Abstract
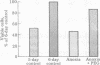
In order to study the relationship between cell swelling and cell death due to ischemia, we have developed an in vitro model by using primary cultures of renal tubular epithelial cells. With this model, we have studied two components of ischemia--namely, anoxia along with substrate deprivation. After 2 hr of anoxia in the absence of substrate, the cultured cells swelled and blebbed. Cells similarly treated in the presence of 8% polyethylene glycol, an oncotic agent, did not swell and bleb, and when cells were counted 18 hr later, similar numbers of cells were seen as in the untreated cultures. However, tubule cells exposed to anoxia without 8% polyethylene glycol had 50% fewer cells 18 hr later. Therefore, if cell swelling is prevented during 2 hr of anoxia, cell viability is improved.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arendshorst W. J., Finn W. F., Gottschalk C. W. Pathogenesis of acute renal failure following temporary renal ischemia in the rat. Circ Res. 1975 Nov;37(5):558–568. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.5.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURSTONE M. S. Histochemical comparison of naphthol AS-phosphates for the demonstration of phosphatases. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1958 Mar;20(3):601–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlington H., Cronkite E. P. Characteristics of cell cultures derived from renal glomeruli. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jan;142(1):143–149. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-36977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frega N. S., DiBona D. R., Leaf A. The protection of renal function from ischemic injury in the rat. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Aug;381(2):159–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00582347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert S. F., Migeon B. R. D-valine as a selective agent for normal human and rodent epithelial cells in culture. Cell. 1975 May;5(1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I., Bulger R. E., Trump B. F., Nagle R. B. Effects of transient hypotension on the structure and function of rat kidney. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1976 Nov 2;22(2):121–133. doi: 10.1007/BF02889210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A. On the mechanism of fluid exchange of tissues in vitro. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):241–248. doi: 10.1042/bj0620241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell W. J., Jr, DiBona D. R., Flores J., Leaf A. The protective effect of hyperosmotic mannitol in myocardial ischemia and necrosis. Circulation. 1976 Oct;54(4):603–615. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.54.4.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. R. Control of water content of non-metabolizing kidney slices by sodium chloride and polyethylene glycol (PEG 6000). J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):227–234. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner G. A., Sophasan S. Kidney pressures after temporary renal artery occlusion in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1976 Apr;230(4):1173–1181. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.4.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trump B. F., Berezesky I. K., Collan Y., Kahng M. W., Mergner W. J. Recent studies on the pathophysiology of ischemic cell injury. Beitr Pathol. 1976 Sep;158(4):363–388. doi: 10.1016/s0005-8165(76)80135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam M. A., Bernard D. B., Donohoe J. F., Levinsky N. G. Ischemic damage and repair in the rat proximal tubule: differences among the S1, S2, and S3 segments. Kidney Int. 1978 Jul;14(1):31–49. doi: 10.1038/ki.1978.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIGGINS P. M. SELECTIVE ACCUMULATION OF POTASSIUM ION BY GEL AND KIDNEY SLICES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 29;88:593–605. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]