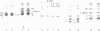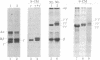Abstract
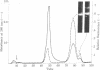
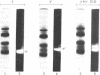
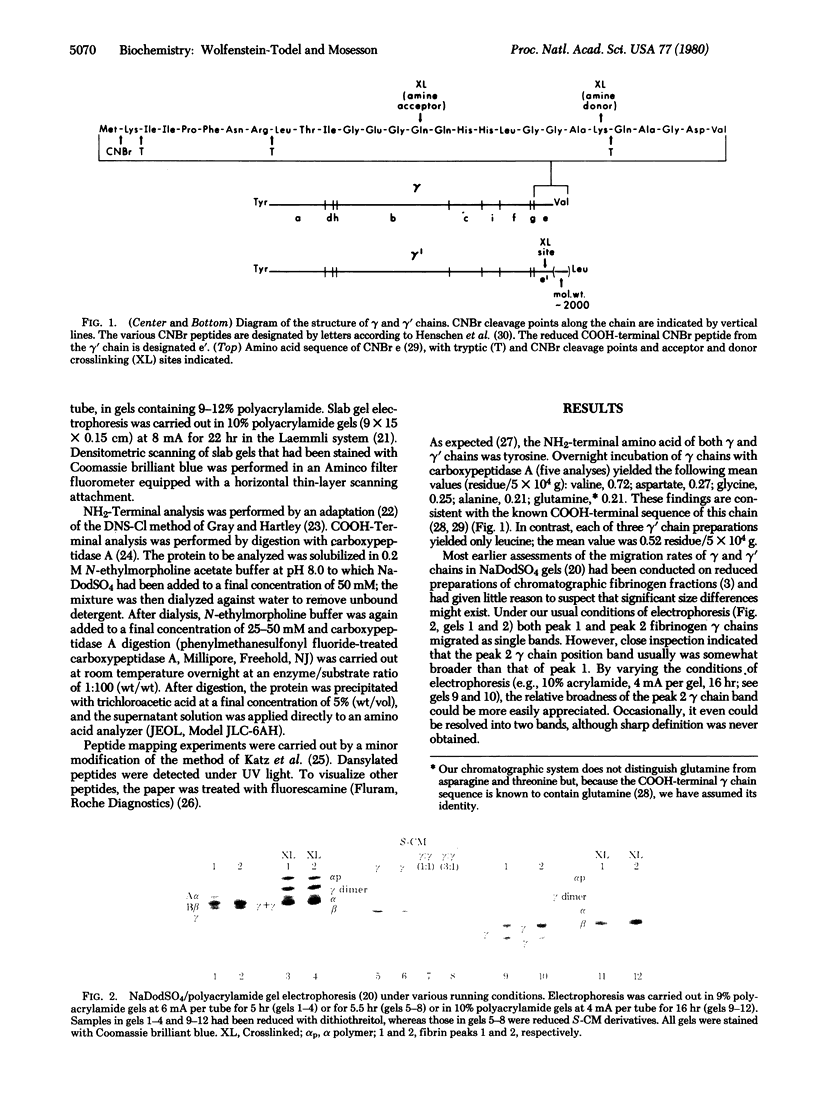
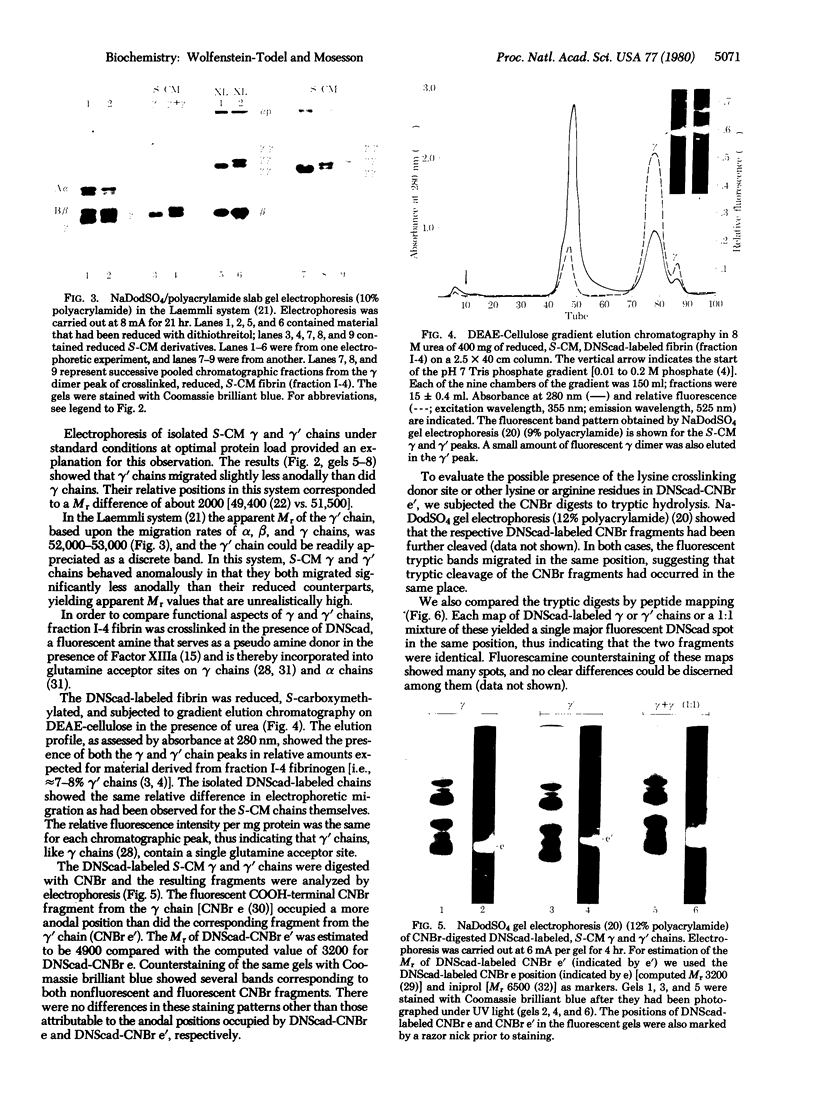
Two types of normal human plasma fibrinogen--peak 1 and peak 2--are distinquishable by DEAE-cellulose gradient elution chromatography. The elution characteristics of peak 2 fibrinogen, which amounts to about 15% of the total, are attributable to the presence of a gamma chain variant, gamma', which is more negatively charged than gamma chains and makes up about half of all such chains in that peak [Mosesson M. W., Finlayson, J. S. & Umfleet, R. A. (1972), J. Biol. Chem. 247, 5223-5227]. Analyses of reduced S-carboxymethylated fibrin that had first been incubated in the presence of Factor XIIIa plus the fluorescent amine donor dansylcadaverine (DNScad) showed that the same amount of this compound could be incorporated covalently into either type of gamma chain. Furthermore, the DNScad-labeled COOH-terminal CNBr fragment (CNBr e) derived from the S-carboxymethylated gamma chain was smaller than the DNScad-labeled fragment (CNBr e') from the gamma' chain (Mr, 3200 and 4900) by about the same amount as the difference in size between the respective parent chains (Mr, 49,400 and 51,500). DNScad-CNBr e or DNScad-cNBR e' could be further cleaved by trypsin to yield a smaller fluorescent fragment corresponding to the penultimate tryptic gamma chain peptide containing the DNScad-glutamine acceptor and lysine donor crosslinking functions. The COOH-terminal amino acids of gamma and gamma' chains were valine and leucine, respectively. The rates of Factor XIIIa-catalyzed crosslinking of peak 1 and peak 2 fibrin were the same, but peak 1 fibrin gamma chains formed only one species of crosslinked dimer (gamma gamma) whereas peak 2 fibrin gamma chains yielded three (gamma gamma, gamma gamma', gamma'gamma'). We conclude that gamma' chains are functionally normal but have an extended COOH-terminal sequence accounting for their more negative charge and larger size relative to gamma chains.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brownstein M. J., Russell J. T., Gainer H. Synthesis, transport, and release of posterior pituitary hormones. Science. 1980 Jan 25;207(4429):373–378. doi: 10.1126/science.6153132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Doolittle R. F. - cross-linking sites in human and bovine fibrin. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4487–4491. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINLAYSON J. S., MOSESSON M. W. CHROMATOGRAPHIC HETEROGENEITY OF ANIMAL FIBRINOGENS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 10;82:415–417. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90318-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS E., WITKOP B. Nonenzymatic cleavage of peptide bonds: the methionine residues in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1856–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanakis D. K., Mosesson M. W., Stathakis N. E. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities: distribution and charge characteristics of chains of A alpha origin. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Sep;92(3):376–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gati W. P., Straub P. W. Separation of both the Bbeta- and the gamma-polypeptide chains of human fibrinogen into two main types which differ in sialic acid content. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1315–1321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Rich A. A UGA termination suppression tRNATrp active in rabbit reticulocytes. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):41–46. doi: 10.1038/283041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerbeck C. M., Yoshikawa T., Montgomery R. Bovine fibrinogen--heterogeneity of the gamma-chains. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Oct;134(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90252-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith I. P. The effect of cross-links on the mobility of proteins in dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):553–560. doi: 10.1042/bj1260553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henschen A., Lottspeich F., Sekita T., Warbinek R. Amino acid sequence of human fibrin. Preliminary note on the order of peptides obtained by cleaving the gamma-chain at the methionyl and arginyl bonds. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Apr;357(4):605–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Monstein H. J., Weissmann C. The readthrough protein A1 is essential for the formation of viable Q beta particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 6;374(2):238–251. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90366-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi K., Webster R. E., Matsuhashi S. Gene products of bacteriophage Q beta. Virology. 1971 Aug;45(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90343-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen H., Demandt A., Moody A. J., Sundby F. Sequence analysis of porcine gut GLI-1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 23;493(2):452–459. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KASSELL B., RADICEVIC M., BERLOW S., PEANASKY R. J., LASKOWSKI M., Sr THE BASIC TRYPSIN INHIBITOR OF BOVINE PANCREAS. I. AN IMPROVED METHOD OF PREPARATION AND AMINO ACID COMPOSITION. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3274–3279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ A. M., DREYER W. J., ANFINSEN C. B. Peptide separation by two-dimensional chromatography and electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2897–2900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazama M., McDonagh J., Wagner R. H., Langdell R. D., McDonagh R. P. Purification and immunochemical characterization of human plasma factor XIII. Haemostasis. 1976;5(6):329–340. doi: 10.1159/000214153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEWY A. G., DUNATHAN K., KRIEL R., WOLFINGER H. L., Jr Fibrinase. I. Purification of substrate and enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1961 Oct;236:2625–2633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Chenoweth D., Gray A. Titration of the acceptor cross-linking sites in fibrin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:155–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Urayama T., De Kiewiet J. W., Nossel H. L. Diagnostic and genetic studies on fibrin-stabilizing factor with a new assay based on amine incorporation. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jun;48(6):1054–1064. doi: 10.1172/JCI106061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSESSON M. W., FINLAYSON J. S. SUBFRACTIONS OF HUMAN FIBRINOGEN; PREPARATION AND ANALYSIS. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Oct;62:663–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J. Metabolic studies on human fibrinogen gamma/gamma' chain heterogeneity. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):417–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh J., Messel H., McDonagh R. P., Jr, Murano G., Blombäck B. Molecular weight analysis of fibrinogen and fibrin chains by an improved sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90262-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez E., Lai C. Y. Reaction of peptides with fluorescamine on paper after chromatography or electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90511-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Amrani D. L., Ménaché D. Studies on the structural abnormality of fibrinogen Paris I. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):782–790. doi: 10.1172/JCI108337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S., Galanakis D. K. The essential covalent structure of human fibrinogen evinced by analysis of derivatives formed during plasmic hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7913–7929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S., Umfleet R. A., Galanakis D. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. I. Structural and related studies of plasma fibrinogens which are high solubility catabolic intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5210–5219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S., Umfleet R. A. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. 3. Identification of chain variants. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5223–5227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Sherry S. The preparation and properties of human fibrinogen of relatively high solubility. Biochemistry. 1966 Sep;5(9):2829–2835. doi: 10.1021/bi00873a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Blout E. R. Heterogeneity of bovine fibrinogen and fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6896–6903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. H., von der Mark K., McEneany L. S., Bornstein P. Characterization of procollagen-derived peptides unique to the precursor molecule. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3243–3250. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen B. R., Guzman N. A., Engel J., Condit C., Aase S. Purification and characterization of a peptide from the carboxy-terminal region of chick tendon procollagen type I. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 28;16(13):3030–3036. doi: 10.1021/bi00632a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzelt C., Tager H. S., Carroll R. J., Steiner D. F. Identification and processing of proglucagon in pancreatic islets. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):260–266. doi: 10.1038/282260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Pizzo S. V., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. The effect of fibrin-stabilizing factor on the subunit structure of human fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1506–1513. doi: 10.1172/JCI106636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. J., Cassman K. G., Doolittle R. F. Amino acid sequence of the carboxy-terminal cyanogen bromide fragment from bovine and human fibrinogen gamma-chains. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):334–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80517-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stathakis N. E., Mosesson M. W., Galanakis D. K., Ménaché D. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. Preparation and characterization of gamma and gamma' chains. Thromb Res. 1978 Sep;13(3):467–475. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Steiner D. F. Isolation of a glucagon-containing peptide: primary structure of a possible fragment of proglucagon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2321–2325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Weber K. A single UGA codon functions as a natural termination signal in the coliphage q beta coat protein cistron. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):837–855. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90213-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]