Abstract
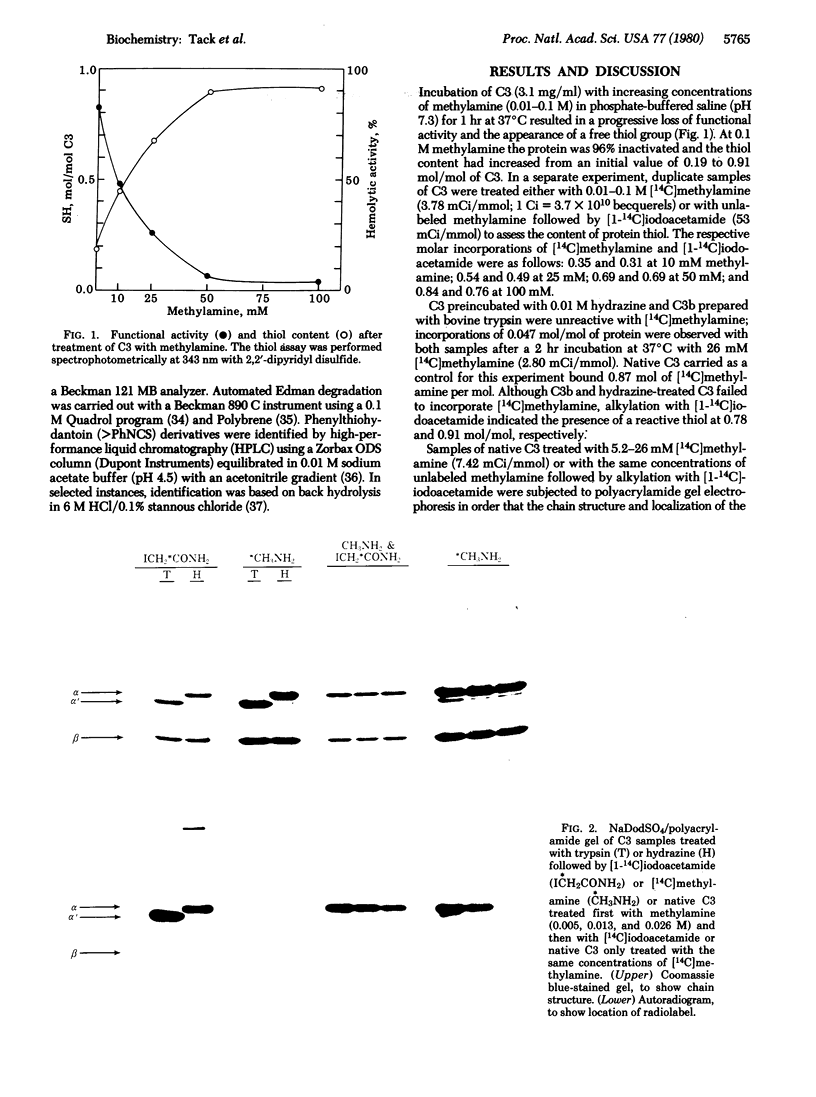
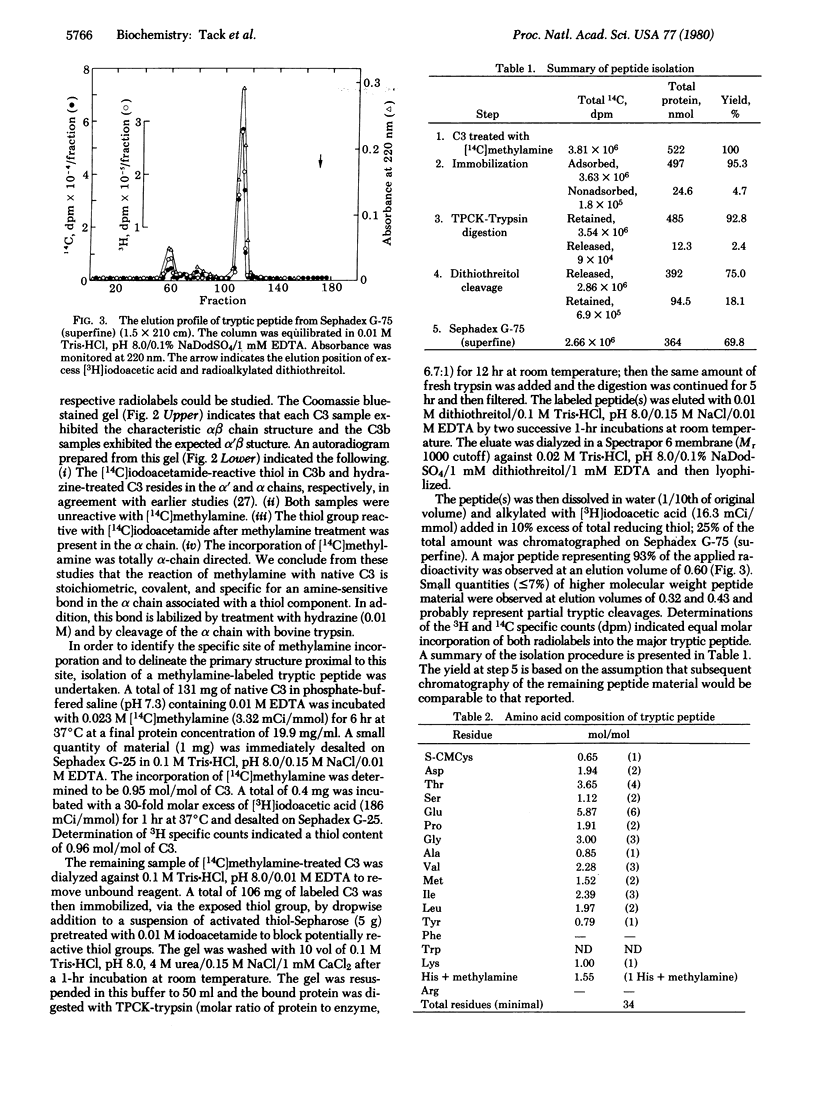
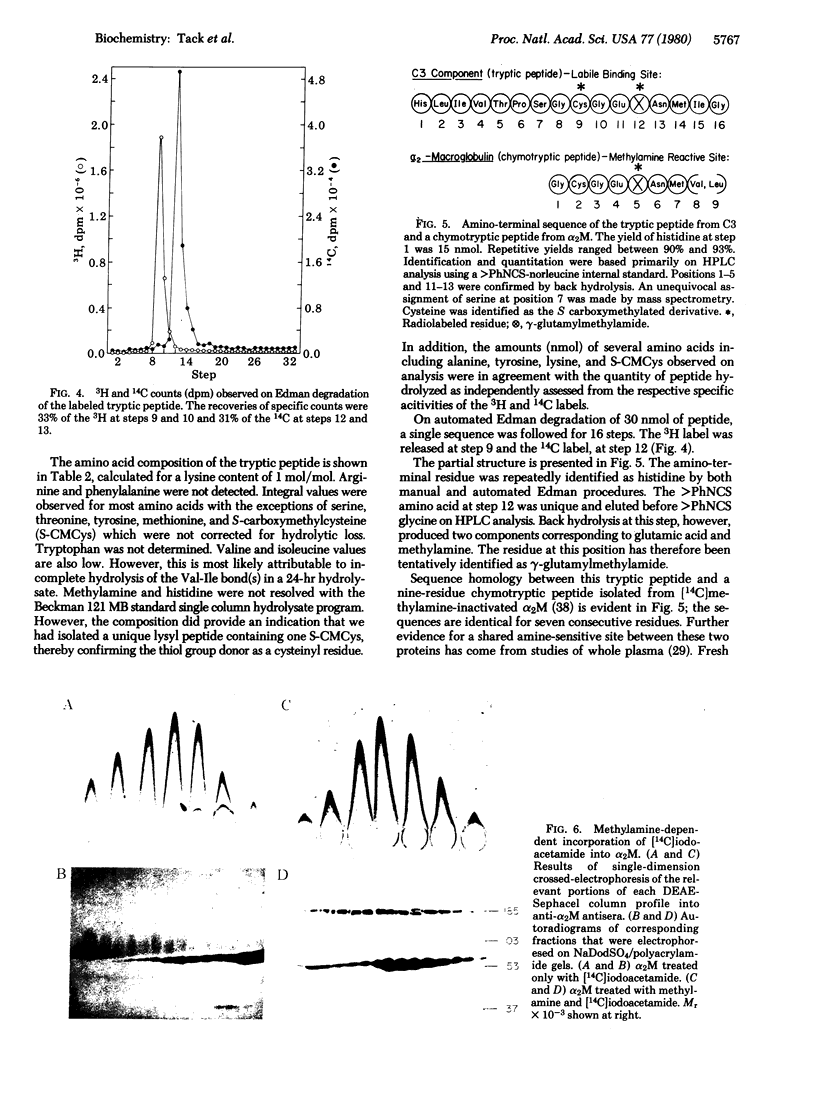
Treatment of the third component of human complement (C3) with methylamine results in a loss of hemolytic function and the appearance of a thiol group. Studies with [14C]methylamine have indicatd a stoichiometric and covalent reaction with the native protein. Hydrazine-inactivated C3 and C3b prepared with bovine trypsin were unreactive with [14C]-methylamine. Alkylation experiments with [1-14C]iodoacetamide have further established a 1:1 correspondence between methylamine incorporation and expression of the reactive thiol. Autoradiographic analyses of [14C]methylamine-treated C3 and methylamine-inactivated [1-14C]carboxyamidomethylated C3 after NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis have shown a specific incorporation of each radiolabel into the alpha polypeptide chain. [14C]Methylamine-treated C3 was immobilized on Sepharose 4B by reaction of the protein thiol with a mixed disulfide. Digestion with bovine trypsin in 4 M urea released 96% of the bound absorbance (at 280 nm) units; the radiolabel remained associated with the Sepharose beads. Peptide material labeled with 14C was eluted with dithiothreitol, carboxymethylated with [3H]iodoacetic acid, and chromatographed on Sephadex G-75. On Edman degradation S-[3H]carboxymethylcysteine was released at step 9 and gamma-glutamyl[14C]-methylamide was released at step 12. We interpret these data to indicate the presence of an internal thiolester bond in native C3. In addition, evidence is presented for an identical reactive site in alpha 2-macroglobulin.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaout M. A., Stossel T. P., Rosen F. S., Alper C. A. Solubilization of C3 fragments deposited on cross-linked dextran gel beads. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Nov;14(3):384–394. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Cochrane C. G. Isolation of a fragment (C3a) of the third component of human complement containing anaphylatoxin and chemotactic activity and description of an anaphylatoxin inactivator of human serum. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1109–1130. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brauer A. W., Margolies M. N., Haber E. The application of 0.1 M quadrol to the microsequence of proteins and the sequence of tryptic peptides. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):3029–3035. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlo J. R., Ruddy S., Studer E. J., Conrad D. H. Complement receptor binding of C3b-coated cells treated with C3b inactivator, beta 1H globulin and trypsin. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):523–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. C3 requirements for formation of alternative pathway C5 convertase. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):630–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dias Da Silva W., Lepow I. H. Complement as a mediator of inflammation. II. Biological properties of anaphylatoxin prepared with purified components of human complement. J Exp Med. 1967 May 1;125(5):921–946. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlenberger A. G., Nussenzweig V. The role of membrane receptors for C3b and C3d in phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):357–371. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Nelson R. A., Jr Complement dependent immune phagocytosis. I. Requirements for C'1, C'4, C'2, C'3. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Jul;51(1):45–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Kaplan H. B., Radin A., Frosch M. Independent effects of IgG and complement upon human polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1282–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. A., Lachmann P. J. Novel cleavage products of the third component of human complement. Mol Immunol. 1980 Feb;17(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E. Human anaphylatoxin (C3a) from the third component of complement. Primary structure. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8293–8301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Capra J. D. Automated amino acid sequence of small peptides utilizing Polybrene. Anal Biochem. 1978 Mar;85(1):126–131. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Fearon D. T., Levine R. P. Action of the C3b-inactivator on the cell-bound C3b. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Levine R. P. Interaction between the third complement protein and cell surface macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2701–2705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Lichtenberg N. A., Levine R. P. Evidence for an ester linkage between the labile binding site of C3b and receptive surfaces. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1388–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medicus R. G., Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Alternative pathway of complement: recruitment of precursor properdin by the labile C3/C5 convertase and the potentiation of the pathway. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1076–1093. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez E., Lai C. Y. Regeneration of amino acids from thiazolinones formed in the Edman degradation. Anal Biochem. 1975 Sep;68(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90677-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Götze O. C3 proactivator convertase and its mode of action. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):1003–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Polley M. J., Calcott M. A. Formation and functional significance of a molecular complex derived from the second and the fourth component of human complement. J Exp Med. 1967 Feb 1;125(2):359–380. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllerèberhard H. J., Dalmasso A. P., Calcott M. A. The reaction mechanism of beta-1C-globulin (C'3) in immune hemolysis. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):33–54. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Stroud R. M. Mechanism of action of the C3b inactivator: requirement for a high molecular weight cofactor (C3b-C4bINA cofactor) and production of a new C3b derivative (C3b'). Immunochemistry. 1977 Nov-Dec;14(11-12):749–756. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(77)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson A., Brade V., Lee G. D., Shin H. S., Mayer M. M. Kinetic studies of the formation of the properdin system enzymes on zymosan: evidence that nascent C3b controls the rate of assembly. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1115–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Human complement C3b inactivator: isolation, characterization, and demonstration of an absolute requirement for the serum protein beta1H for cleavage of C3b and C4b in solution. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):257–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Polley M. J. Specificity of human lymphocyte complement receptors. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):1163–1180. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. P., Howard J. B. Characterization of alkylamine-sensitive site in alpha 2-macroglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4313–4316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. D., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: purification from plasma and physicochemical characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4513–4521. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. F., Morris S. C., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: structural analysis of the polypeptide chains of C3 and C3b. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1497–1503. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt W., Schmidt G., Von Buttlar B., Dieminger L. A new function of the activated third component of complement: binding to C5, an essential step for C5 activation. Immunology. 1978 Jan;34(1):29–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K., Ruddy S. Modulation of C3b hemolytic activity by a plasma protein distinct from C3b inactivator. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1011–1013. doi: 10.1126/science.948757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman C. L., Pisano J. J. High-performance liquid chromatography of amino acid derivatives. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:45–51. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]