Abstract
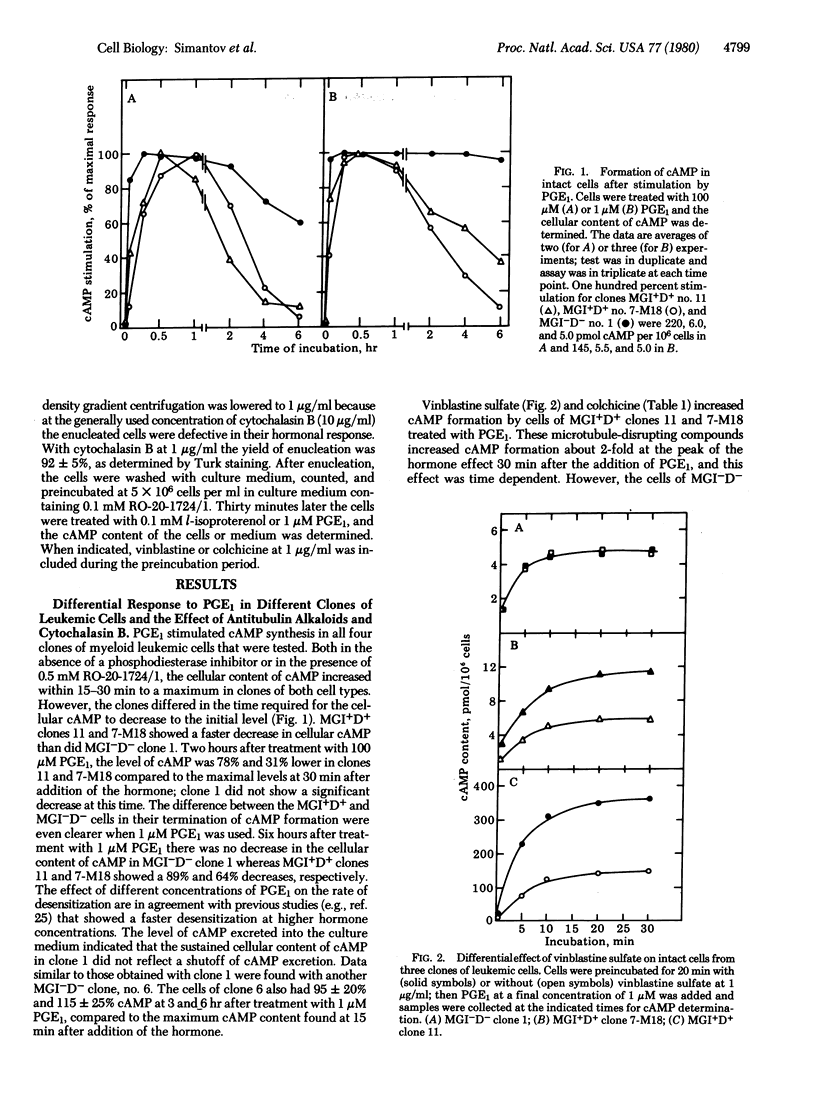
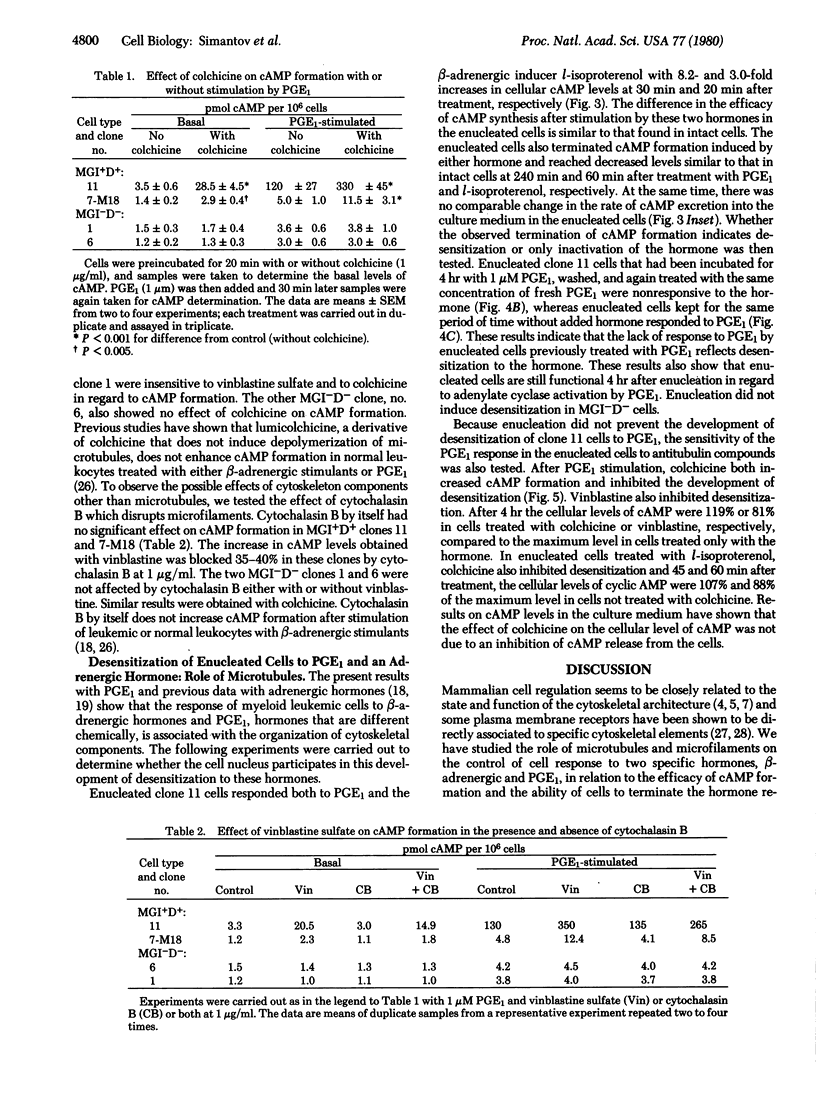
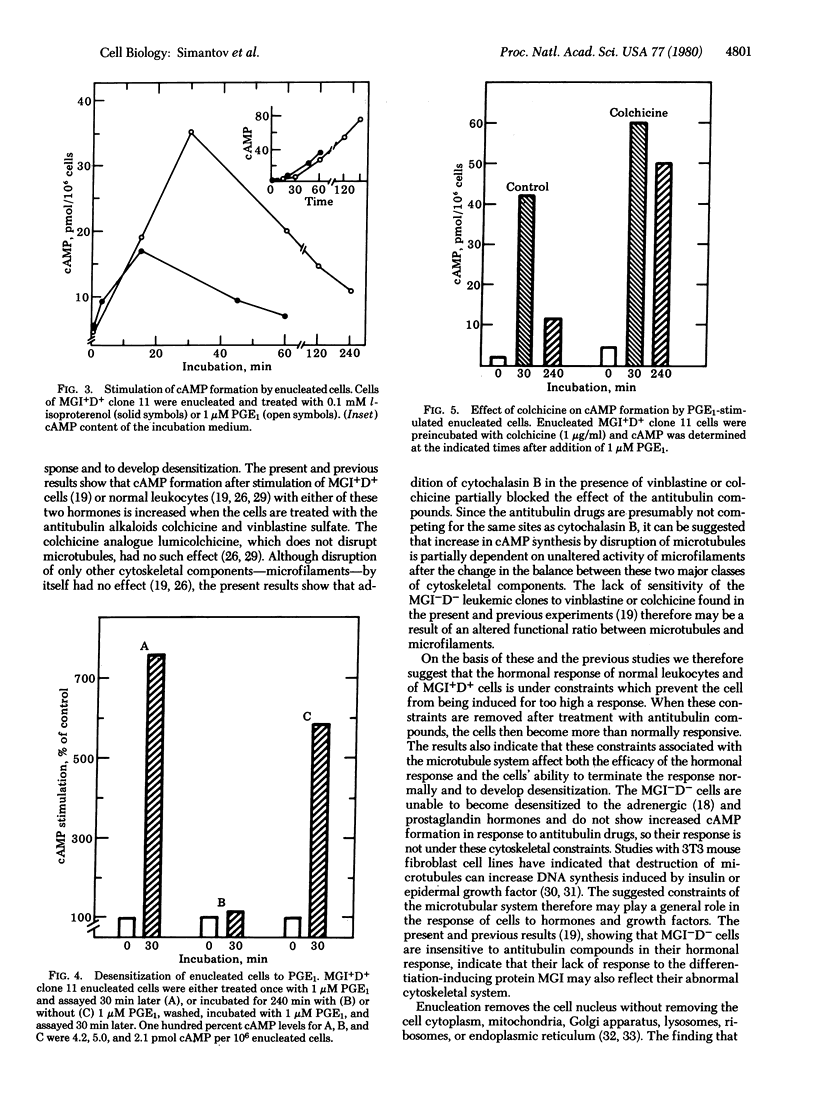
Prostaglandin E1 and the beta-adrenergic hormone l-isoproterenol stimulated cyclic AMP formation in both nucleated and enucleated myeloid leukemic cells that could be induced to differentiate normally to mature cells by the macrophage- and granulocyte-inducing protein MGI (MGI+D+ cells). Enucleated as well as nucleated MGI+D+ cells also desensitized to these hormones, indicating that this desensitization is an extranuclear process. Nucleated or enucleated mutant myeloid leukemic cells that are not induced to differentiate (MGI-D- cells) were not desensitized to these hormones. The antitubulin alkaloids colchicine and vinblastine, but not the antimicrofilament compound cytochalasin B, increased the maximal hormone-induced formation of cyclic AMP in nucleated MGI+D+ cells but not in the MGI-D- cells. These alkaloids also inhibited the development of desensitization to l-isoproterenol and prostaglandin E1 in enucleated MGI+D+ cells. The results indicate that in MGI+D+ cells the cytoskeletal system puts constraints on the cells' ability to respond to these hormones and that these constraints are absent in the mutant MGI-D- cells. Because MGI+D+ but not MGI-D- cells can be induced to differentiate by the macrophage- and granulocyte-inducing protein, cytoskeletal constraints, which are also found in normal myeloid cells, may be necessary for cell competence to differentiate. The results support the suggestion that membrane cytoskeletal constraints generate may control the normal response and desensitization to membrane-mediated cell inducers.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Mechanism of adenylate cyclase activation through the beta-adrenergic receptor: catecholamine-induced displacement of bound GDP by GTP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4155–4159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Membrane receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):169–214. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Surface modulation in cell recognition and cell growth. Science. 1976 Apr 16;192(4236):218–226. doi: 10.1126/science.769162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J., Koch G. L. Cross-linked surface Ig attaches to actin. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):278–281. doi: 10.1038/273278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedkin M., Legg A., Rozengurt E. Antitubulin agents enhance the stimulation of DNA synthesis by polypeptide growth factors in 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3909–3912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D., Pollack R. Uses of enucleated cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1974;8(0):123–143. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunspan-Swirsky A., Pick E. Enhancement of macrophage adenylate cyclase by microtubule disrupting drugs. Immunopharmacology. 1978 Dec;1(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(78)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmreich E. J., Zenner H. P., Pfeuffer T. Signal transfer from hormone receptor to adenylate cyclase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;10:41–87. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152810-2.50009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsie A. W., Puck T. T. Morphological transformation of Chinese hamster cells by dibutyryl adenosine cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate and testosterone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Kennedy M. S. Colchicine potentiates beta-adrenoreceptor-stimulated cyclic AMP in lymphoma cells by an action distal to the receptor. Nature. 1978 Jun 8;273(5662):471–473. doi: 10.1038/273471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G. L., Smith M. J. An association between actin and the major histocompatibility antigen H-2. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):274–278. doi: 10.1038/273274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan N., Krishna G. A simple and sensitive assay for guanylate cyclase. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):18–31. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Lefkowitz R. J. Adenylate cyclase-coupled beta adrenergic receptors effect of membrane lipid-perturbing agents on receptor binding and enzyme stimulation by catecholamines. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;12(4):559–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Genetic dissection of the control of normal differentiation in myeloid leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5554–5558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. E., Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. beta-Adrenergic receptor: ligand binding properties and the interaction with adenylyl cyclase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977;8:1–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Trans-membrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. II. Surface changes associated with transformation and malignancy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 30;458(1):1–72. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(76)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orly J., Schramm M. Coupling of catecholamine receptor from one cell with adenylate cyclase from another cell by cell fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4410–4414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostlund R. E., Jr, Pfleger B., Schonfeld G. Role of microtubules in low density lipoprotein processing by cultured cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):75–84. doi: 10.1172/JCI109281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck T. T. Cyclic AMP, the microtubule-microfilament system, and cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4491–4495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck T. T., Waldren C. A., Hsie A. W. Membrane dynamics in the action of dibutyryl adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate and testosterone on mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1943–1947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph S. A., Greengard P., Malawista S. E. Effects of colchicine on cyclic AMP levels in human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3404–3408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs L. Control of normal cell differentiation and the phenotypic reversion of malignancy in myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):535–539. doi: 10.1038/274535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shay J. W., Porter K. R., Prescott D. M. The surface morphology and fine structure of CHO (Chinese hamster ovary) cells following enucleation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3059–3063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard J. R. Catecholamine hormone receptor differences identified on 3T3 and simian virus-transformed 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1091–1094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Sachs L. Cytoskeleton regulates beta-adrenergic hormonal stimulation in normal and leukemic white blood cells. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 1;90(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. Molecular biology of cellular membranes with applications to immunology. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):1–66. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su Y. F., Harden T. K., Perkins J. P. Isoproterenol-induced desensitization of adenylate cyclase in human astrocytoma cells. Relation of loss of hormonal responsiveness and decrement in beta-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):38–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng M. H., Bartholomew J. C., Bissell M. J. Synergism between anti-microtubule agents and growth stimulants in enhancement of cell cycle traverse. Nature. 1977 Aug 25;268(5622):739–741. doi: 10.1038/268739a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomopoulos P., Roth J., Lovelace E., Pastan I. Insulin receptors in normal and transformed fibroblasts: relationship to growth and transformation. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., De Larco J. E., Cohen S. Transformation by murine and feline sarcoma viruses specifically blocks binding of epidermal growth factor to cells. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):26–31. doi: 10.1038/264026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Sachs L. Indirect induction of differentiation in myeloid leukemic cells by lipid A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M. H., Weinstein I. B. A preparative method for obtaining enucleated mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 7;63(3):669–674. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zor U., Strulovici B., Lindner H. R. Implication of microtubules and microfilaments in the response of the ovarian adenylate cyclase-cyclic AMP system to gonadotropins and prostaglandin E2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91342-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



