Abstract
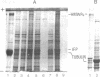
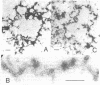
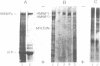
High molecular weight polypeptides (HMWPs) of 270,000 to 340,000 were found to be major components of intermediate filaments prepared by Triton X-100 extraction after spreading of rat glioma C6, HeLa, Chinese hamster ovary, and simian virus 40-transformed Chinese hamster lung cells. C6 HMWPs were shown to resemble high molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins from hog brain by four criteria: (i) comigration in electrophoresis on high-resolution sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels, (ii) one-dimensional peptide mapping, (iii) phosphorylation in vitro with [gamma-32P]ATP, and (iv) ability to promote microtubule assembly in vitro. HMWPs were also found to be major components of one-time polymerized C6 microtubule preparations, which contained a sizable amount of intermediate filaments. The predominant part of HMWPs present in these microtubule preparations was found not to copurify with microtubules in cycles of temperature-dependent assembly/disassembly but to remain with the cold-insoluble intermediate filaments. These results provide an explanation for the low yields that have hampered attempts to purify microtubule-associated porteins, in particular HMWPs, from cultured cells in the past. Moreover, they suggest that HMWPs might have a dual role in the cell, serving not only as regulators of microtubule assembly but also as linker components between microtubules and intermediate filaments.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F. Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. Membrane, soluble, and periplasmic fractions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):634–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amos L. A. Arrangement of high molecular weight associated proteins on purified mammalian brain microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1977 Mar;72(3):642–654. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.3.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulinski J. C., Borisy G. G. Self-assembly of microtubules in extracts of cultured HeLa cells and the identification of HeLa microtubule-associated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):293–297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Spiegelman B. M., Kirschner M. W. Conservation of microtubule associated proteins. Isolation and characterization of tau and the high molecular weight microtubule associated protein from chicken brain and from mouse fibroblasts and comparison to the corresponding mammalian brain proteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12670–12678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. A., Kalnins V. I., Cleveland D. W., Kirschner M. W. Intracellular localization of the high molecular weight microtubule accessory protein by indirect immunofluorescence. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):781–786. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corces V. G., Manso R., De La Torre J., Avila J., Nasr A., Wiche G. Effects of DNA on microtubule assembly. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):7–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D. The role of three cytoplasmic fibers in BHK-21 cell motility. I. Microtubules and the effects of colchicine. J Cell Biol. 1971 Dec;51(3):752–762. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr T. L., White H. D., Purich D. L. Characterization of brain microtubule proteins prepared by selective removal of mitochondrial and synaptosomal components. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6107–6111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner M. W., Honig L. S., Williams R. C. Quantitative electron microscopy of microtubule assembly in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 5;99(2):263–276. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein I., Willingham M., Pastan I. A high molecular weight phosphoprotein in cultured fibroblasts that associates with polymerized tubulin. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jun;114(1):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumarasamy R., Symons R. H. The tritium labeling of small amounts of protein for analysis by electrophoresis on sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide slab gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jun;95(2):359–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90739-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Borisy G. G. Association of high-molecular-weight proteins with microtubules and their role in microtubule assembly in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2696–2700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle B. W., Doenges K. H., Bryan J. Assembly of tubulin from cultured cells and comparison with the neurotubulin model. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):573–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runge M. S., Detrich H. W., 3rd, Williams R. C., Jr Identification of the major 68,000-dalton protein of microtubule preparations as a 10-nm filament protein and its effects on microtubule assembly in vitro. Biochemistry. 1979 May 1;18(9):1689–1698. doi: 10.1021/bi00576a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele R. B., Borisy G. G. Comparison of the sedimentation properties of microtubule protein oligomers prepared by two different procedures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 3;70(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherline P., Lee Y. C., Jacobs L. S. Binding of microtubules to pituitary secretory granules and secretory granule membranes. J Cell Biol. 1977 Feb;72(2):380–389. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherline P., Schiavone K. Immunofluorescence localization of proteins of high molecular weight along intracellular microtubules. Science. 1977 Dec 9;198(4321):1038–1040. doi: 10.1126/science.337490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloboda R. D., Rudolph S. A., Rosenbaum J. L., Greengard P. Cyclic AMP-dependent endogenous phosphorylation of a microtubule-associated protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):177–181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starger J. M., Brown W. E., Goldman A. E., Goldman R. D. Biochemical and immunological analysis of rapidly purified 10-nm filaments from baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jul;78(1):93–109. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherbee J. A., Luftig R. B., Weihing R. R. Binding of adenovirus to microtubules. II. Depletion of high-molecular-weight microtubule-associated protein content reduces specificity of in vitro binding. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):732–742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.732-742.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherbee J. A., Luftig R. B., Weihing R. R. In vitro polymerization of microtubules from HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jul;78(1):47–57. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Cole R. D. Reversible in vitro polymerization of tubulin from a cultured cell line (rat glial cell clone C6). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1227–1231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Corces V. G., Avila J. Preferential binding of hog brain microtubule-associated proteins to mouse satellite versus bulk DNA preparations. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):403–405. doi: 10.1038/273403a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Honig L. S., Cole R. D. Microtubule protein preparations from C6 glial cells and their spontaneous polymer formation. J Cell Biol. 1979 Mar;80(3):553–563. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.3.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Honig L. S., Cole R. D. Polymerising ability of C6 glial cell microtubule protein decays much faster than its colchicine-binding activity. Nature. 1977 Sep 29;269(5627):435–436. doi: 10.1038/269435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zingsheim H. P., Herzog W., Weber K. Differences in surface morphology of microtubules reconstituted from pure brain tubulin using two different microtubule-associated proteins: the high molecular weight MAP 2 proteins and tau proteins. Eur J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;19(2):175–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]