Abstract
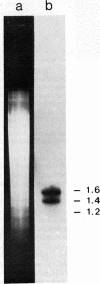
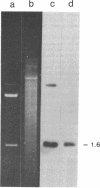
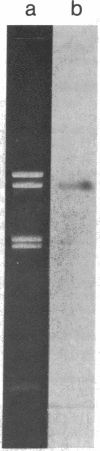
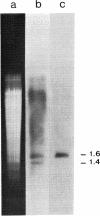
Previous work has shown that the macronuclear DNA of the hypotrichous ciliate Oxytricha fallax is arranged as short achromosomal pieces, 22 to 0.5 kilobase pairs (kb) in length. Micronuclear DNA has a typical chromosomal organization. Macronuclear DNA is derived from micronuclear DNA through a process of polytene chromosome fragmentation with a resultant decrease in DNA sequence complexity. Three putative actin genes have been identified in macronuclear DNA by using a cloned yeast actin gene as a hybridization probe. A restriction fragment of the yeast gene containing both actin coding and noncoding DNA hybridizes strongly to two macronuclear DNA pieces, 1.6 and 1.4 kb in length, and weakly to a 1.2-kb piece. The entire 1.6-kb piece has been cloned in plasmid pBR322 and the resulting recombinant plasmid has been designated pOfACT(1.6). The 1.6-kb pOfACT(1.6) insert hybridizes only to those restriction fragments of the yeast actin gene containing actin coding sequences. When hybridized to macronuclear DNA under conditions that allow the yeast probe to hybridize to all three macronuclear pieces, the pOfACT(1.6) insert hybridizes only to the 1.6-kb piece. Under less stringent conditions the insert also hybridizes to the 1.4-kb piece, but it shows no hybridization to the 1.2-kb DNA. The three macronuclear pieces homologous to the yeast actin gene thus differ in sequence and are interpreted as a related family of actin genes. Each of these pieces could accommodate an actin coding sequence, which in yeast, Dictyostelium discoideum, and Drosophila melanogaster is 1.1 kb, and an additional 0.1-0.5 kb of noncoding DNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender W., Davidson N., Kindle K. L., Taylor W. C., Silverman M., Firtel R. A. The structure of M6, a recombinant plasmid containing Dictyostelium DNA homologous to actin messenger RNA. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):779–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90263-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M., Spudich J. A. Nonmuscle contractile proteins: the role of actin and myosin in cell motility and shape determination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:797–822. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Kindle K. L., Davidson N., Kindle K. L. The actin genes of Drosophila: a dispersed multigene family. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Seidel R. Molecular cloning of the actin gene from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):1043–1059. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I., Gibson W. Identification and characterization of multiple forms of actin. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):793–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenstein E., Rich A., Weihing R. R. Actin associated with membranes from 3T3 mouse fibroblast and HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jan;64(1):223–234. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick G., Wesley R. D. Isolation and characterization of a highly repetitious inverted terminal repeat sequence from Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. The mechanism of muscular contraction. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1356–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L., Firtel R. A. Identification and analysis of Dictyostelium actin genes, a family of moderately repeated genes. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):763–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90262-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauth M. R., Spear B. B., Heumann J., Prescott D. M. DNA of ciliated protozoa: DNA sequence diminution during macronuclear development of Oxytricha. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90256-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M. Gene-sized DNA molecules of the Oxytricha macronucleus have the same terminal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4325–4328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott D. M., Murti K. G., Bostock C. J. Genetic apparatus of Stylonychia sp. Nature. 1973 Apr 27;242(5400):576, 597-600. doi: 10.1038/242576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott D. M., Murti K. G. Chromosome structure in ciliated protozoans. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:609–618. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae P. M., Spear B. B. Macronuclear DNA of the hypotrichous ciliate Oxytricha fallax. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4992–4996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Jay E., Wu R. Terminal labeling and addition of homopolymer tracts to duplex DNA fragments by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jan;3(1):101–116. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein P. A., Spudich J. A. Actin microheterogeneity in chick embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):120–123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear B. B. Isolation and mapping of the rRNA genes in the macronucleus of Oxytricha fallax. Chromosoma. 1980;77(2):193–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00329544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storti R. V., Coen D. M., Rich A. Tissue-specific forms of actin in the developing chick. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):521–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak H. F., Flavell R. A. A method for the recovery of DNA from agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2321–2332. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Mammalian cytoplasmic actins are the products of at least two genes and differ in primary structure in at least 25 identified positions from skeletal muscle actins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of Physarum actin. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):720–721. doi: 10.1038/276720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesley R. D. Inverted repetitious sequences in the macronuclear DNA of hypotrichous ciliates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):678–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Butler-Browne G. S., Gros F. Protein synthesis and actin heterogeneity in calf muscle cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2018–2022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]