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezalla P. D., Lis M., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M. Lipotropin, melanotropin and endorphin: in vivo catabolism and entry into cerebrospinal fluid. Can J Neurol Sci. 1978 May;5(2):183–188. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100024537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S. I., Klee W. A., Pettigrew K. D., Ohno K. Entry of opioid peptides into the central nervous system. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):84–86. doi: 10.1126/science.7350645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng L. F., Loh H. H., Li C. H. Beta-Endorphin as a potent analgesic by intravenous injection. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):239–240. doi: 10.1038/263239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng L. F., Loh H. H., Li C. H. Human beta-endorphin: development of tolerance and behavioral activity in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):390–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90316-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng L. F., Loh H. H., Li C. H. betah-endorphin: antidiuretic effects in rats. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1978 Sep;12(3):173–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1978.tb02882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw S. L., Frantz A. G. Measurement of beta-endorphin in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Jan;48(1):176–180. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-1-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H., Richard C. W., 3rd, Barchas J. D. Evidence for two separate opiate peptide neuronal systems. Nature. 1978 Sep 21;275(5677):226–228. doi: 10.1038/275226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann E., Saito T., Linfoot J. A., Li C. H. Specific radioimmunoassay of human beta-endorphin in unextracted plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Sep;49(3):478–480. doi: 10.1210/jcem-49-3-478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMASHIRO D. PARTITION CHROMATOGRAPHY OF OXYTOCIN ON 'SEPHADEX'. Nature. 1964 Jan 4;201:76–77. doi: 10.1038/201076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



