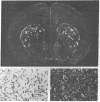
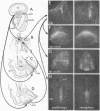
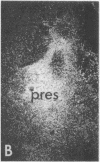
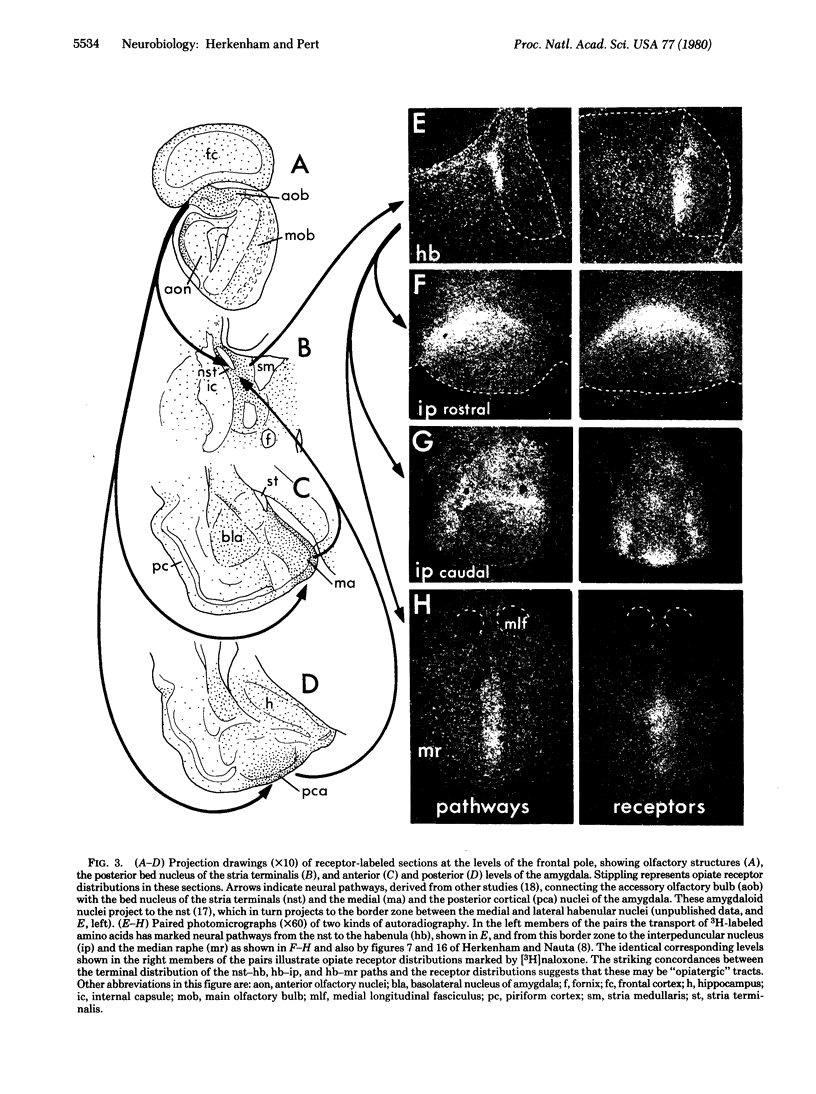
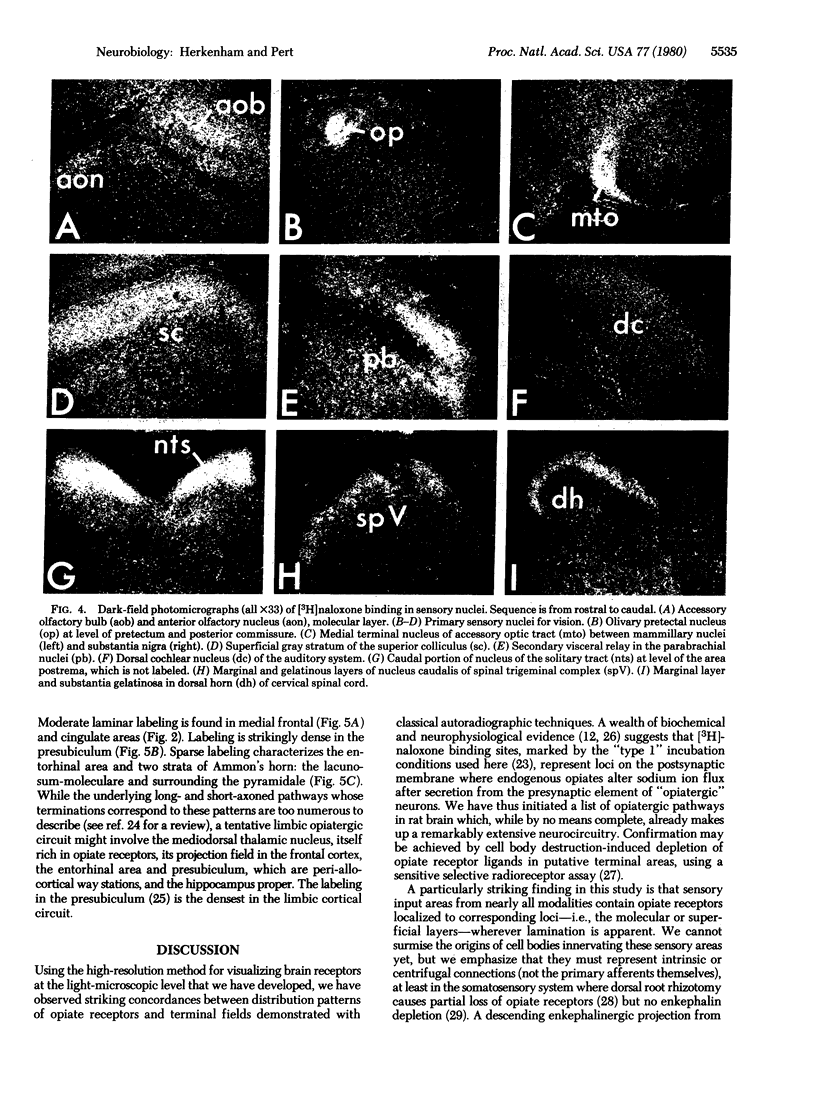
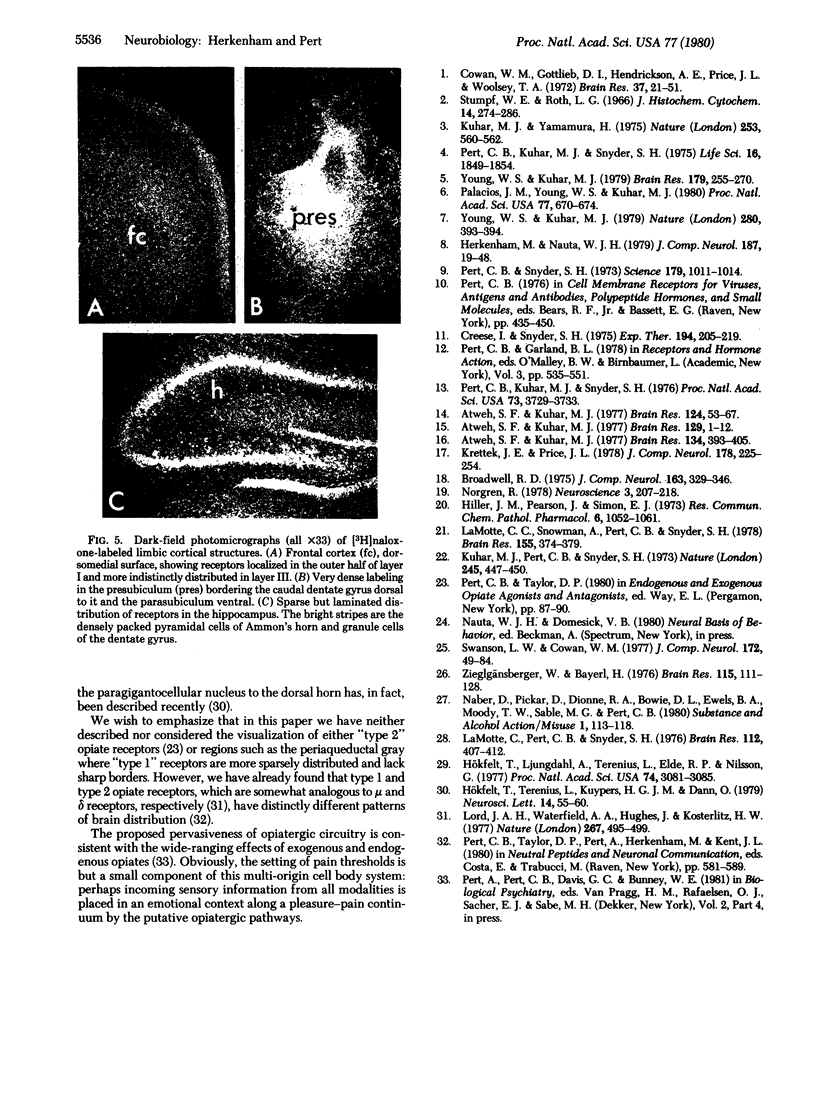
Abstract
Slide-mounted sections of unfixed frozen rat brain can be labeled in vitro with [3H]naloxone to show the mu-like ligand selectivity characterized in previous studies. We have developed an autoradiographic technique using hot paraformaldehyde vapors to prevent diffusion of ligands with reversible binding. Resolution at the light level is sufficient to detect concordance between receptor patterns and terminal fields of axonal projections marked by tract-tracing techniques. The opiate receptor distribution suggests the existence of widespread intrinsic and several longer multisynaptic "opiatergic pathways within sensory and limbic circuits. One multisynaptic pathway may link olfactory structures with limbic circuits in the amygdala and habenula. Another may lie in limbic cortical structures. Opiate receptors are numerous also in sensory systems, and within primary sensory nuclei (visual, auditory, olfactory, somatic) they are found superficially in laminated structures. Together, the opiate receptors are well placed to control incoming sensory and subsequent limbic information processing.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. I. Spinal cord and lower medulla. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 18;124(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90863-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. II. The brain stem. Brain Res. 1977 Jun 24;129(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90965-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. III. The telencephalon. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 14;134(3):393–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90817-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadwell R. D. Olfactory relationships of the telencephalon and diencephalon in the rabbit. I. An autoradiographic study of the efferent connections of the main and accessory olfactory bulbs. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Oct 1;163(3):329–345. doi: 10.1002/cne.901630306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan W. M., Gottlieb D. I., Hendrickson A. E., Price J. L., Woolsey T. A. The autoradiographic demonstration of axonal connections in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 1972 Feb 11;37(1):21–51. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Snyder S. H. Receptor binding and pharmacological activity of opiates in the guinea-pig intestine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Jul;194(1):205–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Nauta W. J. Efferent connections of the habenular nuclei in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Sep 1;187(1):19–47. doi: 10.1002/cne.901870103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller J. M., Pearson J., Simon E. J. Distribution of stereospecific binding of the potent narcotic analgesic etorphine in the human brain: predominance in the limbic system. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1973 Nov;6(3):1052–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Ljungdahl A., Terenius L., Elde R., Nilsson G. Immunohistochemical analysis of peptide pathways possibly related to pain and analgesia: enkephalin and substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3081–3085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Kuypers H. G., Dann O. Evidence for enkephalin immunoreactive neurons in the medulla oblongata projecting to the spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 1979 Sep;14(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)95343-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krettek J. E., Price J. L. Amygdaloid projections to subcortical structures within the basal forebrain and brainstem in the rat and cat. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Mar 15;178(2):225–254. doi: 10.1002/cne.901780204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Regional distribution of opiate receptor binding in monkey and human brain. Nature. 1973 Oct 26;245(5426):447–450. doi: 10.1038/245447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Yamamura H. I. Light autoradiographic localisation of cholinergic muscarinic receptors in rat brain by specific binding of a potent antagonist. Nature. 1975 Feb 13;253(5492):560–561. doi: 10.1038/253560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMotte C. C., Snowman A., Pert C. B., Synder S. H. Opiate receptor binding in rhesus monkey brain: association with limbic structures. Brain Res. 1978 Oct 27;155(2):374–379. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamotte C., Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor binding in primate spinal cord: distribution and changes after dorsal root section. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 13;112(2):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgren R. Projections from the nucleus of the solitary tract in the rat. Neuroscience. 1978;3(2):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in the rat cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):670–674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Autoradiograhic localization of the opiate receptor in rat brain. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1849–1853. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: autoradiographic localization in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3729–3733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: demonstration in nervous tissue. Science. 1973 Mar 9;179(4077):1011–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4077.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf W. E., Roth L. J. High resolution autoradiography with dry mounted, freeze-dried frozen sections. Comparative study of six methods using two diffusible compounds 3H-estradiol and 3H-mesobilirubinogen. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Mar;14(3):274–287. doi: 10.1177/14.3.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Cowan W. M. An autoradiographic study of the organization of the efferent connections of the hippocampal formation in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1977 Mar 1;172(1):49–84. doi: 10.1002/cne.901720104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. A new method for receptor autoradiography: [3H]opioid receptors in rat brain. Brain Res. 1979 Dec 28;179(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90442-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localisation of benzodiazepine receptors in the brains of humans and animals. Nature. 1979 Aug 2;280(5721):391–394. doi: 10.1038/280393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieglgänsberger W., Bayerl H. The mechanism of inhibition of neuronal activity by opiates in the spinal cord of cat. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 8;115(1):111–128. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90826-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]