Abstract
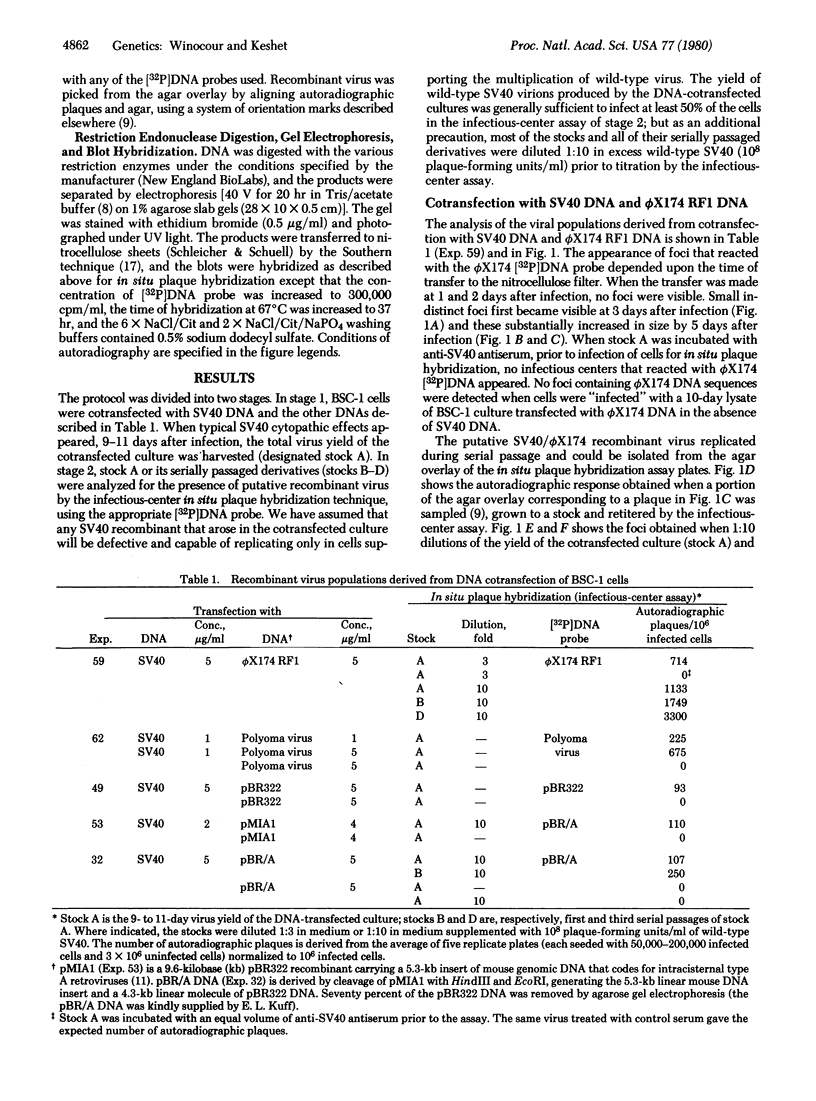
DNA transfection of African green monkey BSC-1 cells with simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA and bacterial virus phi X174 replicative form DNA ("cotransfection") yielded stocks containing SV40/phi X174 recombinant virus, which was detected by an infectious-center in situ plaque hybridization procedure and which was sensitive to anti-SV40 antiserum. The recombinant virus replicated during serial passage. Restriction endonuclease cleavage of the SV40/phi X174 DNA indicated that several different types of recombinant DNA structures had arisen. Similar SV40 DNA cotransfection experiments with polyoma virus DNA, bacterial plasmid (pBR322) DNA, and a plasmid-cloned segment of the mouse genome (coding for intracisternal type A particles) yielded stocks that generated recombinant plaques as judged by in situ plaque hybridization with the appropriate labeled probe. It appears, therefore, that an active indiscriminate recombination process, incapable of distinguishing between diverse DNAs of prokaryotic and eukaryotic origin, occurs in SV40-infected monkey cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crumpacker C. S., Levin M. J., Wiese W. H., Rowe W. P., Lewis A. M., Jr Adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrid population: evidence for a hybrid deoxyribonucleic acid molecule and the absence of adenovirus-encapsidated circular simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1970 Dec;6(6):788–794. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.6.788-794.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fareed G. C., Davoli D. Molecular biology of papovaviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:471–522. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Kuff E. L., Winocour E. Recombination between endogenous and exogenous simian virus 40 genes. I. Rescue of a simian virus 40 temperature-sensitive mutant by passage in permissive transformed monkey lines. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):534–540. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.534-540.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi S., Winocour E. Acquisition of sequences homologous to host deoxyribonucleic acid by closed circular simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):309–316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.309-316.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Intracisternal A-particle genes: identification in the genome of Mus musculus and comparison of multiple isolates from a mouse gene library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3571–3575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Kuff E. L., Winocour E. The presence of common host sequences in different populations of substituted SV40 DNA. Virology. 1976 Sep;73(2):419–430. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90403-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Lavi S., Winocour E. The structure of a cloned substituted SV40 genome. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):404–421. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90448-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J. Restriction and modification enzymes and their recognition sequences. Gene. 1980 Mar;8(4):329–343. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J. The isolation of defective variants of simian virus 40 whose genomes contain sequences derived from adenovirus 2 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1978 Feb;38(2):313–327. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal L. P., Berg P. Hybridization in situ of SV40 plaques: detection of recombinant SV40 virus carrying specific sequences of nonviral DNA. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):183–185. doi: 10.1126/science.191907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel T., Gluzman Y., Winocour E. Recombination between endogenous and exogenous simian virus 40 genes. II. Biochemical evidence for genetic exchange. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):541–550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.541-550.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakamiya T., McCutchan T., Rosenberg M., Singer M. Structure of simian virus 40 recombinants that contain both host and viral DNA sequences. I. The structure of variant CVPS/1/P2 (EcoRI res). J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3584–3591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]