Abstract
Understanding how relevant cell types respond to wear particles will reveal new avenues for treating osteolysis following joint replacements. In this study, we investigate the effects of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) particles on preosteoblast migration and function. We infused UHMWPE particles or saline into the left femur of mice and injected luciferase-expressing preosteoblasts (MC3T3 cells) into each left ventricle. Bioluminescence imaging (BLI) confirmed systemic administration of MC3T3 cells. BLI throughout the 28-day experiment showed greater MC3T3 migration to the site of particle infusion than to the site of saline infusion, with significant differences on days 0, 4, and 6 (p≤0.055). Immunostaining revealed a greater number of osteoblasts and osteoclasts in the particle-infused femora, indicating greater bone turnover. The bone mineralization of the particle-infused femora increased significantly when compared to saline-infused femora (an increase of 146.4±27.9 vs. 12.8±8.7 mg/mL, p=0.008). These results show that infused preosteoblasts can migrate to the site of wear particles. Additionally, as the migrated cells were associated with increased bone mineralization in spite of the presence of particles, increasing osteoblast recruitment is a potential strategy for combating bone loss due to increased osteoclast/macrophage number and decreased osteoblast function.
Introduction
In 2006, surgeons in the United States performed 542,000 total knee replacements and 482,000 hip replacements. However, that same year, surgeons also performed 39,000 revision knee and 38,000 revision hip replacements due to complications following the primary procedures.1 The most common etiology leading to these revision surgeries was aseptic loosening and osteolysis associated with particulate wear debris.2,3 Wear particles exert their effect by altering the proliferation and function of cells from the monocyte/macrophage and mesenchymal lineages.4–10 Ultimately, if one can elucidate the mechanisms underlying this biological response to wear particles, novel pharmacological interventions may facilitate the slowing or reversal of osteolysis progression.
Cells of monocyte/macrophage origin have a clearly demonstrated role in the progression of osteolysis.4–10 Particles stimulate macrophages to release cytokines, chemokines, and other inflammatory substances. These factors then recruit circulating monocytes/macrophages and promote the differentiation and proliferation of osteoclasts.4–10 This recruitment of macrophages is not just local, but systemic in nature.10–12 The increased number of macrophages and osteoclasts increase bone resorption, leading to osteolysis.
Although cells of the monocyte/macrophage lineage play a prominent role in osteolysis, cells of mesenchymal origin (i.e., mesenchymal stem cells [MSCs], preosteoblasts, etc.) also participate. In addition to increased bone resorption by osteoclasts, increased bone formation by osteoblasts is a hallmark sign of osteolysis, in an attempt to re-establish bone homeostasis.13 However, wear particles adversely affect the health of osteoblasts and their precursors by impairing their proliferation, differentiation, and osteogenicity.14–16 Ultimately, maintaining the number and health of osteoblasts could help slow or reverse the progression of osteolysis. To this end, it has recently been shown that polymethyl methacrylate particle-conditioned media induced migration of MSCs, an effect that was blocked by neutralizing the macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α), a chemokine also known to attract monocyte/macrophages.17 These preliminary results suggest that some of the same chemokines that recruit circulating monocytes/macrophages could also recruit osteoprogenitor cells.
MSCs, the source of osteoprogenitor cells, have wide applications for therapeutic use, and thus researchers in varied fields have studied their migration in a variety of experimental models. Such studies have revealed the importance of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) in MSC migration in breast cancer18 and in the ischemic heart19 of stromal cell-derived factor-1 in fracture healing,20,21 and of MCP-1, MIP-1α, and interleukin-6 in MSC migration to the ischemic brain.22 However, to date, no one has explored the effect of clinically relevant wear debris on the in vivo migration of osteoblast precursors.
To study cell migration, researchers often use bioluminescence imaging (BLI), which detects a luminescent signal emitted from reporter cells engineered to express luciferase.23–25 These cells are generally injected intravenously into the lateral tail vein. A significant problem of this method remains the accumulation of the cells in the lungs during the cells' first pass from venous to arterial circulation.11,12,26,27 Intracardiac injection (ICI) into the left ventricle, on the other hand, directly introduces the cells into systemic circulation. Cancer researchers have explored this method of cell delivery as a model for metastasis, but its utility in other fields has not been established.28–30
In this study, we aim to (1) demonstrate the in vivo migration of exogenously injected osteoprogenitor cells to the site of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) particle infusion and (2) determine the effect of these migrated cells on bone quantity at the site of particle infusion. In addition, we present ICI as a successful method of delivering preosteoblasts in bone cell migration studies.
Materials and Methods
Animals and experimental design
Our university's animal facility housed and cared for the sixteen 12-week-old male nude mice (Charles River Laboratories) used in the experiment. Eight control animals received pumps containing saline, and eight experimental animals received pumps containing UHMWPE particles. In the course of the 28-day experiment, two of the pumps in the control animals became disconnected, and thus the analysis excluded them.
UHMWPE particles and pumps
Metal-on-conventional (nonhighly cross-linked) UHMWPE wear simulator testing generated the UHMWPE particles used in this study (generously donated by Dr. Timothy Wright of the Hospital for Special Surgery). After isolation by ultracentrifugation,1 scanning electron microscopy (Hitachi S-3400N; Hitachi High-Tech) determined the length of the particles to be 1.0±0.1 μm (mean±standard error [SE]). A Limulus Amebocyte Lysate kit (BioWhittaker) confirmed the absence of endotoxin on the particles. Particles were suspended in sterile saline at a concentration of 15 mg/mL, or based on the volume and density of the isolated particles, 3.1×1010 particles/mL. The suspended particles were loaded into a Model 2006 Alzet osmotic pump (Durect Corp.) with a mean loading volume of 243 μL and a pumping rate of 0.15 μL/h. Based on the pumping rate and duration of the study, ∼100 μL (3.0×109 particles) of the pump contents emptied into the medullary canal during the experiment. A silicon tube connected the pump to a 6-mm-long hollow titanium rod.
Surgical procedure
Our university's guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were strictly followed. The procedure was adapted from a previously described rat model31 and has been validated.32,33 The animals were anesthetized using 3%–5% isoflurane in 100% oxygen and kept on a warm, sterile small animal surgery station. A medial parapatellar incision was made and the medullary cavity was exposed via the intercondylar notch of the distal left femur. Drilling with progressively smaller needles (25–21 gauge) into the medullary canal created a hole slightly smaller than the titanium rod that would act as a conduit to infuse the particles. A second incision between the scapulae exposed a subcutaneous pouch for the diffusion pump. From the interscapular space, we then passed the tubing that connects the osmotic pump to the titanium rod subcutaneously toward the region of the left distal femur, where the titanium rod was press fit into the drill hole. The quadriceps–patellar complex was then relocated and the parapatellar arthrotomy and dorsal incision were repaired with sutures and biocompatible glue. A subcutaneous buprenorphine (0.1 mg/kg; Ben Venue Laboratories) injection controlled animal pain immediately after surgery.
Cells, ICI and BLI
Lentiviral transfected murine MC3T3-E1 subclone 14 preosteoblasts (Cat. No. CRL-2594; ATCC) expressed the bioluminescent optical reporter gene firefly luciferase, which allowed for bioluminescent tracking of the injected cells.23–25 We injected these cells after the animals' wounds had healed (7–10 days postoperation). Animals were anesthetized using 3%–5% isoflurane in 100% oxygen during cell injection and imaging. After suspending the cells in 0.1 mL of phosphate-buffered saline with 30 units/mL heparin, we injected the cells directly into each mouse's left ventricle.34 Immediately after cell injection, each mouse received an intraperitoneal injection of 3 mg of luciferase substrate D-luciferin (Biosynth International). Five minutes later, an in vitro imaging system coupled with a cooled charge-coupled camera (Caliper Life Sciences; housed in our university's Small Animal Imaging Facility) detected the luminescence signal from the mouse. We imaged the entire prone mouse at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 14, 21, and 28 days following cell injection. During analysis, we drew a two-dimensional, uniform region of interest (ROI) around the implant area and recorded the radiance values in units of photon/second/cm2/steradian (p/s/cm2/sr). Dividing the signal in the operated limb by the signal in the nonoperated limb allowed for comparison between the two groups. To compare the distribution of cells after ICI to that after tail vein injection, we used BL images from an unpublished preliminary experiment from our laboratory in which we intravenously injected MC3T3 cells into the tail veins of comparable animals.
Histology and immunohistochemistry
After completion of the imaging studies, we harvested the femora from three randomly chosen experimental animals and three randomly chosen control animals. Frozen sections from throughout the distal half of each femur were collected for histological analysis.
With immunostaining, we aimed to identify exogenous cells, total osteoblasts, and total osteoclasts. In the first staining protocol, the rabbit antiluciferase polyclonal antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) tagged exogenous cells and goat anti-rabbit IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488 (Invitrogen) identified the tagged cells. In the second staining protocol, the mouse anti-human vitronectin receptor αVβ3 and the rabbit anti-mouse osteocalcin (both Santa Cruz Biotechnology) tagged osteoclasts and osteoblasts, respectively. The cross reactivity of the mouse anti-human vitronectin receptor antibody was previously confirmed in our laboratory. Goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488 identified tagged osteoclasts and goat anti-rabbit IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor 594 (both Invitrogen) identified tagged osteoblasts. Briefly, we first fixed sections in a phosphate-buffered saline-buffered paraformaldehyde solution (4%) and blocked inherent tissue fluorescence with Image-iT™ FX Signal Enhancer (Invitrogen) for 1 h. We then incubated the sections overnight with the appropriate primary antibodies at 4°C followed by 1 h at room temperature with the secondary antibodies. ProLong Gold Antifade Reagent with DAPI (Invitrogen) was used to mount the slides. For reach randomly selected sample, we imaged six to eight sections with a fluorescent microscope (Axio Observer Z1; Carl Zeiss, Inc.). Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (Sigma) staining revealed general tissue morphology and a leukocyte acid phosphatase kit stained for tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) (Sigma), thus identifying osteoclasts.
MicroCT
On five anesthetized animals from each group, we performed two μCT scans: the first immediately before pump implantation and the second at the end of the experiment. Before scanning, we taped each animal gently into the scanning bed to minimize motion artifacts and then scanned each using an eXplore RS microCT scanner (GE Medical Systems) at a resolution of 49 μm. After euthanasia by carbon dioxide, but before microCT scanning, we removed the titanium rods from each left femur. Each image was acquired and reconstructed using the eXplore Evolver and eXplore Reconstruction interface software (GE Medical Systems), respectively. Scans were calibrated using the calibration function in the GEMS MicroView software (GE Medical Systems) and a Hounsfield unit (HU) placed under the mice in each scan. After calibration, we drew a three-dimensional ROI with dimensions 4×4×3 mm (distal–proximal×anterior–posterior×left–right) around the distal femur, beginning 3 mm from the end of the femoral condyles and proceeding proximally along the femur. Dividing the bone mineral content (threshold: 1700 HU) of each ROI by the volume of the ROI yielded the bone mineral density (BMD) of each ROI in mg/mL. Subtracting pretreatment values from post-treatment values normalized each animal's BMD.
Data analysis
A two-tailed heteroscedastic student t-test was used to analyze the BL ratio of the operated femora to the nonoperated femora within the ROI, as well as for analysis of TRAP staining and antiluciferase immunostaining. A two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test was used to analyze the BMD data. Both tests were implemented using statistiXL.
Results
Bioluminescence imaging
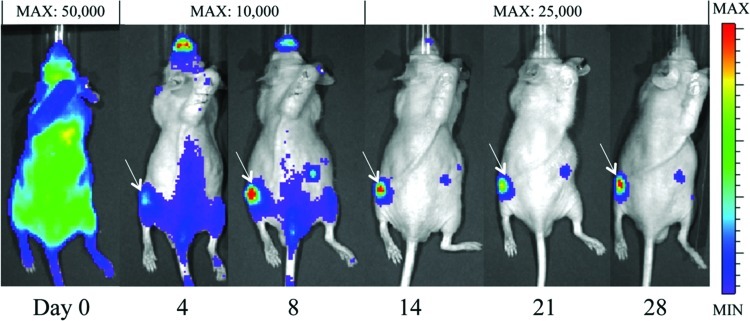
Immediately after injection, the BL signal after MC3T3 ICI was either diffuse throughout the body (Fig. 1A) or slightly concentrated in the lung region (Fig. 1B). In contrast, the signal after tail vein MC3T3 injection (in a preliminary experiment) was highly concentrated only in the lung region (Fig. 1C). By the fourth day after cell ICI, the signal in the left femur intensified (Fig. 2). This intensity of the signal in the left femur (the site of UHMWPE infusion) continued to increase throughout the remainder of the 28-day experiment, while the BLI signal elsewhere in the body decreased. In the saline controls, a qualitative difference between the signals in the right and left femora did not appear until day eight, after which the signal in the left femur steadily increased (images not shown). When cells were injected via the intravenous route (in a previous study), no signal was appreciated emanating from either femur using BLI.
FIG. 1.
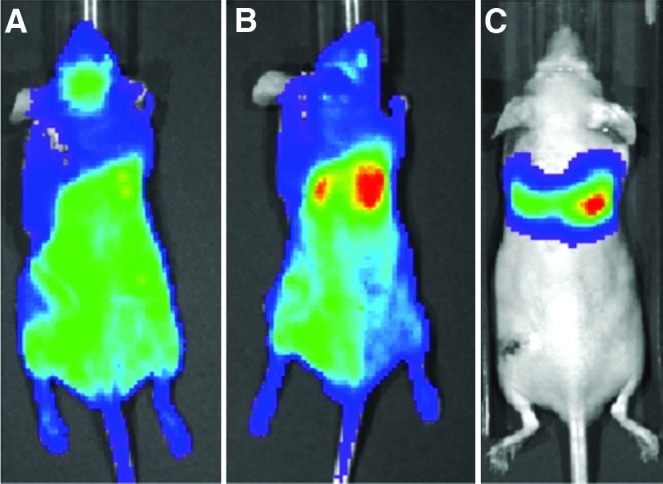
Representative bioluminescence images immediately following intracardiac injection (ICI) of MC3T3 cells (A, B) and intravenous injection (C) via the tail vein. ICI was associated with either a completely diffuse bioluminescence signal (A) or a diffuse signal with a slight concentration in the lungs (B). In contrast, the entire bioluminescence signal came from the lungs following intravenous (tail vein) injection (C). The maximum signal in all three images is ∼50,000 photon/second/cm2/steradian (p/sec/cm2/sr). Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tea
FIG. 2.
The bioluminescent signal at selected time points from a representative experimental animal with particle infusion in the left femur. By day 4, the signal begins to localize at the left femur. The intensity of the signal in the left femur compared to the intensity of the signal elsewhere increases throughout the experiment. White arrows denote a signal in the left femur. The MAX values listed indicate the maximum luminescence value in the image (the value corresponding to the red regions). Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tea
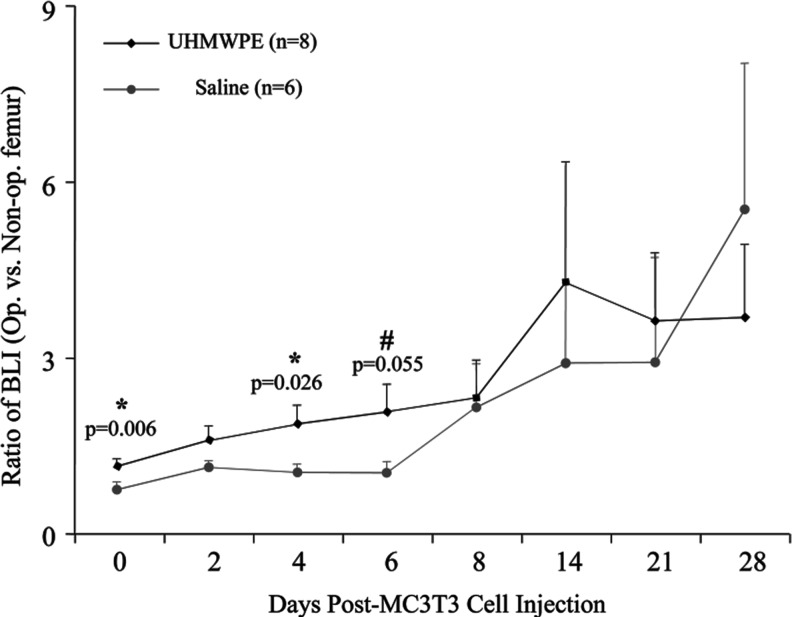
The BL signal ratio between the left and right femora of the animals infused with particles increased steadily from day 0 to 14 (Fig. 3). In the saline controls, the signal remained relatively unchanged for the first 6 days, after which it increased steadily. The signal from the animals receiving particles exceeded the signal in control animals from day 0 to 21. At day 0, the ratio of 1.17±0.13 (mean±SE) in the experimental animals was significantly higher than the ratio of 0.70±0.08 in the saline controls (p=0.006). This trend continued at day 4 (1.90±0.28 vs. 1.07±0.15, p=0.026) and day 6 (2.12±0.42 vs. 1.06±0.27, p=0.055).
FIG. 3.
The ratio of the bioluminescence signal in the operated limb to that in the nonoperated limb at chosen intervals after MC3T3 injection. When compared to the saline control animals, the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE)-receiving animals had a higher BL signal from days 0 to 21, with a significantly higher signal at days 0, 4, and 6. Error bars correspond to standard error.
Histology and immunohistochemistry
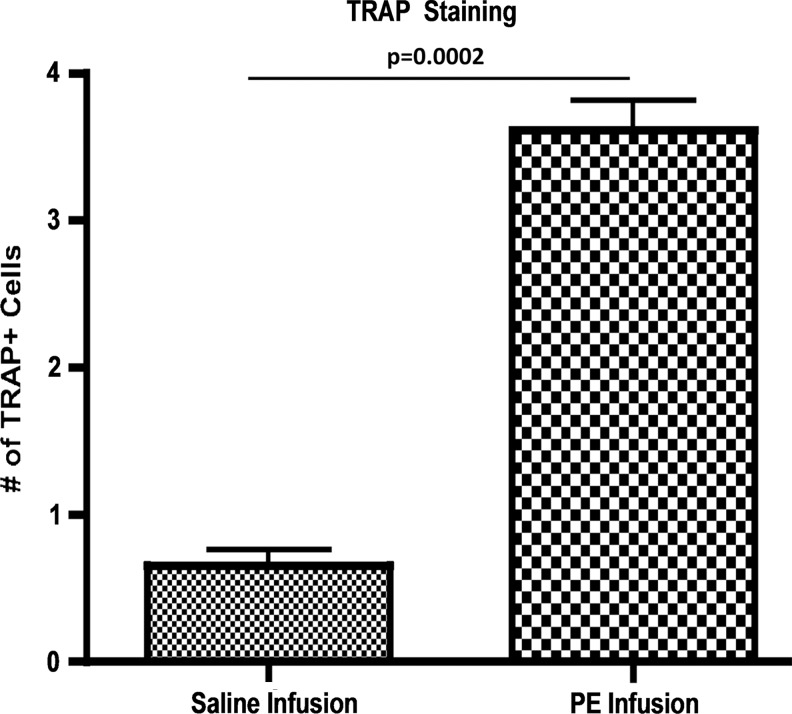
H&E staining highlighted the characteristic femoral cross section; TRAP staining showed increased numbers of TRAP-positive cells evident in the particle-infused (3.61±0.20) compared to saline-infused femora (0.65±0.11, p=0.0002) (Fig. 4).
FIG. 4.
TRAP staining identified osteoclast activity in saline and particle-infused femora. Images were taken at 40×and TRAP-positive cells were manually counted for five sections per femur, with three femurs per group. Particle-infused femora had 3.61±0.20 TRAP-positive cells compared to saline-infused femora with 0.65±0.11 (p=0.0002).
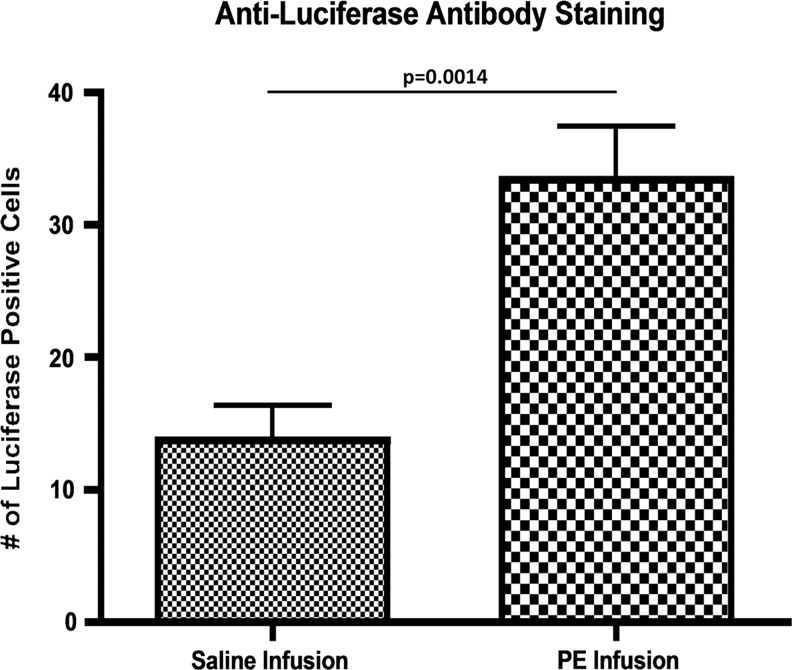
The reliability of BLI decreases as a function of time after cell injection, due to cell death, cell differentiation, gene silencing, and post-transcriptional modifications. Thus, we utilized immunohistochemistry to directly identify reporter cells. Exogenous cells (luciferase-expressing MC3T3 cells) were detected in both groups using an antiluciferase antibody (Fig. 5). A greater number of migrated cells were identified in the cortex of the particle-infused femora (33.43±3.99) than in the cortex of the saline-infused femora (13.71±2.61) (p=0.0014). To confirm the specificity of the antiluciferase antibody, an identical staining protocol was repeated on control femora from a prior experiment from our laboratory, in which no cells were injected and either saline or UHMWPE was infused from the pump.12 No luciferase-positive cell staining was seen in these sections.
FIG. 5.
Antiluciferase staining of sections from a particle-infused femur and a saline-infused femur at day 28 postcell injection. All sections were obtained from the diaphyseal cortex. DAPI identified all cells, antiluciferase antibody identified exogenous cells, and an overlay identified any costaining. Sections were imaged at 20×, and cells that were positive for both DAPI and antiluciferase staining were counted using ImageJ Software. A greater number of exogenous cells was found in sections from particle-infused femora. The increase in luciferase-positive staining cells in the PE-infused femur confirms that MC3T3 cells were recruited systemically to the site of wear-particle-induced osteolysis.
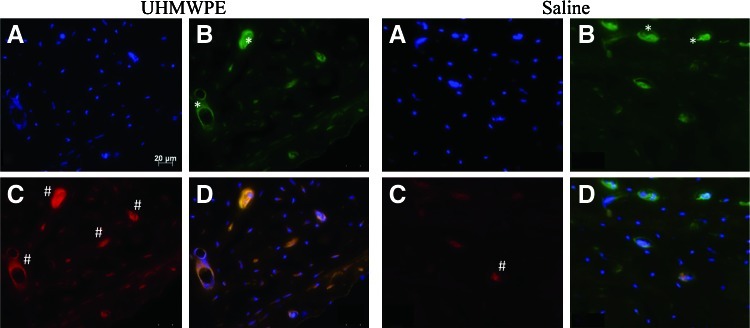
The antivitronectin receptor αVβ3 identified osteoclasts and antiosteocalcin identified osteoblasts in both control and experimental femoral sections (Fig. 6). Osteoclasts were predominantly found along the trabecular bone and the endosteal cortices in the saline controls. In particle-infused femora, osteoclasts were found within the cortical bone as well. Qualitatively, there was very little osteoblast staining in saline-infused femora and a high degree of osteoblast staining in particle-infused femora.
FIG. 6.
Immunohistochemical staining of a particle-infused femur (left block) and a saline-infused femur (right block). All sections were obtained from the diaphyseal cortex. DAPI identified all cells (A), antihuman vitronectin receptor αVβ3 identified osteoclasts (B), antiosteocalcin identified osteoblasts (C), and overlaying all three identified any costaining (D). Osteoclasts reside along the trabecular bone and the endosteal cortices (representative areas denoted by *), predominantly so in the case of saline-infused femora. The experimental femora had a much greater extent of osteoblast staining (representative areas indicated with #). All images are 200×magnification. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tea
MicroCT
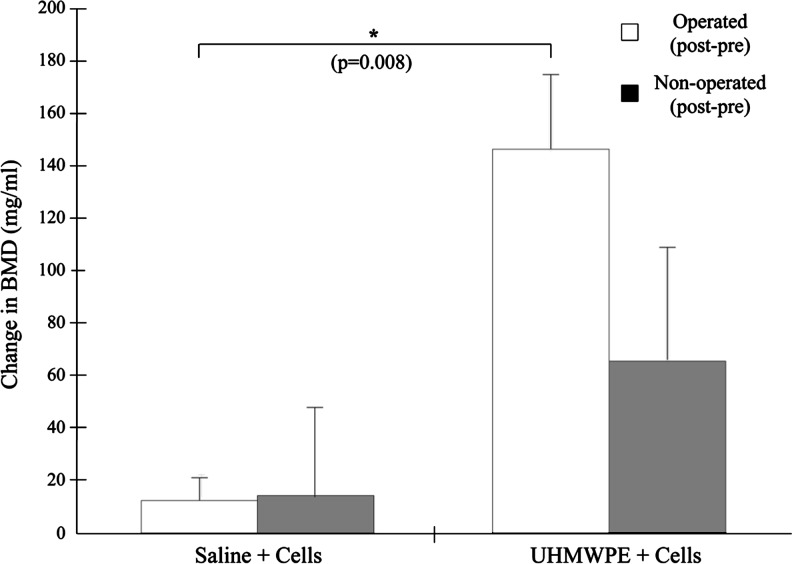
The BMD in both femora of the two groups increased throughout the course of the experiment (Fig. 7). In the operated limb, BMD increased by 146.4±27.9 mg/mL in particle-infused animals, compared to an increase of 12.8±8.7 mg/mL in the control animals (p=0.008). In the nonoperated femora, the BMD of the experimental animals increased more than in the control animals (65.7±42.3 mg/mL vs. 14.1±65.7 mg/mL), though this result was not significant. The cortical thickness of the particle-infused femur appeared thicker than that of the saline-infused femur (Fig. 8A, B) and the BMD in the diaphysis of the particle-infused femur appeared greater than in the saline-infused femur (Fig. 8C, D).
FIG. 7.
The average change in the bone mineral density (BMD) of the distal femur, found by subtracting the preoperated BMD from the postoperated BMD. The injection of MC3T3 cells was correlated with increased BMD in both limbs, with a significant increase in BMD in the operated limb. Error bars correspond to standard error.
FIG. 8.
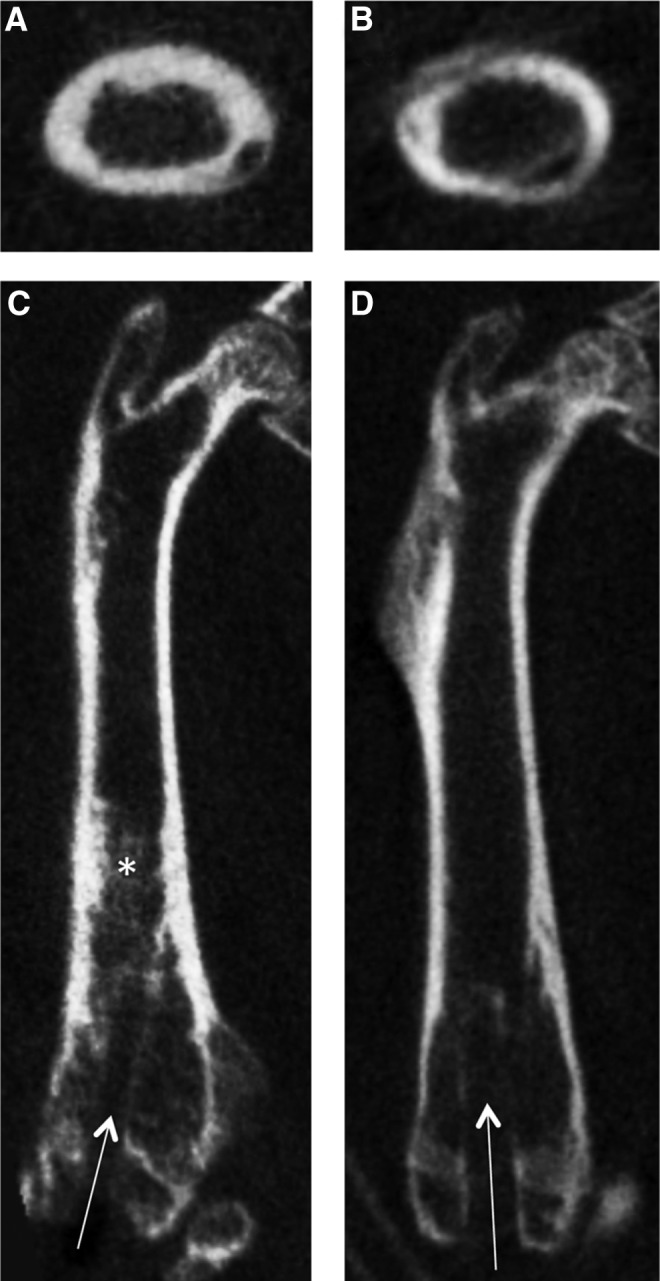
MicroCT images of a representative particle-infused (A, C) and saline-infused (B, D) femur. The drill hole is visible in both femora (arrows). The cortex of the particle-infused femur appears thicker than that of the saline-infused femur (transverse sections, A and B). The BMD in the diaphysis of the particle-infused femur (*) appears greater than that in the saline-infused femur (coronal sections, C and D).
Discussion
In this study, we aimed to demonstrate the migration of exogenous preosteoblastic cells to particle-infused femora and to quantify the effect on bone quantity. In addition, we hoped to present the utility of ICI as a cell-delivery method. We conclude that polyethylene particles elicit the migration of circulating preosteoblasts to the site of particle infusion, and that the recruited osteoblasts in turn increase BMD. These circulating preosteoblasts were successfully delivered via ICI.
The diffusely systemic bioluminescence signal detected after ICI of the MC3T3 cells (Fig. 1) indicates successful delivery of the cells into the systemic circulation and agrees with the distribution seen in other experiments utilizing ICI.29,30 Conversely, the concentrated BL signal in the lungs after tail vein injection points to cell entrapment by the lung capillary system. Previous research has confirmed the presence of circulating osteoprogenitor cells available for recruitment.35,36 The distribution seen after ICI more accurately mimics this in vivo distribution of osteoprogenitors, in which cells are evenly distributed in the bloodstream rather than concentrated in the lungs. Additionally, previous work by Ren et al. demonstrated that there was no increase in bioluminescence (reflecting systemic exogenous reporter cell trafficking) if reporter cells were not injected.12
Injecting cells into a small, rapidly beating heart is more difficult than injecting cells into the tail vein, which is visible and remains still. We used the presence of blood in the syringe to indicate correct placement of the needle, but its placement throughout the duration of the injection is difficult to confirm. However, the utility of BLI is that it can corroborate successful injection within a few minutes by revealing a diffuse signal throughout the entire mouse vasculature.
The localization of the BL signal to the site of particle infusion beginning on day 4 indicates that luciferase-expressing MC3T3 cells migrated to this site (Fig. 2). This signal continued to intensify throughout the experiment, suggesting either continued migration of MC3T3 cells to the site of particle infusion or their proliferation at the site (Figs. 2 and 3). Based on qualitative image review, localization of the BLI signal in the control animals did not occur until day 8, but given the sensitivity of the technique, reporter cells most likely migrated earlier to this site. The surgical procedure and continued infusion of saline do cause some local tissue damage and inflammation, and it is not surprising that they caused minor migration of preosteoblastic cells, which have the potential for repair. However, the higher BLI ratio in the experimental animals, when compared to the control animals, during the first 8 days of the experiment indicates that the presence of wear particles elicited migration of exogenous cells more quickly than the infusion of saline alone (Fig. 3). Interestingly, there was a small, but persistent BLI signal from the contralateral limb in the majority of experimental animals, but in none of the control animals (Fig. 2). Previous work studying fracture healing,37 macrophage migration in osteolysis,11 and rheumatoid arthritis38 have all demonstrated this paired response.
The reliability of BLI decreases as a function of time after cell injection due to the fact that the reporter cells will continue to divide, differentiate, and die with time. While cell division and continued migration will presumably increase the signal in an area,39 a combination of cell death, cell differentiation, gene silencing, and post-transcriptional modifications all work to simultaneously decrease the amount and activity of luciferase.40 Given this information, we utilized immunohistochemistry to directly identify exogenous cells present at the end of the experiment rather than relying on BLI alone.
Immunohistochemical staining confirmed the migration of exogenous MC3T3 cells to the femora. Sections from particle-infused femora had a large degree of luciferase-positive staining, indicating the presence of exogenous cells (Fig. 5). As expected, the infusion of saline elicited a much smaller cell migration, as evidenced by the slight degree of luciferase-positive staining. The contralateral limb in the experimental animals stained positively for luciferase, though not to the extent of the operated, particle-infused limb. This is consistent with the presence of a small BLI signal from the nonoperated limb in the experimental animals (Fig. 2). Femoral sections obtained from animals in a different experiment from our laboratory, one in which no cells were injected, only displayed background antiluciferase staining. This result confirms the specificity of our antibody.
Together, the results of BLI and immunohistochemistry confirm the migration of circulating preosteoblastic cells to the site of particle infusion. Although in vivo osteoprogenitor migration to wear particles had not been studied before this experiment, others have confirmed their migration in response to fracture.41,42 Taken together, these results suggest that osteoprogenitor cells have the ability to migrate from distant sites to areas of bone trauma or inflammatory stimuli to re-establish bone homeostasis.
Immunohistochemistry also allowed a comparison of the relative number of osteoblasts and osteoclasts between the particle-infused and saline-infused femora (Fig. 6). TRAP staining confirmed the presence of osteoclasts in both groups, but with a greater degree of staining in the experimental femora. Inflammatory stimuli induced by phagocytosed UHMWPE particles lead to the recruitment of monocyte/macrophages to the particle infusion site. This occurs primarily through the MCP-1-CCR2 ligand receptor axis.12,43 These cells become activated, further releasing chemokines for macrophages and reparative cells, such as preosteoblasts, and also stimulate osteoclast differentiation and maturation. Osteoclasts locally resorb bone, thereby releasing other chemotactic substances, such as osteocalcin, and may make the bony matrix available as a scaffold for the injected MC3T3 cells to increase bone mass and mitigate wear particle-induced bone loss. The large number of osteoblasts in the particle-infused femora agrees with the results of the BLI and immunohistochemistry, which demonstrated the migration of preosteoblasts to the particle-infused femora. Histological evidence confirmed that UHMWPE particles stimulated osteoclast and osteoblast activity, a result that is consistent with other studies.4–10,13
One critical question of our study was whether the recruited preosteoblasts would have a beneficial effect on bone. Increased osteoblast number is a characteristic sign of osteolysis, but this increased osteoblast presence does not translate into improved bone quality or quantity.13 Kadoya et al. previously showed a significant increase in osteoblast activity and bone formation at the interface membrane in aseptically loosened joint replacements, suggesting that systemic recruitment of preosteoblastic cells could help tip the balance between ongoing bone resorption and formation toward reparative formation and healing in patients.13 Additionally, it has been shown that wear particles adversely affect the differentiation, proliferation, and osteogenicity of osteoblast precursors.14–16 However, in our study, the migrated exogenous MC3T3 cells correlated with a significant local increase in BMD and cortical thickness. The increased BMD is a combined effect of resident osteoblasts and migrated preosteoblasts that were able to differentiate into mature osteoblasts. Given the fact that the BMD in the saline-infused group remained low despite the injection of MC3T3 cells, the increased BMD is probably due to chemokine-induced reporter cell migration. Whether these effects are due to a paracrine effect of the migrated cells on host mesenchymal lineage cells, or direct bone formation by the injected migrated cells is unknown. The end result suggests that continued, substantial recruitment of preosteoblasts can mitigate or potentially reverse the decrease in BMD attributable to the presence of wear particles.
Although our model does not involve a weight-bearing prosthesis similar to the human situation, it provides a preclinical model that simulates the cellular processes involved during continuous infusion of wear particles and subsequent bone destruction and attempts at repair. Furthermore, the model provides a potential strategy for mitigating osteolysis by increasing mesenchymal lineage recruitment.
Conclusion
The local and systemic response of osteoclasts, osteoblasts, and their precursors to wear particles determines the success of total joint replacements. Elucidating the mechanisms underlying osteolysis will reveal new methods with which to combat its progression. In this study, we show that the exogenous preosteoblasts migrate to the site of wear particles, thus confirming that wear particles have not only a local, but also a systemic effect on osteoblast precursors. Further, the recruited preosteoblasts significantly increased BMD compared to controls. This reveals the potential use of osteoprogenitor cell therapies to treat osteolysis.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Timothy Wright for supplying the UHMWPE particles (Hospital for Special Surgery, New York City, NY) and Dr. Chris Contag, Dr. Lane Smith and Glen Kajiyama (Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA) for their helpful advice. This study was supported by Grant R01 AR055650-04 from the National Institute of Health.
Disclosure Statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
- 1.Campbell P. Ma S. Yeom B., et al. Isolation of predominantly submicron-sized UHMWPE wear particles from periprosthetic tissues. J Biomed Mater Res. 1995;29:127. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820290118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sharkey P.F. Hozack W.J. Rothman R.H., et al. Insall Award paper. Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;404:7. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200211000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Clohisy J.C. Calvert G. Tull F., et al. Reasons for revision hip surgery: a retrospective review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;429:188. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000150126.73024.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Archibeck M.J. Jacobs J.J. Roebuck K.A. Glant T.T. The basic science of periprosthetic osteolysis. Instr Course Lect. 2001;50:185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Purdue P.E. Koulouvaris P. Potter H.G., et al. The cellular and molecular biology of periprosthetic osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;454:251. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000238813.95035.1b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Revell P.A. The combined role of wear particles, macrophages and lymphocytes in the loosening of total joint prostheses. J R Soc Interface. 2008;5:1263. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tuan R.S. Lee F.Y. T Konttinen Y, et al. What are the local and systemic biologic reactions and mediators to wear debris, and what host factors determine or modulate the biologic response to wear particles? J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008;16(Suppl 1):S42. doi: 10.5435/00124635-200800001-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Revell P.A. al-Saffar N. Kobayashi A. Biological reaction to debris in relation to joint prostheses. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 1997;211:187. doi: 10.1243/0954411971534304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bauer T.W. Particles and periimplant bone resorption. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;405:138. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200212000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Goodman S.B. Ma T. Cellular chemotaxis induced by wear particles from joint replacements. Biomaterials. 2010;31:5045. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.03.046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ren P.G. Huang Z. Ma T., et al. Surveillance of systemic trafficking of macrophages induced by UHMWPE particles in nude mice by noninvasive imaging. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;94:706. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.32744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ren P.G. Irani A. Huang Z., et al. Continuous infusion of UHMWPE particles induces increased bone macrophages and osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469:113. doi: 10.1007/s11999-010-1645-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kadoya Y. Revell P.A. al-Saffar N., et al. Bone formation and bone resorption in failed total joint arthroplasties: histomorphometric analysis with histochemical and immunohistochemical technique. J Orthop Res. 1996;14:473. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100140318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chiu R. Ma T. Smith R.L. Goodman S.B. Ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene wear debris inhibits osteoprogenitor proliferation and differentiation in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;89:242. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.32001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Goodman S.B. Ma T. Chiu R., et al. Effects of orthopaedic wear particles on osteoprogenitor cells. Biomaterials. 2006;27:6096. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.08.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dean D.D. Schwartz Z. Blanchard C.R., et al. Ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene particles have direct effects on proliferation, differentiation, and local factor production of MG63 osteoblast-like cells. J Orthop Res. 1999;17:9. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100170104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Huang Z. Ma T. Ren P.G., et al. Effects of orthopedic polymer particles on chemotaxis of macrophages and mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;94:1264. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.32803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dwyer R.M. Potter-Beirne S.M. Harrington K.A., et al. Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 secreted by primary breast tumors stimulates migration of mesenchymal stem cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:5020. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Belema-Bedada F. Uchida S. Martire A., et al. Efficient homing of multipotent adult mesenchymal stem cells depends on FROUNT-mediated clustering of CCR2. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2:566. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ito H. Chemokines in mesenchymal stem cell therapy for bone repair: a novel concept of recruiting mesenchymal stem cells and the possible cell sources. Mod Rheumatol. 2011;21:113. doi: 10.1007/s10165-010-0357-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Granero-Molto F. Weis J.A. Miga M.I., et al. Regenerative effects of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells in fracture healing. Stem Cells. 2009;27:1887. doi: 10.1002/stem.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wang L. Li Y. Chen X., et al. MCP-1, MIP-1, IL-8 and ischemic cerebral tissue enhance human bone marrow stromal cell migration in interface culture. Hematology. 2002;7:113. doi: 10.1080/10245330290028588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Contag P.R. Olomu I.N. Stevenson D.K. Contag C.H. Bioluminescent indicators in living mammals. Nat Med. 1998;4:245. doi: 10.1038/nm0298-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.De A. Lewis X.Z. Gambhir S.S. Noninvasive imaging of lentiviral-mediated reporter gene expression in living mice. Mol Ther. 2003;7:681. doi: 10.1016/s1525-0016(03)00070-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Contag C.H. Bachmann M.H. Advances in in vivo bioluminescence imaging of gene expression. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2002;4:235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bioeng.4.111901.093336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kuppen P.J. Marinelli A. Camps J.A., et al. Biodistribution of lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cells in Wag rats after hepatic-artery or jugular-vein infusion. Int J Cancer. 1992;52:266. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Togel F. Yang Y. Zhang P., et al. Bioluminescence imaging to monitor the in vivo distribution of administered mesenchymal stem cells in acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;295:F315. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00098.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Arguello F. Baggs R.B. Frantz C.N. A murine model of experimental metastasis to bone and bone marrow. Cancer Res. 1988;48:6876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Drake J.M. Gabriel C.L. Henry M.D. Assessing tumor growth and distribution in a model of prostate cancer metastasis using bioluminescence imaging. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2005;22:674. doi: 10.1007/s10585-006-9011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jenkins D.E. Hornig Y.S. Oei Y., et al. Bioluminescent human breast cancer cell lines that permit rapid and sensitive in vivo detection of mammary tumors and multiple metastases in immune deficient mice. Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7:R444. doi: 10.1186/bcr1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kim K.J. Kobayashi Y. Itoh T. Osteolysis model with continuous infusion of polyethylene particles. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;352:46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ma T. Huang Z. Ren P.G., et al. An in vivo murine model of continuous intramedullary infusion of polyethylene particles. Biomaterials. 2008;29:3738. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.05.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ortiz S.G. Ma T. Epstein N.J., et al. Validation and quantification of an in vitro model of continuous infusion of submicron-sized particles. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;84:328. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.30875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Arguello F. Furlanetto R.W. Baggs R.B., et al. Incidence and distribution of experimental metastases in mutant mice with defective organ microenvironments (genotypes Sl/Sld and W/Wv) Cancer Res. 1992;52:2304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kuznetsov S.A. Mankani M.H. Gronthos S., et al. Circulating skeletal stem cells. J Cell Biol. 2001;153:1133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.153.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Eghbali-Fatourechi G.Z. Modder U.I. Charatcharoenwitthaya N., et al. Characterization of circulating osteoblast lineage cells in humans. Bone. 2007;40:1370. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2006.12.064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kumagai K. Vasanji A. Drazba J.A., et al. Circulating cells with osteogenic potential are physiologically mobilized into the fracture healing site in the parabiotic mice model. J Orthop Res. 2008;26:165. doi: 10.1002/jor.20477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kelly S. Dunham J.P. Donaldson L.F. Sensory nerves have altered function contralateral to a monoarthritis and may contribute to the symmetrical spread of inflammation. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;26:935. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cao F. Lin S. Xie X., et al. In vivo visualization of embryonic stem cell survival, proliferation, and migration after cardiac delivery. Circulation. 2006;113:1005. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.588954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Krishnan M. Park J.M. Cao F., et al. Effects of epigenetic modulation on reporter gene expression: implications for stem cell imaging. FASEB J. 2006;20:106. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-4551fje. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Shirley D. Marsh D. Jordan G., et al. Systemic recruitment of osteoblastic cells in fracture healing. J Orthop Res. 2005;23:1013. doi: 10.1016/j.orthres.2005.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Devine M.J. Mierisch C.M. Jang E., et al. Transplanted bone marrow cells localize to fracture callus in a mouse model. J Orthop Res. 2002;20:1232. doi: 10.1016/S0736-0266(02)00051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gibon E. Ma T. Ren P.-G., et al. Selective inhibition of the MCP-1-CCR2 ligand-receptor axis decreases systemic trafficking of macrophages in the presence of UHMWPE particles. J Orthop Res. 2012;30:547. doi: 10.1002/jor.21548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]