Abstract
The loss of the lectin-like activity of a 26,000-dalton carbohydrate-binding protein (CBP-26) results in the loss of aggregation competence and cell-cell cohesiveness in developing cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. The lesion responsible for this phenotype behaves like a mutation in the structural gene for CBP-26, maps in linkage group II, and has been designated cbpA1. In aggregation-competent revertants, the degree of aggregation competence and cell-cell cohesiveness is directly related to the specific activity of CBP-26. Thus, CBP-26 appears to play an essential role in cell aggregation through the cell-cell cohesion process.
Full text
PDF

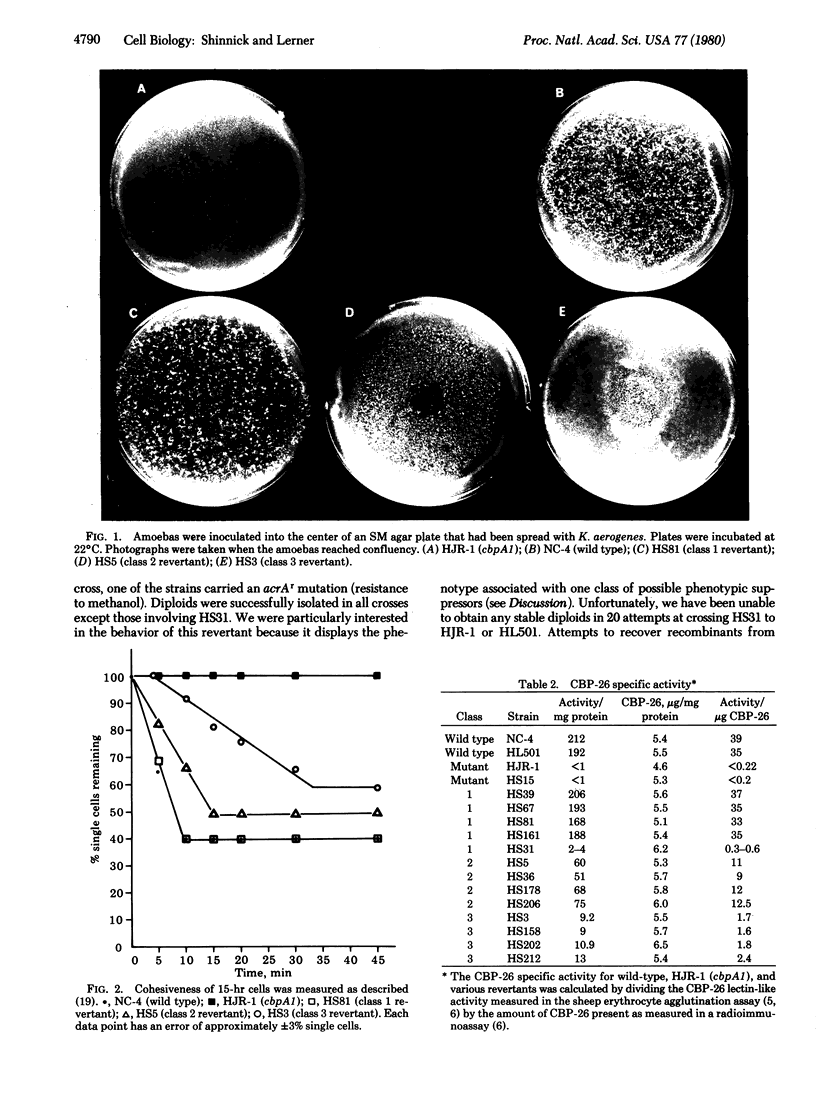
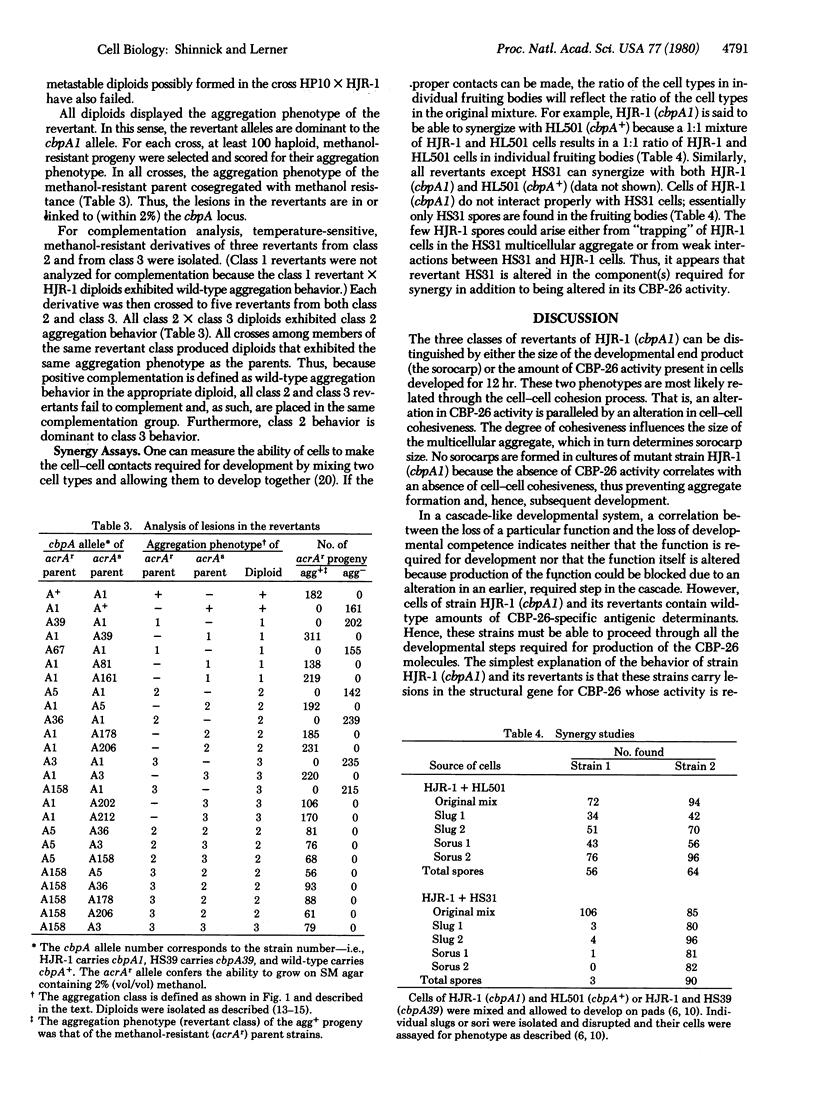

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beug H., Katz F. E., Gerisch G. Dynamics of antigenic membrane sites relating to cell aggregation in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biol. 1973 Mar;56(3):647–658. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. M., Reitherman R. W., Rosen S. D., Barondes S. H. Cell surface location of discoidin, a developmentally regulated carbohydrate-binding protein from Dictyostelium discoideum. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Oct 1;95(1):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90618-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Free S. J., Schimke R. T. The structural gene for alpha-mannosidase-1 in Dictyostellium discoideum. Genetics. 1976 Oct;84(2):159–174. doi: 10.1093/genetics/84.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geltosky J. E., Weseman J., Bakke A., Lerner R. A. Identification of a cell surface glycoprotein involved in cell aggregation in D. discoideum. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E. R., Sussman M. Parasexual recombination in Dictyostelium discoideum: selection of stable diploid heterozygotes and stable haploid segregants (clones-temperature sensitive-ploidy-fruiting bodies-spore-slime mold). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):495–498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Jr Temperature-sensitive mutants of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):65–69. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.65-69.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray J., Shinnick T., Lerner R. A mutation altering the function of a carbohydrate binding protein blocks cell-cell cohesion in developing Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature. 1979 May 17;279(5710):215–221. doi: 10.1038/279215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitherman R. W., Rosen S. D., Frasier W. A., Barondes S. H. Cell surface species-specific high affinity receptors for discoidin: developmental regulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3541–3545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen S. D., Kafka J. A., Simpson D. L., Barondes S. H. Developmentally regulated, carbohydrate-binding protein in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2554–2557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen S. D., Reitherman R. W., Barondes S. H. Distinct lectin activities from six species of cellular slime molds. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Oct 1;95(1):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90621-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSSMAN M. Synergistic and antagonistic interactions between morphogenetically deficient variants of the slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Feb;10(1):110–120. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-1-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu C. H., Lerner R. A., Ma G., Firtel R. A., Loomis W. F. Developmentally regulated proteins of the plasma membrane of Dictyostelium discoideum. The carbohydrate-binding protein. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 15;100(2):157–178. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. L., Kessin R. H., Newell P. C. Parasexual genetics in Dictyostelium discoideum: mitotic analysis of acriflavin resistance and growth in axenic medium. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):59–69. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]