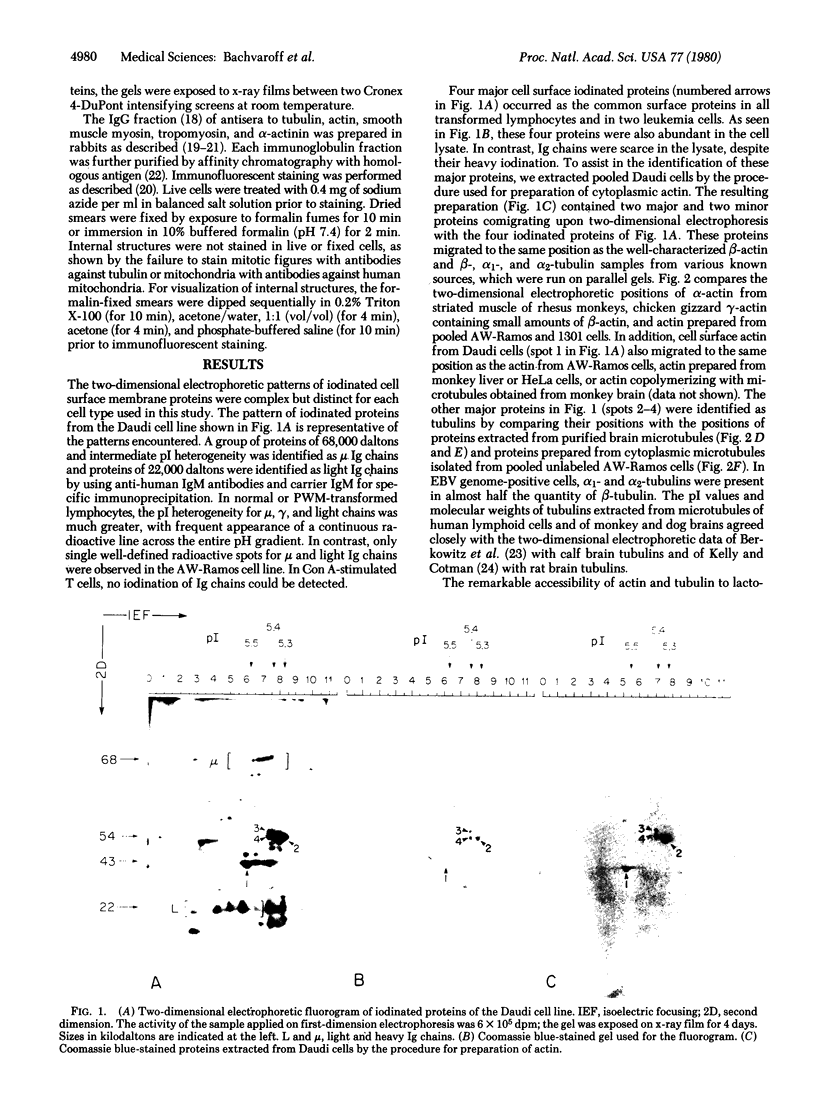
Abstract
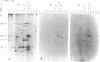
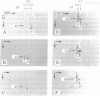
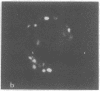
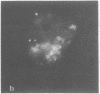
Lactoperoxidase iodination and two-dimensional electrophoresis of the labeled proteins have demonstrated well-characterized cytoskeletal proteins (actin and tubulins) on the surface of human lymphocytes undergoing blastogenic transformation and of certain malignant human cells. Such proteins could not be detected on the surface of normal resting human lymphocytes. The most prominent cytoskeletal protein identified on the surface membrane of mitogen-transformed T and B lymphocytes was actin. In Epstein-Barr virus genome-positive Burkitt's lymphoma and lymphoblastoid cell lines and in two leukemia cells, the major iodinated membrane protein components were actin and alpha 1-, alpha 2-, and beta-tubulins. These proteins were firmly connected to the cytoplasmic skeleton and could not be removed by Triton X-100. Concurrent immunofluorescence studies with specific antibodies and F(ab')2 fragments confirmed the appearance of cytoskeletal components on the biochemical data, and indicated that such cytoskeletal proteins formed distinctive patterns on the cell surface, ranging from small patches to large projections. Five-hour labeling with [35S]methionine indicates that all such cells released large quantities of labeled actin and tubulins into the culture medium. These materials were not readsorbed to the membrane surfaces of the cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P., Molgaard J., Andersen I., Andersen H. K. Smooth-muscle antibodies and antibodies to cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus in leukaemias and lymphomata. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Apr;84(2):86–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachvaroff R. J., Rapaport F. T. Active secretion of cytoskeletal and mechanochemical proteins in EBV-genome-positive human lymphocytes. Transplant Proc. 1980 Mar;12(1):205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachvaroff R. J., Rapaport F. T. Studies of mechanisms of antibody formation. III. Effects of 5-bromodeoxyuridine upon normal and neoplastic B-lymphocyte function. Cell Immunol. 1977 Jun 1;31(1):98–119. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz S. A., Katagiri J., Binder H. K., Williams R. C., Jr Separation and characterization of microtubule proteins from calf brain. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5610–5617. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F. M., Sternberger L. A., Zschocke D., Rafelson M. E., Jr Ultrastructural localization of contractile protein (thrombosthenin) in human platelets using an unlabeled antibody-peroxidase staining technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1971 Sep;19(9):540–550. doi: 10.1177/19.9.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley R. C., Trayer I. P. Affinity chromatography of immobilized actin and myosin. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;149(2):365–379. doi: 10.1042/bj1490365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron J. M., Berlin R. D. Interaction of microtubule proteins with phospholipid vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):665–671. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feit H., Shelanski M. L. Is tubulin a glycoprotein? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 6;66(3):920–927. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90728-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D., Lazarides E., Pollack R., Weber K. The distribution of actin in non-muscle cells. The use of actin antibody in the localization of actin within the microfilament bundles of mouse 3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Feb;90(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90323-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness M. H., Wang K., Singer S. J. Intracellular distributions of mechanochemical proteins in cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3883–3887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holborow E. J., Hemsted E. H., Mead S. V. Smooth muscle autoantibodies in infectious mononucleosis. Br Med J. 1973 Aug 11;3(5875):323–325. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5875.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jockusch B. M., Kelley K. H., Meyer R. K., Burger M. M. An efficient method to produce specific anti-actin. Histochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;55(3):177–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00495757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. T., Cotman C. W. Synaptic proteins. Characterization of tubulin and actin and identification of a distinct postsynaptic density polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1978 Oct;79(1):173–183. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G. L., Smith M. J. An association between actin and the major histocompatibility antigen H-2. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):274–278. doi: 10.1038/273274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Weber K. Actin antibody: the specific visualization of actin filaments in non-muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2268–2272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller F., Lazarides E., Elias J. Application of immunologic probes for contractile proteins to tissue sections. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 May;5(3):416–428. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Marcus A. J., Safier L. B. Platelet thrombosthenin: subcellular localization and function. J Clin Invest. 1967 Aug;46(8):1380–1389. doi: 10.1172/JCI105630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Turner M. W. Localization of Gm markers to different molecular regions of the Fc fragment. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 May;8(5):685–700. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olden K., Willingham M., Pastan I. Cell surface myosin in cultured fibroblasts. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Born T., Koitsch H. J., Weber K. Stereo immunofluorescence microscopy: I. Three-dimensional arrangement of microfilaments, microtubules and tonofilaments. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):477–488. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., Auger J., Barber B. H., Edwards A. J., Walsh F. S., Crumpton M. J. Actin may be present on the lymphocyte surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4484–4488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. G., Sheetz M., Singer S. J. Detection and ultrastructural localization of human smooth muscle myosin-like molecules in human non-muscle cells by specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1359–1363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdue J. F. The distribution, ultrastructure, and chemistry of microfilaments in cultured chick embryo fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):265–283. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinitz M., Klein G. Comparison between growth characteristics of an Epstein--Barr virus (EBV)-genome-negative lymphoma line and its EBV-converted subline in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3518–3520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E. Major membrane protein differences in cilia and flagella: evidence for a membrane-associated tubulin. Biochemistry. 1977 May 17;16(10):2047–2058. doi: 10.1021/bi00629a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Suter M. M., Littman D. R., Kirschner M. W. Properties of the depolymerization products of microtubules from mammalian brain. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 31;13(27):5529–5537. doi: 10.1021/bi00724a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]