Abstract
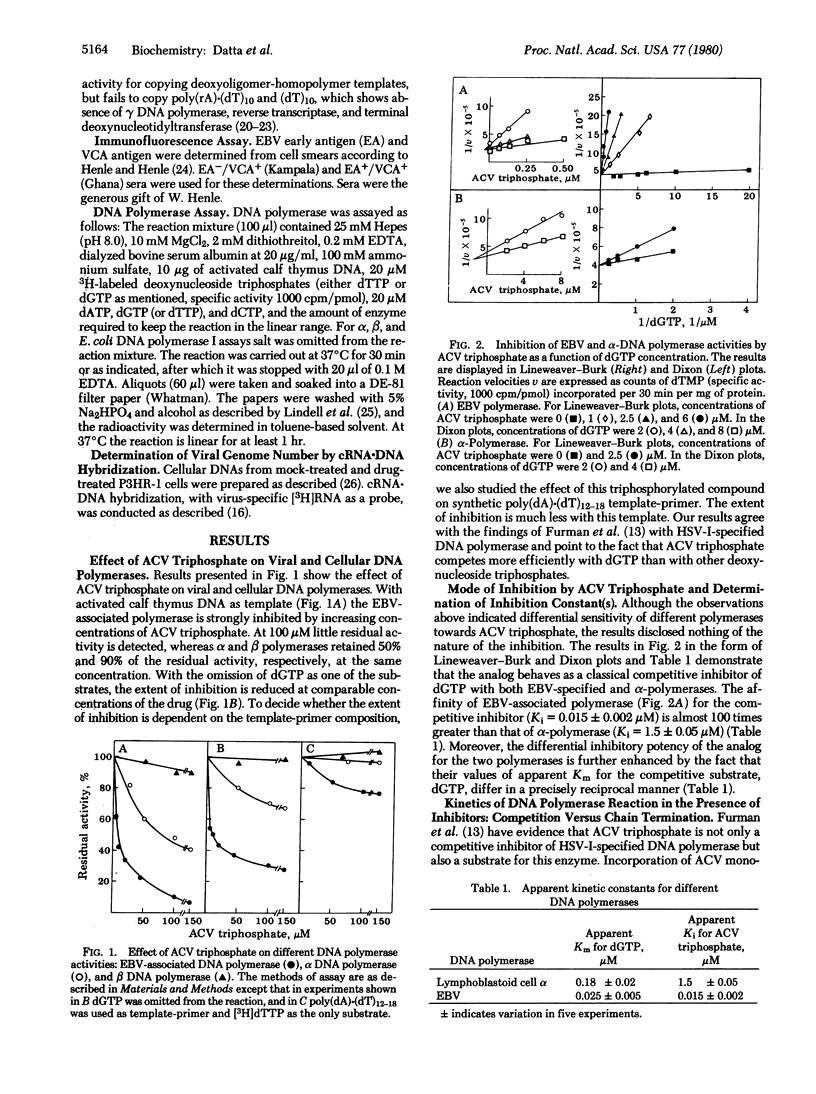
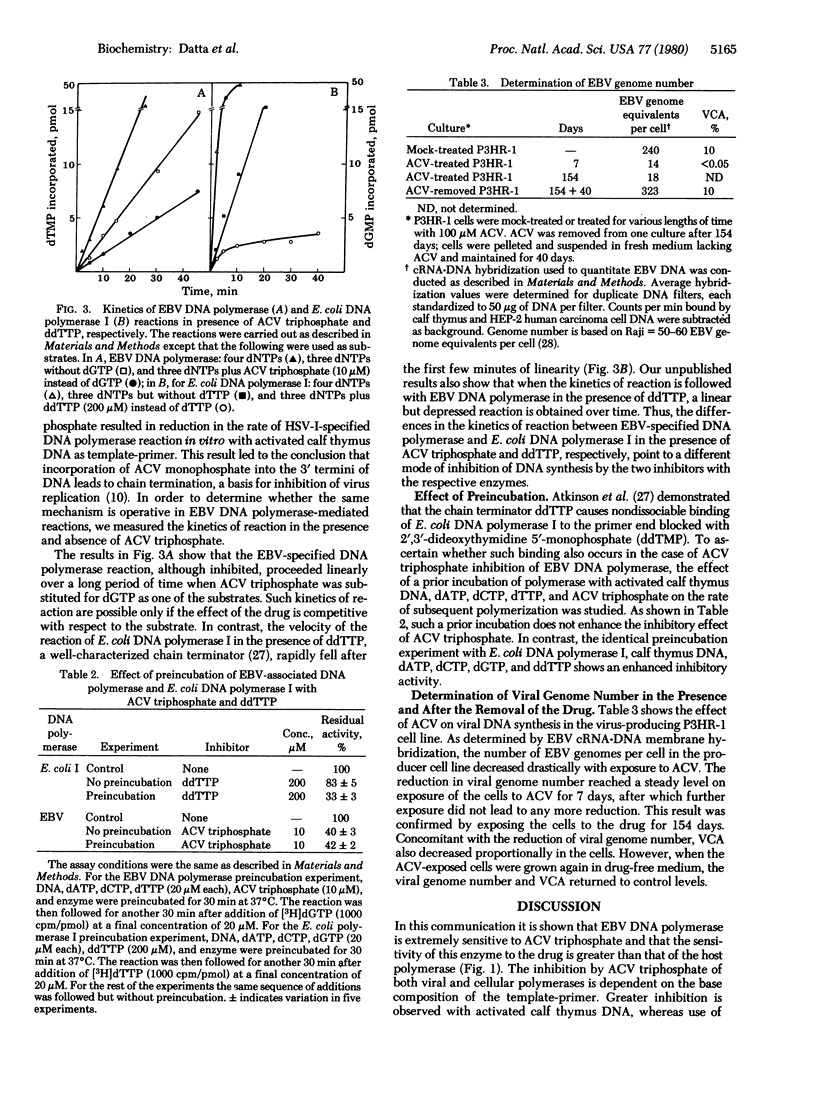
Acyclovir [9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine] triphosphate inhibits Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated DNA polymerase (DNA nucleotidyltransferase; EC 2.7.7.7) to a greater extent than it inhibits host alpha and beta DNA polymerases. The affinity of the compound for viral polymerase is 100-fold higher than for alpha-polymerase. The extent of inhibition is dependent upon the base composition of the template-primer. The inhibition is prevented by increasing concentrations of deoxyguanosine triphosphate. The EBV-associated DNA polymerase reaction in the presence of the inhibitor, although depressed, proceeds at a linear rate over a long period of time. In contrast, the reaction of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I in the presence of 2',3'-dideoxythymidine 5'-triphosphate, a DNA chain terminator, levels off after initial linearity. Preincubation of acyclovir triphosphate with DNA and enzyme does not increase its inhibitory activity. The virus-producing cell line P3HRF-1 consistently shows reduced viral genome numbers and viral capsid antigen on prolonged exposure to acyclovir. The number of EBV genomes returns to the control level when the cells are grown in drug-free medium. The results suggest that a competitive mechanism is the major mode of acyclovir inhibition of EBV replication.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. R., Deutscher M. P., Kornberg A., Russell A. F., Moffatt J. G. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXXIV. Termination of chain growth by a 2',3'-dideoxyribonucleotide. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):4897–4904. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1209–1211. doi: 10.1038/2261209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolden A., Noy G. P., Weissbach A. DNA polymerase of mitochondria is a gamma-polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3351–3356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. M., Bollum F. J. Doxynucleotide-polymerizing enzymes of calf thymus gland. IV. Inhibition of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase by metal ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):1041–1048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Domin B. A., Sharma R. A., Bobek M. Antiviral action and cellular toxicity of four thymidine analogues: 5-ethyl-,5-vinyl-, 5-propyl-, and 5-allyl-2'- deoxyuridine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):119–122. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Goz B., Neenan J. P., Ward D. C., Prusoff W. H. Selective inhibition of herpes simplex virus by 5-amino-2,5-dideoxy-5-iodouridine. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1284–1285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1284-1285.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Hoffmann P. J., Ostrander M., Grill S., Caradonna S., Tsou J., Chen J. Y., Gallagher M. R., Flanagan T. D. Properties of herpesvirus-specific thymidine kinase, DNA polymerase and DNase and their implication in the development of specific antiherpes agents. Adv Ophthalmol. 1979;38:173–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Schaffer P. A. Two distinct loci confer resistance to acycloguanosine in herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2265–2269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby B. M., Shaw J. E., Elion G. B., Pagano J. S. Effect of acyclovir [9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine] on Epstein-Barr virus DNA replication. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):560–568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.560-568.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P., Bauer D. J. Relative potencies of anti-herpes compounds. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:49–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb21936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumpacker C. S., Schnipper L. E., Zaia J. A., Levin M. J. Growth inhibition by acycloguanosine of herpesviruses isolated from human infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):642–645. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. K., Feighny R. J., Pagano J. S. Induction of Epstein-Barr virus-associated DNA polymerase by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5120–5125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion G. B., Furman P. A., Fyfe J. A., de Miranda P., Beauchamp L., Schaeffer H. J. Selectivity of action of an antiherpetic agent, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5716–5720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faras A. J., Taylor J. M., Levinson W. E., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. RNA-directed DNA polymerase of Rous sarcoma virus: initiation of synthesis with 70 S viral RNA as template. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 5;79(1):163–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. A., Wang T. S., Korn D. Enzymological characterization of DNA polymerase alpha. Basic catalytic properties processivity, and gap utilization of the homogeneous enzyme from human KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6128–6137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Fyfe J. A., Rideout J. L., Keller P. M., Elion G. B. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerase activity and viral DNA replication by 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine and its triphosphate. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.72-77.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe J. A., Keller P. M., Furman P. A., Miller R. L., Elion G. B. Thymidine kinase from herpes simplex virus phosphorylates the new antiviral compound, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8721–8727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry G. A., Aswell J. F. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus replication by araT. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):294–296. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Konn M., Yamaguchi J., Wudarski D. J., Blakeslee J. R., Jr, Grace J. T., Jr Immunofluorescence and herpes-type virus particles in the P3HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma cell line. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):1045–1051. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.1045-1051.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., Englund P. T., Bertsch L. L. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXVI. Physical and chemical studies of a homogeneous deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 10;244(11):2996–3008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J., Weinberg F., Morris P. W., Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerase II by alpha-amanitin. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Zahn R. K., Arendes F., Falke D. Phosphorylation of arabinofuranosylthymine in non-infected and herpesvirus (TK+ and TK-)-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1979 May;43(2):261–271. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North T. W., Cohen S. S. Erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl)adenine as a specific inhibitor of herpes simplex virus replication in the presence and absence of adenosine analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4684–4688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer H. J., Beauchamp L., de Miranda P., Elion G. B., Bauer D. J., Collins P. 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine activity against viruses of the herpes group. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):583–585. doi: 10.1038/272583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut I., Cooper G. M., Greer S. Selective inhibition of the replication of herpes simplex virus by 5-halogenated analogues of deoxycytidine. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Mar;11(2):153–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnipper L. E., Crumpacker C. S. Resistance of herpes simplex virus to acycloguanosine: role of viral thymidine kinase and DNA polymerase loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2270–2273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smoler D., Molineux I., Baltimore D. Direction of polymerization by the avian myeloblastosis virus deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7697–7700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


