Abstract
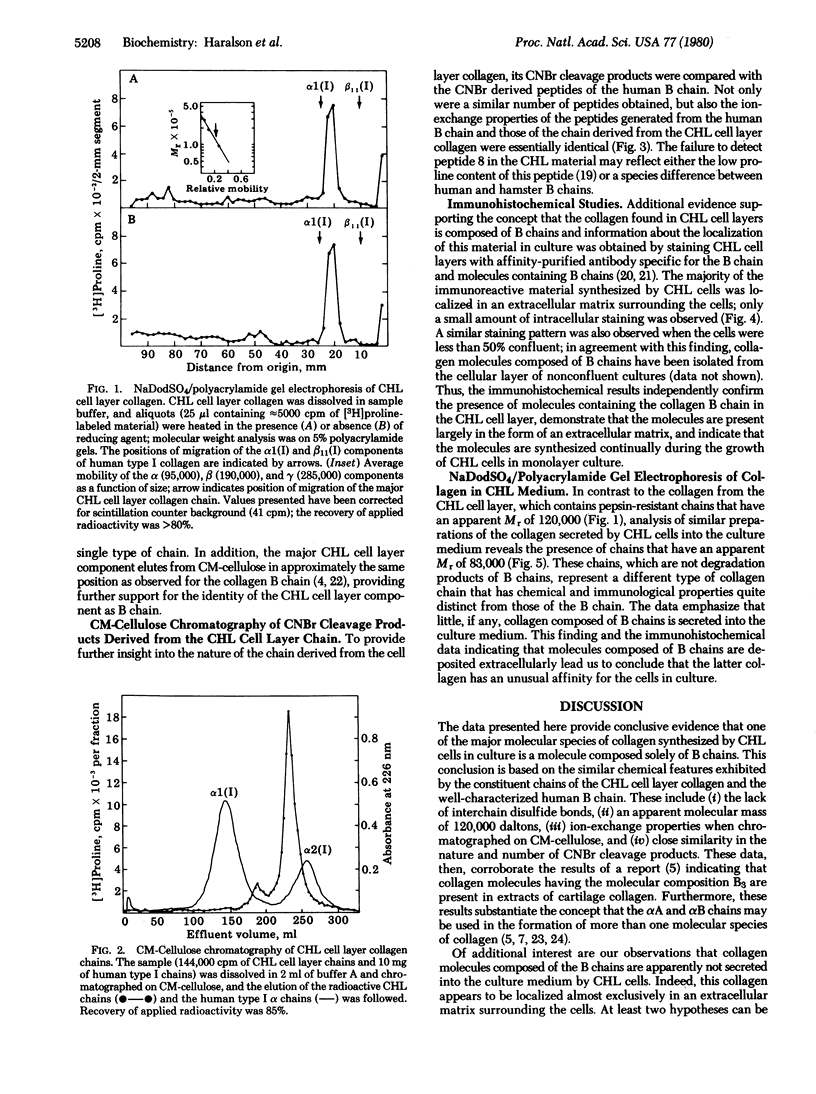
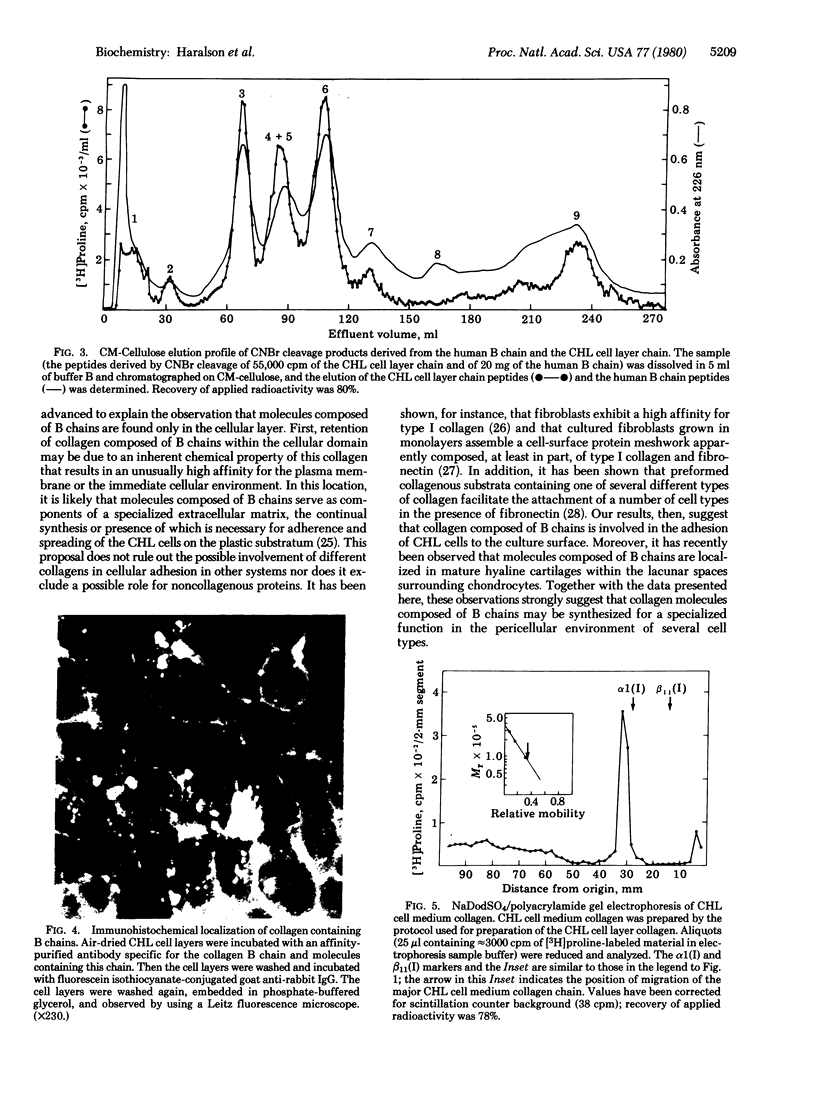
The acid-soluble collagen extracted from cultured Chinese hamster lung (CHL) cell layers has been isolated after limited pepsin digestion and differential salt fractionation. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of this material under denaturing conditions showed the presence of collagen chains with an apparent molecular mass of 120,000 daltons both before and after reduction, indicating the absence of interchain disulfide bonds in the native molecule. When chromatographed on CM-cellulose under denaturing conditions, the majority (> 90%) of the CHL cell layer collagen chains eluted as relatively basic components slightly before the human alpha 2(I) chain and coincident with the human B chain. In addition, the CM-cellulose elution profiles of the cyanogen bromide peptides derived from the human B chain and from the CHL cell layer chain were essentially identical. Examination of CHL cells in culture by using affinity-purified antibody to human B chain revealed this collagen to be localized in an extracellular matrix surrounding the cells. Furthermore, analysis of the culture medium indicated the absence of any comparable collagen chain. These data provide additional evidence for the existence of a molecular form of collagen composed solely of B chains and suggest that this molecular form of collagen has an unusual affinity for the cell layer in this system.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentz H., Bächinger H. P., Glanville R., Kühn K. Physical evidence for the assembly of A and B chains of human placental collagen in a single triple helix. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec;92(2):563–567. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Ash J. F. Cell surface-associated structural proteins in connective tissue cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2480–2484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgeson R. E., El Adli F. A., Kaitila I. I., Hollister D. W. Fetal membrane collagens: identification of two new collagen alpha chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2579–2583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung E., Miller E. J. Collagen polymorphism: characterization of molecules with the chain composition (alpha 1 (3)03 in human tissues. Science. 1974 Mar;183(130):1200–1201. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4130.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung E., Rhodes K., Miller E. J. Isolation of three collagenous components of probable basement membrane origin from several tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):1167–1174. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehm P., Kefalides N. A. The collagenous component of lens basement membrane. The isolation and characterization of an alpha chain size collagenous peptide and its relationship to newly synthesized lens components. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6680–6686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deyl Z., Macek K., Adam M. Collagen alpha A and alpha B chains constitute two separate molecular species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 27;89(2):627–634. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit S. N., Kang A. H. Anterior lens capsule collagens: cyanogen bromide peptides of the C chain. Biochemistry. 1979 Dec 11;18(25):5686–5692. doi: 10.1021/bi00592a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Characterization of collagen peptides by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jun;41(2):510–516. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay R. E., Buckingham R. B., Prince R. K., Gay S., Rodnan G. P., Miller E. J. Collagen types synthesized in dermal fibroblast cultures from patients with early progressive systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Feb;23(2):190–196. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S., Miller E. J. Characterization of lens capsule collagen: evidence for the presence of two unique chains in molecules derived from major basement membrane structures. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Dec;198(2):370–378. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville R. W., Rauter A., Fietzek P. P. Isolation and characterization of a native placental basement-membrane collagen and its component alpha chains. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr 2;95(2):383–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg B. Binding of soluble type I collagen molecules to the fibroblast plasma membrane. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell F. Cellular adhesiveness and extracellular substrata. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;53:65–144. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haralson M. A., Frey K. L., Mitchell W. M. Collagen biosynthesis by cultured Chinese hamster lung cells. Cell-free synthesis of procollagen alpha chains. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 7;17(5):864–868. doi: 10.1021/bi00598a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haralson M. A., Sonneborn J. H., Mitchell W. M. Chinese hamster lung cell polysomes direct the synthesis of a single molecular weight species of procollagen alpha chains. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5536–5542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S. A., Yankowski R., Bashey R. I. Identification of two new collagen alpha-chains in extracts of lathyritic chick embryo tendons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 28;81(4):1298–1306. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Murray J. C., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R. Connective tissue structure: cell binding to collagen. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Jul;71(1):9–11. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12543641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresina T. F., Miller E. J. Isolation and characterization of basement membrane collagen from human placental tissue. Evidence for the presence of two genetically distinct collagen chains. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 10;18(14):3089–3097. doi: 10.1021/bi00581a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne R., Vail M. S., Miller E. J. Characterization of the collagen chains synthesized by cultured smooth muscle cells derived from rhesus monkey thoracic aorta. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):446–452. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Biochemical characteristics and biological significance of the genetically-distinct collagens. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Dec 10;13(3):165–192. doi: 10.1007/BF01731779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes R. K., Miller E. J. Physicochemical characterization and molecular organization of the collagen A and B chains. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 22;17(17):3442–3448. doi: 10.1021/bi00610a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes R. K., Miller E. J. The isolation and characterization of the cyanogen bromide peptides from the B chain of human collagen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12084–12087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roufa D. J., Reed S. J. Temperature-sensitive mutants of a Chinese hamster cell line. I. Selection of clones with defective macromolecular biosynthesis. Genetics. 1975 Jul;(3):549–566. doi: 10.1093/genetics/80.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Bornstein P. Characterization of a novel collagen chain in human placenta and its relation to AB collagen. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3815–3822. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Woodbury R. G., Bornstein P. Structural studies on human type IV collagen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9893–9900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. I., Gay R., Gay S., Miller E. J. Association of collagen with preimplantation and peri-implantation mouse embryos. Dev Biol. 1980 Feb;74(2):470–478. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90446-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]