Abstract
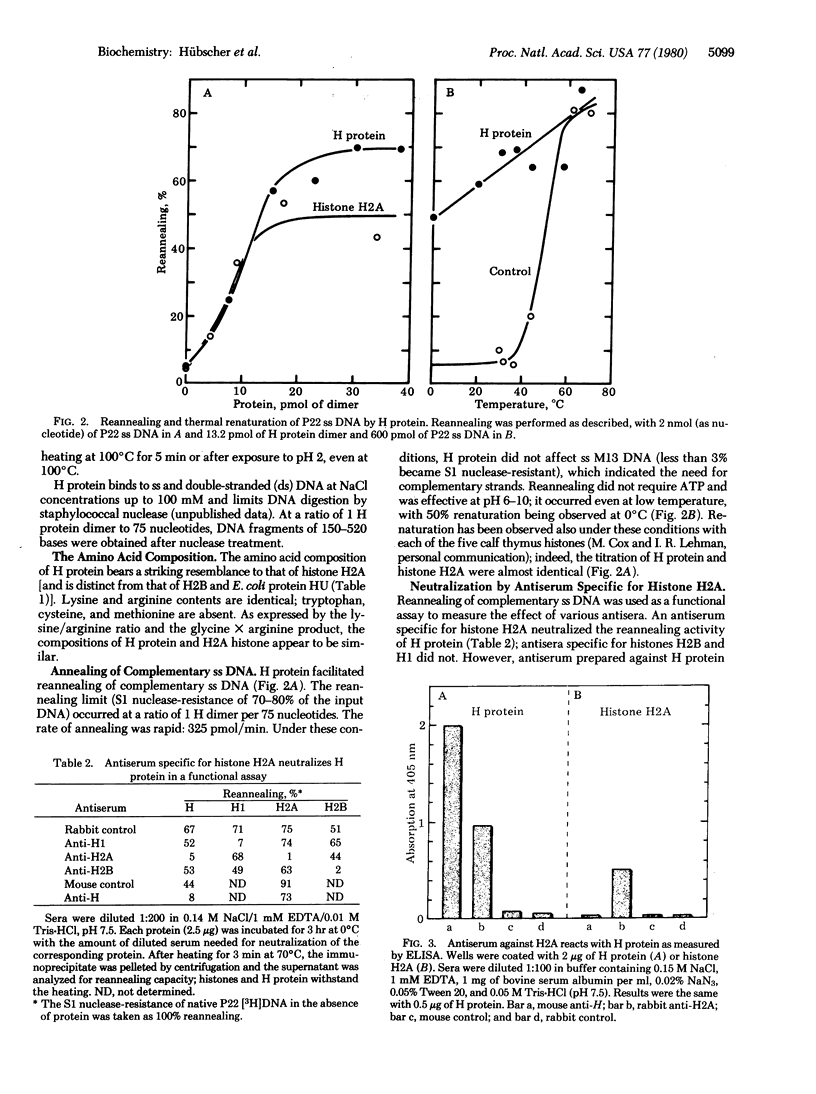
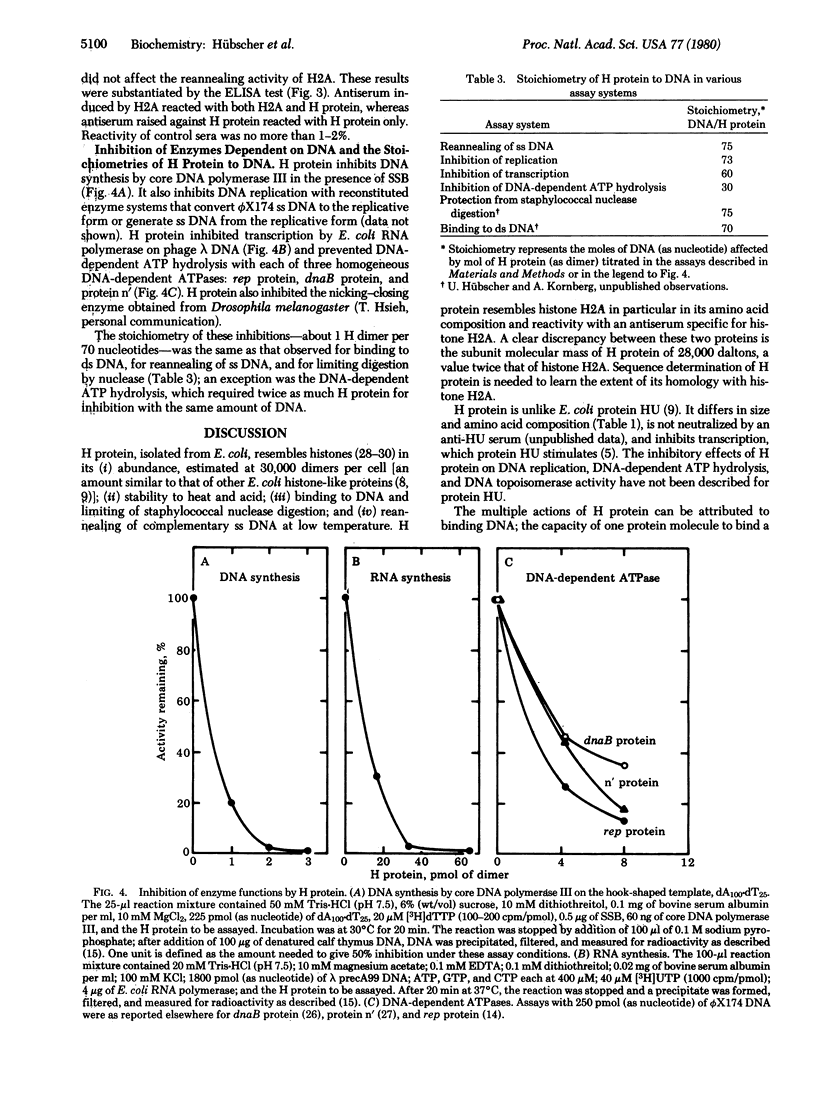
A histone-like protein (H) from Escherichia coli has been purified to more than 98% homogeneity by using its capacity to inhibit DNA functions. H protein behaves as a dimer of 28,000-dalton subunits. The histone H2A-like properties of H protein are: (i) binding to DNA at a stoichiometry of 1 H protein dimer per 75 bases; (ii) abundance of about 30,000 molecules per cell, sufficient to bind about 20% of the chromosome; (iii) limiting digestion of double-stranded DNA by micrococcal nuclease; (iv) reannealing of complementary single-stranded DNA; (v) amino acid composition resembling that of eukaryotic histone H2A; (vi) neutralization of H protein by antibody specific for H2A; (vii) heat stability; and (viii) acid solubility. The capacity of H protein to bind DNA prevents its template or substrate functions n several reactions in vitro: DNA synthesis by several polymerases; transcription by RNA polymerase; DNA topoisomerase activity; and DNA-dependent ATP hydrolysis by rep protein, dnaB protein, or protein n'. Together with other histone-like proteins of E. coli, H protein may organize the E. coli chromosome into nucleosomes, such as in eukaryotic chromatin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B., Sternglanz R. Recent excitement in the DNA replication problem. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):655–661. doi: 10.1038/269655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthold V., Geider K. Interaction of DNA with DNA-binding proteins. The characterization of protein HD from Escherichia coli and its nucleic acid complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):443–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. L., Soll L., Richardson C. C. Isolation and partial characterization of a mutant of Escherichia coli deficient in DNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2090–2094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Proteins that affect DNA conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:449–479. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukier-Kahn R., Jacquet M., Gros F. Two heat-resistant, low molecular weight proteins from Escherichia coli that stimulate DNA-directed RNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3643–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Harbers B., Hours C., Denhardt D. T. The mechanism of replication of phiX174 DNA. XII. Non-random location of gaps in nascent phiX174 RF II DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 25;99(1):107–123. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franze de Fernandez M. T., Hayward W. S., August J. T. Bacterial proteins required for replication of phage Q ribonucleic acid. Pruification and properties of host factor I, a ribonucleic acid-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):824–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Echols H. Purification and properties of D protein: a transcription factor of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3660–3664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt D., Bustin M. Exposure of histone antigenic determinants in chromatin. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1689–1695. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D. Visualization of prokaryotic DNA in a regularly condensed chromatin-like fiber. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):563–567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselkorn R., Rouvière-Yaniv J. Cyanobacterial DNA-binding protein related to Escherichia coli HU. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1917–1920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U., Kornberg A. The delta subunit of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme is the dnaX gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6284–6288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg I. Histones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:159–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg T., Lockwood A., Worcel A. Replication of the Escherichia coli chromosome with a soluble enzyme system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3189–3193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. R., Shlomai J., Kobori J., Bates D. L., Rowen L., McMacken R., Ueda K., Kornberg A. Enzymatic conversion of single-stranded phiX174 and G4 circles to duplex forms: discontinuous replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):289–293. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Genetic recombination: strand transfer and mismatch repair. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:847–880. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière-Yaniv J., Gros F. Characterization of a novel, low-molecular-weight DNA-binding protein from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3428–3432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière-Yaniv J. Localization of the HU protein on the Escherichia coli nucleoid. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):439–447. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière-Yaniv J., Yaniv M., Germond J. E. E. coli DNA binding protein HU forms nucleosomelike structure with circular double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders G. C., Bartlett M. L. Double-antibody solid-phase enzyme immunoassay for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Nov;34(5):518–522. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.5.518-522.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. F., Kornberg A. Purification of the rep protein of Escherichia coli. An ATPase which separates duplex DNA strands in advance of replication. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3292–3297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomai J., Kornberg A. An Escherichia coli replication protein that recognizes a unique sequence within a hairpin region in phi X174 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):799–803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein D. B., Searcy D. G. Physiologically important stabilization of DNA by a prokaryotic histone-like protein. Science. 1978 Oct 13;202(4364):219–221. doi: 10.1126/science.694528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stonington O. G., Pettijohn D. E. The folded genome of Escherichia coli isolated in a protein-DNA-RNA complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):6–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., McMacken R., Kornberg A. dnaB protein of Escherichia coli. Purification and role in the replication of phiX174 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):261–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Nedospasov S. A., Bakayev V. V., Bakayeva T. G., Georgiev G. P. Histone-like proteins in the purified Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleoprotein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2725–2745. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Burgi E. On the structure of the folded chromosome of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):127–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]