Abstract
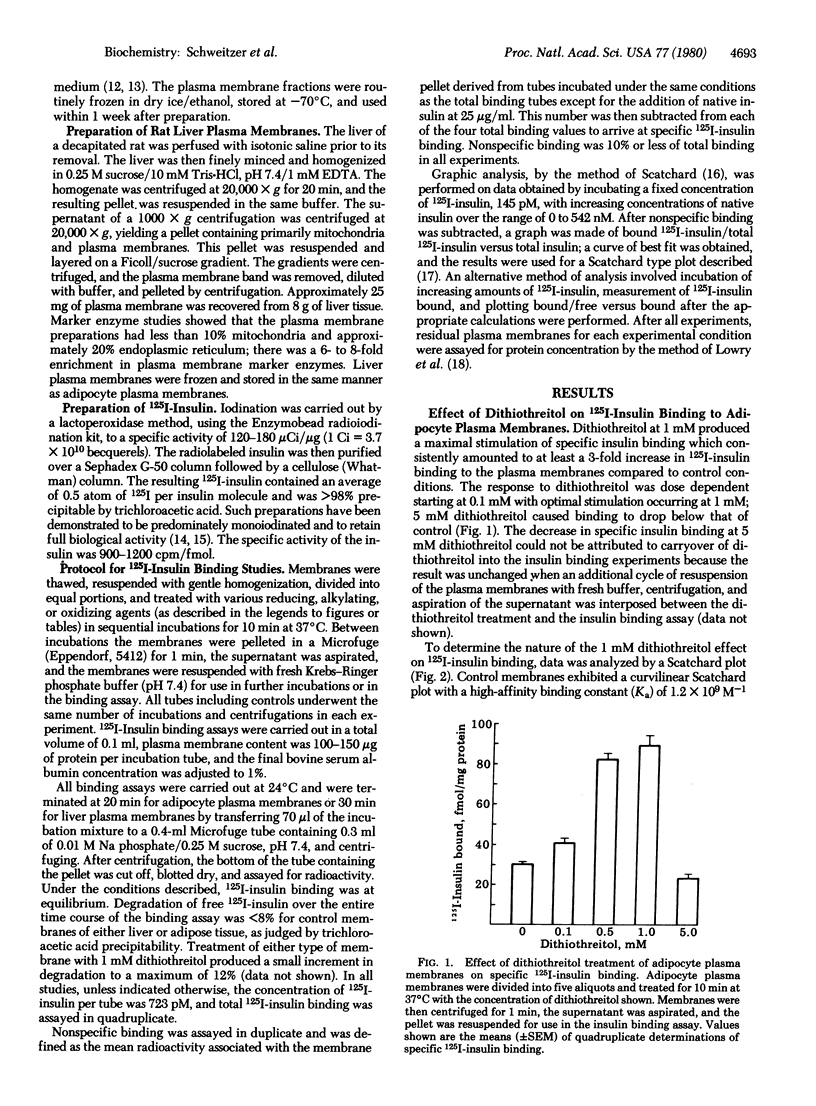
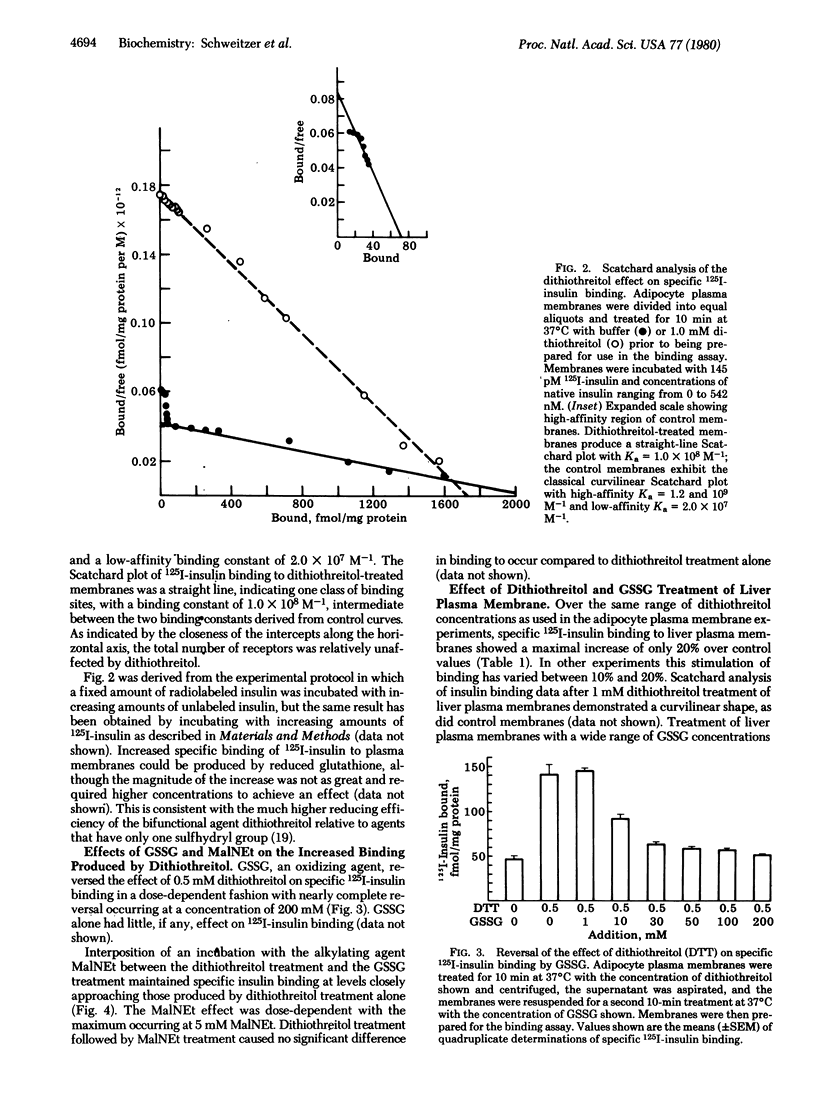
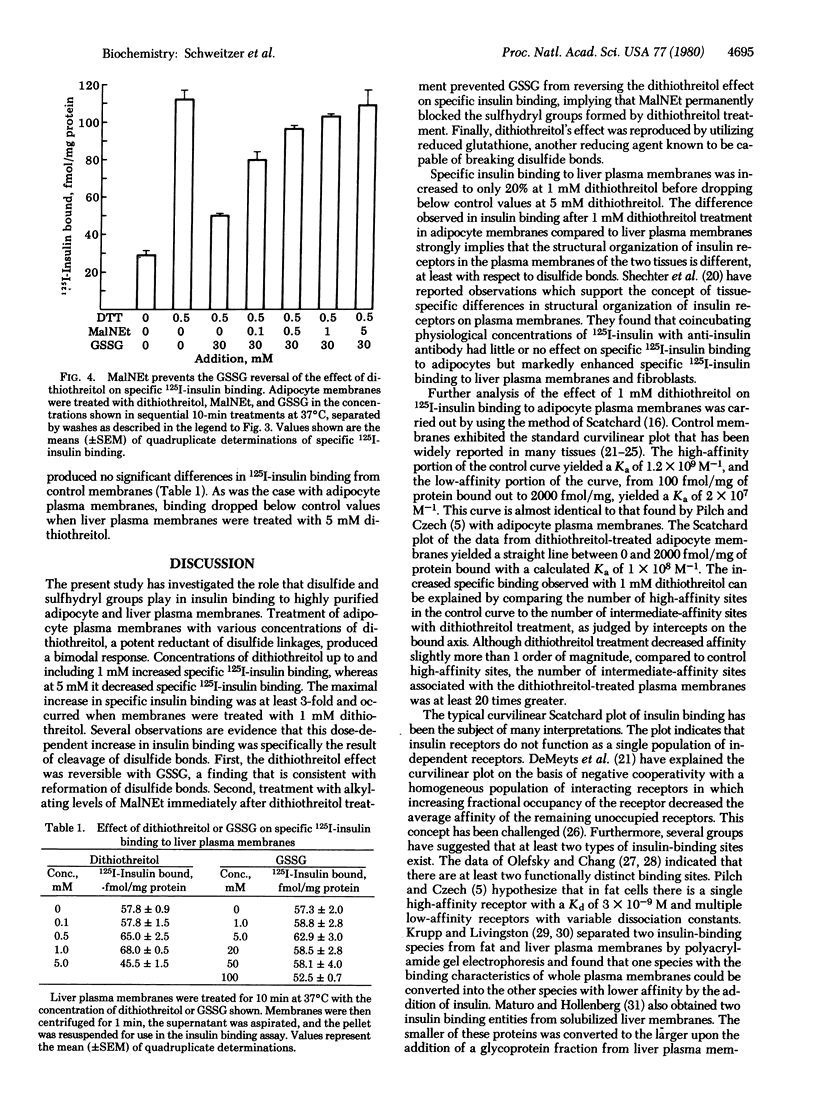
Binding of 125I-labeled insulin to rat liver and adipocyte plasma membranes has been investigated after treatment of the membranes with agents that modify disulfide bonds or sulfhydryl groups. Dithiothreitol, a disulfide-reducing agent, produced a bimodal response in adipocyte plasma membranes with dose-dependent increases in binding occurring over the range of 0-1 mM dithiothreitol; 5 mM dithiothreitol produced decreased binding. Insulin binding reached its maximal increase at 1 mM and was 3 times control values. Scatchard analysis of the 1 mM dithiothreitol effect revealed a straight line plot indicative of one class of sites with a Ka of 1.0 x 10(8) M-1 which is intermediate between the two Kas obtained from the curvilinear Scatchard plot of control membranes. There was a 20-fold increase in the number of intermediate-affinity receptors compared to high-affinity receptors. The increased 125I-labeled insulin binding after dithiothreitol treatment was reversed by oxidized glutathione in a dose-dependent manner. Interposition of treatment with N-ethylmaleimide, an alkylating agent, prevented oxidized glutathione from reversing the dithiothreitol effect. Reduced glutathione produced the same effect as dithiothreitol. Liver plasma membranes treated with up to 1 mM dithiothreitol exhibited a maximum increase in insulin binding of 20% compared to control. Dithiothreitol at 5 mM decreased insulin binding below that of control membranes. The results indicate that the dithiothreitol effect on insulin binding to adipocyte plasma membranes is due to disruption of disulfide bonds, and that the structural organization of the insulin receptor on the plasma membranes is different for liver and for adipose tissue. The data imply that the insulin receptors on the plasma membrane of adipocytes possess at least two functionally distinct subclasses of disulfide bond but liver insulin receptors do not.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLELAND W. W. DITHIOTHREITOL, A NEW PROTECTIVE REAGENT FOR SH GROUPS. Biochemistry. 1964 Apr;3:480–482. doi: 10.1021/bi00892a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Laudat M. H., Laudat P., Rosselin G., Kahn C. R., Gorden P., Roth J. Impairment of insulin binding to the fat cell plasma membrane in the obese hyperglycemic mouse. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Monoiodoinsulin: demonstration of its biological activity and binding to fat cells and liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Gorden P., Roth J., Archer J. A., Buell D. N. Characteristics of the human lymphocyte insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2202–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Gardner J. D., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin action in isolated rat thymocytes. I. Binding of 125 I-insulin and stimulation of -aminoisobutyric acid transport. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6919–6926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond J. M., Jarett L., Mariz I. K., Daughaday W. H. Heterogeneity of insulin receptors on fat cell membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):1122–1128. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90329-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazum E., Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Role of disulphide and sulphydryl groups in clustering of enkephalin receptors in neuroblastoma cells. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):626–628. doi: 10.1038/282626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Hazum E., Shechter Y., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor: covalent labeling and identification of subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4918–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Smith R. M. Effect of cytochalasin B and D on groups of insulin receptors and on insulin action in rat adipocytes. Possible evidence for a structural relationship of the insulin receptor to the glucose transport system. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):571–579. doi: 10.1172/JCI109338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Smith R. M. The natural occurrence of insulin receptors in groups on adipocyte plasma membranes as demonstrated with monomeric ferritin-insulin. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(1):45–59. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Quantitative aspects of the insulin-receptor interaction in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2249–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M. N., Livingston J. N. Effects of insulin on insulin-binding components extracted from rat fat cell membranes. Nature. 1979 Mar 1;278(5699):61–62. doi: 10.1038/278061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M. N., Livingston J. N. Insulin binding to solubilized material from fat cell membranes: evidence for two binding species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2593–2597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard G. E., Wardzala L. J. Cytochalasin B reacts with thiols. FEBS Lett. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas R. J., Morimoto H., Bennett E. L. Effects of thio-group modification and Ca2+ on agonist-specific state transitions of a central nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2384–2395. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maturo J. M., 3rd, Hollenberg M. D. Insulin receptor: interaction with nonreceptor glycoprotein from liver cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3070–3074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. M., Bruns D. E., Jarett L. Characterization of calcium binding to adipocyte plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5345–5351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeel D. W., Jarett L. Preparation and characterization of a plasma membrane fraction from isolated fat cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 Feb;44(2):417–432. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Chang H. Further evidence for functional heterogeneity of adipocyte insulin receptors. Endocrinology. 1979 Feb;104(2):462–466. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-2-462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Chang H. Insulin binding to adipocytes. Evidence for functionally distinct receptors. Diabetes. 1978 Sep;27(9):946–958. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.9.946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa Y., Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Smith F. The role of sulfhydryl groups in thyrotropin binding and adenylate cyclase activities of thyroid plasma membranes. Endocrinology. 1979 Nov;105(5):1221–1225. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-5-1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. The subunit structure of the high affinity insulin receptor. Evidence for a disulfide-linked receptor complex in fat cell and liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1722–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollet R. J., Standaert M. L., Haase B. A. Insulin binding to the human lymphocyte receptor. Evaluation of the negative cooperativity model. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5828–5834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B., Straus E., Yalow R. S. Some considerations in the preparation of raioiodoinsulin for radioimmunoassay and receptor assay. Diabetes. 1976 Apr;25(4):260–267. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.4.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., Jarett L. Activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase by direct addition of insulin to an isolated plasma membrane/mitochondria mixture: evidence for generated of insulin's second messenger in a subcellular system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):77–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., McDonald J. M., Jarett L. Insulin effect on protein phosphorylation of plasma membranes and mitochondria in a subcellular system from rat adipocytes. I. Identification of insulin-sensitive phosphoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6991–6996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y., Chang K. J., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Modulation of binding and bioactivity of insulin by anti-insulin antibody: relation to possible role of receptor self-aggregation in hormone action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2720–2724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vauquelin G., Bottari S., Kanarek L., Strosberg A. D. Evidence for essential disulfide bonds in beta1-adrenergic receptors of turkey erythrocyte membranes. Inactivation by dithiothreitol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4462–4469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meyts P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, Gavin J. R., 3rd, Lesniak M. A. Insulin interactions with its receptors: experimental evidence for negative cooperativity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 1;55(1):154–161. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


