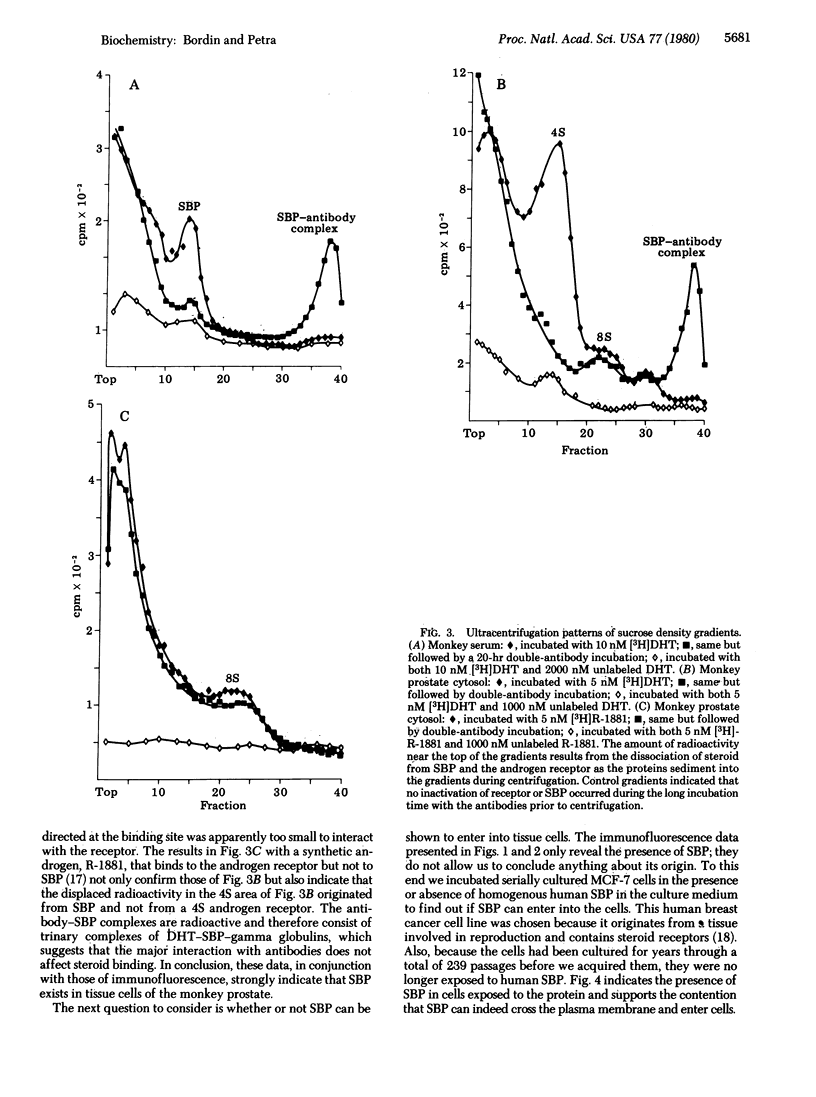
Abstract
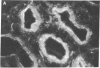
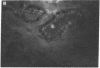
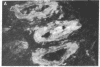
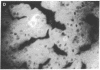
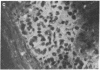
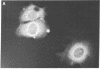
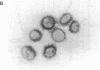
The sex steroid-binding protein (SBP) present in the serum of the monkey Macaca nemestrina is shown to exist in cells of tissue involved in reproduction. The localization was demonstrated by immunofluorescence with monospecific antibodies raised against homogeneous human SBP. These antibodies were previously shown to crossreact with monkey SBP. The protein appears to be located in the cytoplasm of epithelial cells lining the prostate alveoli, the ducti of the epididymis, and the seminiferous tubula of the testes of the monkey. The protein is also present in the cytoplasm of parenchymal cells of the liver, where SBP is believed to be synthesized, and in cells of the adrenal cortex, where steroids are known to be synthesized. Controls appear dark and illustrate specificity of the immunofluorescence, ruling out both tissue autofluorescence and other nonspecific interactions. In all cases, the relative intensity of fluorescence appears minimal in the nuclei of cells. Experiments performed with cultured MCF-7 cells indicate that SBP can across the plasma membrane and enter into the cytoplasm but not into the nucleus. Additional studies indicate that the monospecific antibodies do not crossreact with the monkey prostate androgen receptor, as shown by ultracentrifugation in sucrose densty gradients. The physiological significance of these observations is not known; however, the existence of this protein in cells of target tissues for sex steroids introduces a new dimension in our thinking about the role of this protein in androgen action.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonne C., Raynaud J. P. Methyltrienolone, a specific ligand for cellular androgen receptors. Steroids. 1975 Aug;26(2):227–232. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(75)80023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordin S., Lewis J., Petra P. H. Monospecific antibodies to the sex steroid-binding protein (SBP) of human and rabbit sera: cross-reactivity with other species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 14;85(1):391–401. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(78)80055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks S. C., Locke E. R., Soule H. D. Estrogen receptor in a human cell line (MCF-7) from breast carcinoma. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6251–6253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., KAPLAN M. H. Localization of antigen in tissue cells; improvements in a method for the detection of antigen by means of fluorescent antibody. J Exp Med. 1950 Jan 1;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan R. A., Cowan S. K., Giles C. A., Grant J. K. Prostatic distribution of sex hormone-binding globulin and cortisol-binding globulin in benign hyperplasia. J Endocrinol. 1976 Oct;71(1):121–131. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0710121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson V., Ritzen E. M., Weddington S. C., McLean W. S., Tindall D. J., Nayfeh S. N., French F. S. Preliminary characterization of a binding protein for androgen in rabbit serum. Comparison with the testosterone-binding globulin (TeBG) in human serum. Endocrinology. 1974 Sep;95(3):690–700. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-3-690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu A. F., Troen P. An androgen binding protein in the testicular cytosol of human testis. Comparison with human plasma testosterone-estrogen binding globulin. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1611–1619. doi: 10.1172/JCI109081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung-Testas I., Mercier-Bodard C. H., Robel P. Protéines de liaison des androgènes dans la prostate humaine. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 1976 Mar-Apr;37(2):97–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier-Bodard C., Renoir J. M., Baulieu E. E. Further characterization and immunological studies of human sex steroid binding plasma protein. J Steroid Biochem. 1979 Jul;11(1A):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(79)90305-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelson K. E., Pétra P. H. Purification and characterization of the sex steroid-binding protein of rabbit serum. Comparison with the human protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5293–5298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelson K. E., Teller D. C., Petra P. H. Characterization of the sex steroid binding protein of human pregnancy serum. Improvements in the purification procedure. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1409–1415. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mischke W., Weise H. C., Graesslin D., Rüsch R., Tamm J. Isolation of highly purified sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG): evidence for microheterogeneity. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1979 Apr;90(4):737–742. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0900737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namkung P. C., Moe R. E., Petra P. H. Stability of estrogen receptors in frozen human breast tumor tissue. Cancer Res. 1979 Mar;39(3):1124–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petra P. H. The serum sex steroid-binding protein. Purification, characterization and immunological properties of the human and rabbit proteins. J Steroid Biochem. 1979 Jul;11(1A):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(79)90304-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pétra P. H., Lewis J. Modification in the purification of the sex steroid-binding protein of human serum by affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jun;105(1):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90440-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen V., Jung I., Baulieu E. E., Robel P. Androgen-binding proteins in human benign prostatic hypertrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Oct;41(4):761–770. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-4-761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steins P., Krieg M., Hollmann H. J., Voigt K. D. In vitro studies of testosterone and 5alpha-dihydrotestosterone binding in benign prostatic hypertrophy. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1974 Apr;75(4):773–784. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0750773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Itagaki E., Mori H., Hosoya T. Isolation of testosterone-binding globulin from bovine serum by affinity chromatography and its molecular characterization. J Biochem. 1977 Jun;81(6):1721–1731. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Okumura Y., Sinohara H. Purification and characterization of testosterone-binding globulin of canine serum. J Biochem. 1979 May;85(5):1195–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigersky R. A., Loriaux D. L., Howards S. S., Hodgen G. B., Lipsett M. B., Chrambach A. Androgen binding proteins of testis, epididymis, and plasma in man and monkey. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1061–1068. doi: 10.1172/JCI108557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]