Abstract
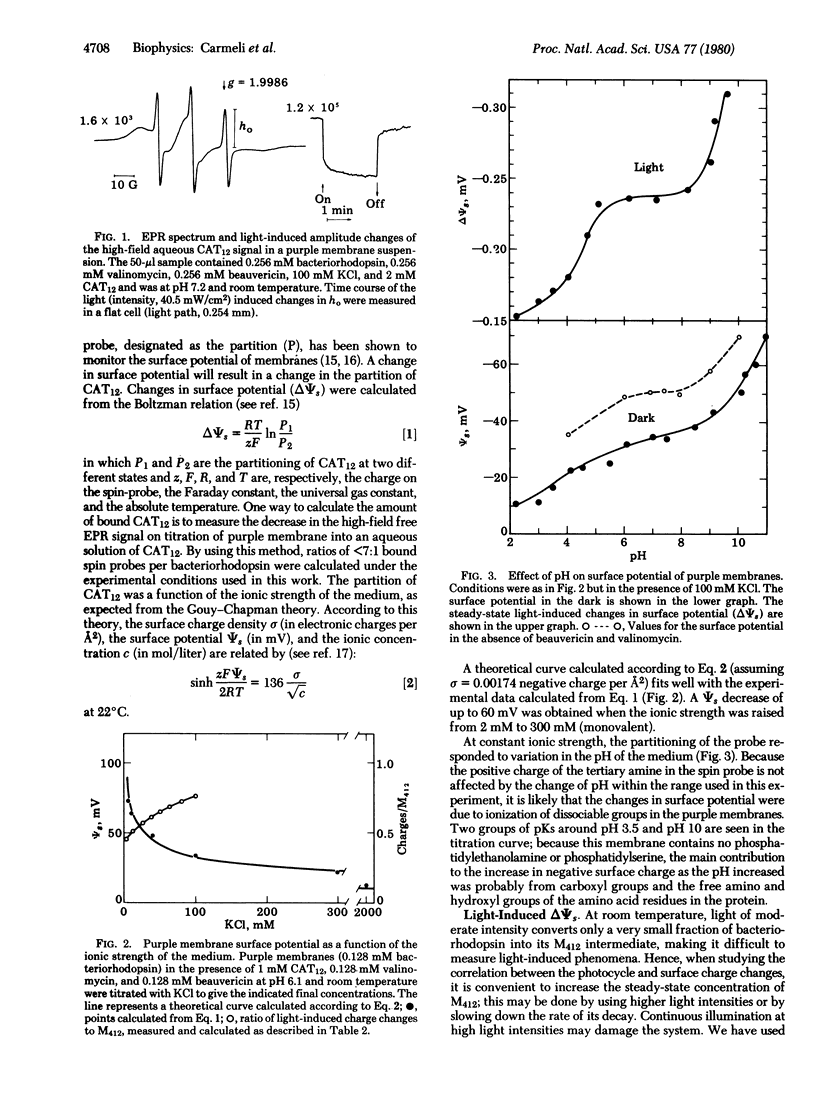
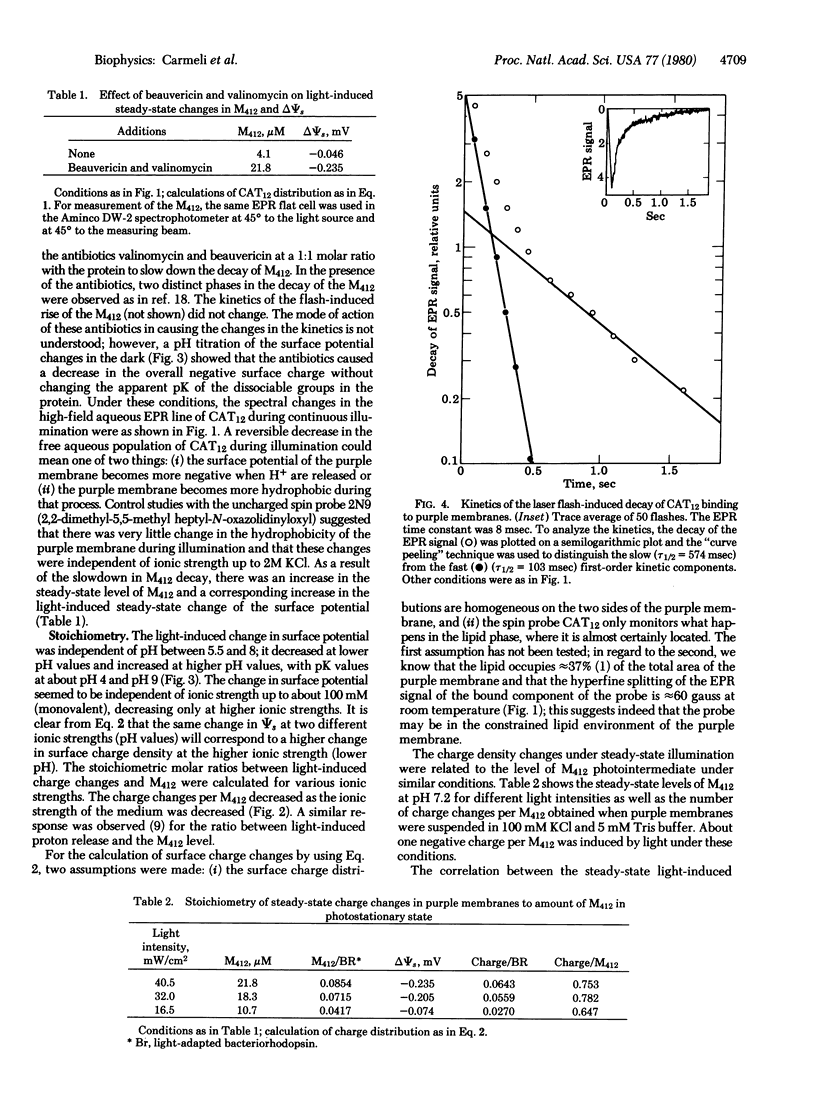
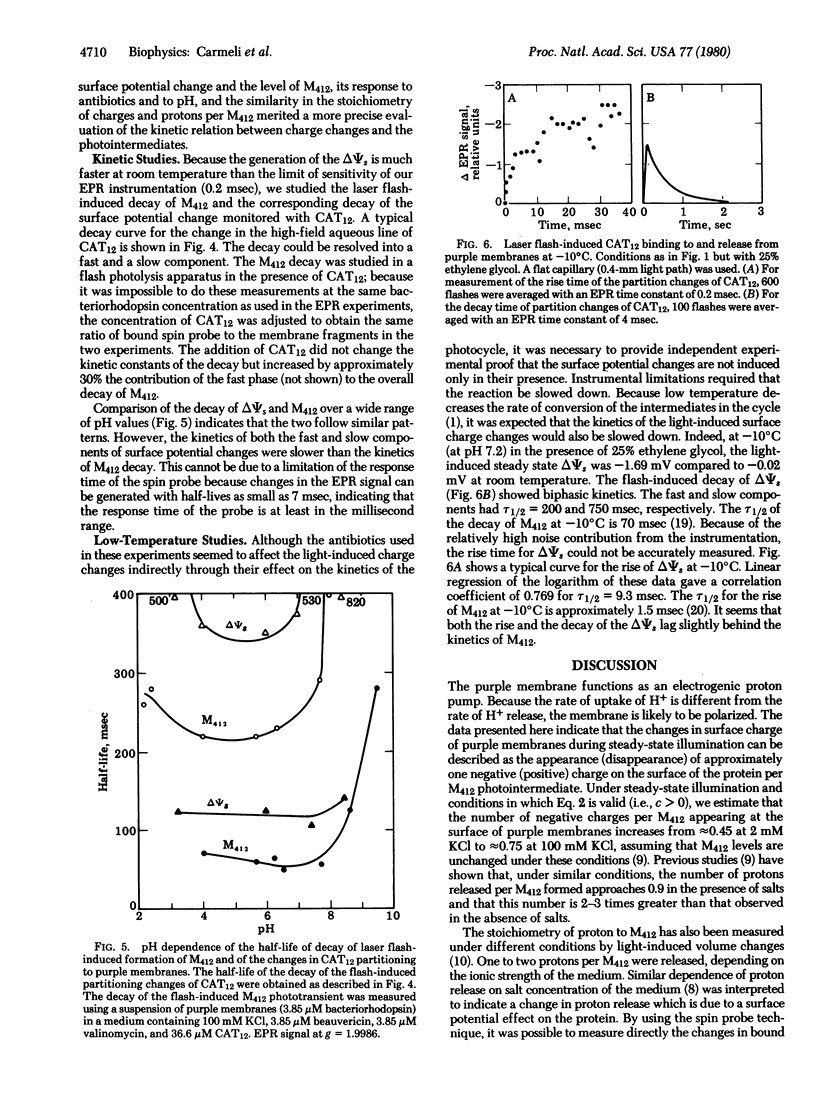
The surface potential of purple membrane fragments, determined from the distribution of the aqueous free and the membrane-bound positively charged, paramagnetic, amphiphilic probe 4-(dodecyldimethylammonium)-1-oxyl-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine bromide varied almost 60 mV as a function of ionic strength and 50 mV as a function of pH of the medium. Light-induced changes in surface potential followed the changes observed in the M412 intermediate of the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin as a function of pH, temperature, and response to antibiotics beauvericin and valinomycin. The number of induced charges per M412 appearing at the surface of purple membranes decreased from about 0.75 to 0.45 as the surface potential became more negative. The stoichiometry would be twice as large if the charge changes were localized exclusively on one side of the purple membrane. Laser flash-induced kinetics of the rise and decay of surface charge changes were slightly slower than the kinetics of the rise and decay of M412 which is associated with the reversible deprotonation of the retinal Schiff base nitrogen in the chromophore. It is suggested that the light-induced charge changes monitor a dissociable amino acid residue which may be a step in the movement of protons across the purple membrane.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avi-Dor Y., Rott R., Schnaiderman R. The effect of antibiotics on the photocycle and protoncycle of purple membrane suspensions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 11;545(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogomolni R. A., Stubbs L., Lanyi J. K. Illumination-dependent changes in the intrinsic fluorescence of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 21;17(6):1037–1041. doi: 10.1021/bi00599a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brith-Lindner M., Avi-Dor Y. Interaction of ionophores with bacteriorhodopsin. A flash photometric study. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):113–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle J. D., Hubbell W. L. Estimation of membrane surface potential and charge density from the phase equilibrium of a paramagnetic amphiphile. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4818–4831. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu Kung M., DeVault D., Hess B., Oesterhelt D. Photolysis of bacterial rhodopsin. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):907–911. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85864-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencher N. A., Heyn M. P. Bacteriorhodopsin monomers pump protons. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80552-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H., Klemperer G., Eisenbach M., Caplan S. R. The direction of light-induced pH changes in purple membrane suspensions. Influence of pH and temperature. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 15;81(2):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80526-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess B., Kuschmitz D. Kinetic interaction between aromatic residues and the retinal chromophore of bacteriorhodopsin during the photocycle. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):334–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80364-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A., Spoonhower J., Bogomolni R. A., Lozier R. H., Stoeckenius W. Tunable laser resonance raman spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4462–4466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin: a light-driven proton pump in Halobacterium Halobium. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):955–962. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85875-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Niederberger W., Bogomolni R. A., Hwang S., Stoeckenius W. Kinetics and stoichiometry of light-induced proton release and uptake from purple membrane fragments, Halobacterium halobium cell envelopes, and phospholipid vesicles containing oriented purple membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 13;440(3):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlhorn R. J., Packer L. Membrane surface potential measurements with amphiphilic spin labels. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:515–526. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Hess B. Reversible photolysis of the purple complex in the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 17;37(2):316–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ort D. R., Parson W. W. Flash-induced volume changes of bacteriorhodopsin-containing membrane fragments and their relationship to proton movements and absorbance transients. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6158–6164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ort D. R., Parson W. W. The quantum yield of flash-induced proton release by bacteriorhodopsin-containing membrane fragments. Biophys J. 1979 Feb;25(2 Pt 1):341–353. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(79)85296-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintanilha A. T., Packer L. Surface potential changes on energization of the mitochondrial inner membrane. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jun 15;78(2):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80296-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenheck K., Brith-Lindner M., Lindner P., Zakaria A., Caplan S. R. Proteolysis and flash photolysis of bacteriorhodopsin in purple membrane fragments. Biophys Struct Mech. 1978 Nov 27;4(4):301–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00537613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman W. V., Caplan S. R. Arrhenius parameters of phototransients in Halobacterium halobium in physiological conditions. Nature. 1975 Dec 25;258(5537):766–768. doi: 10.1038/258766a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



