Abstract
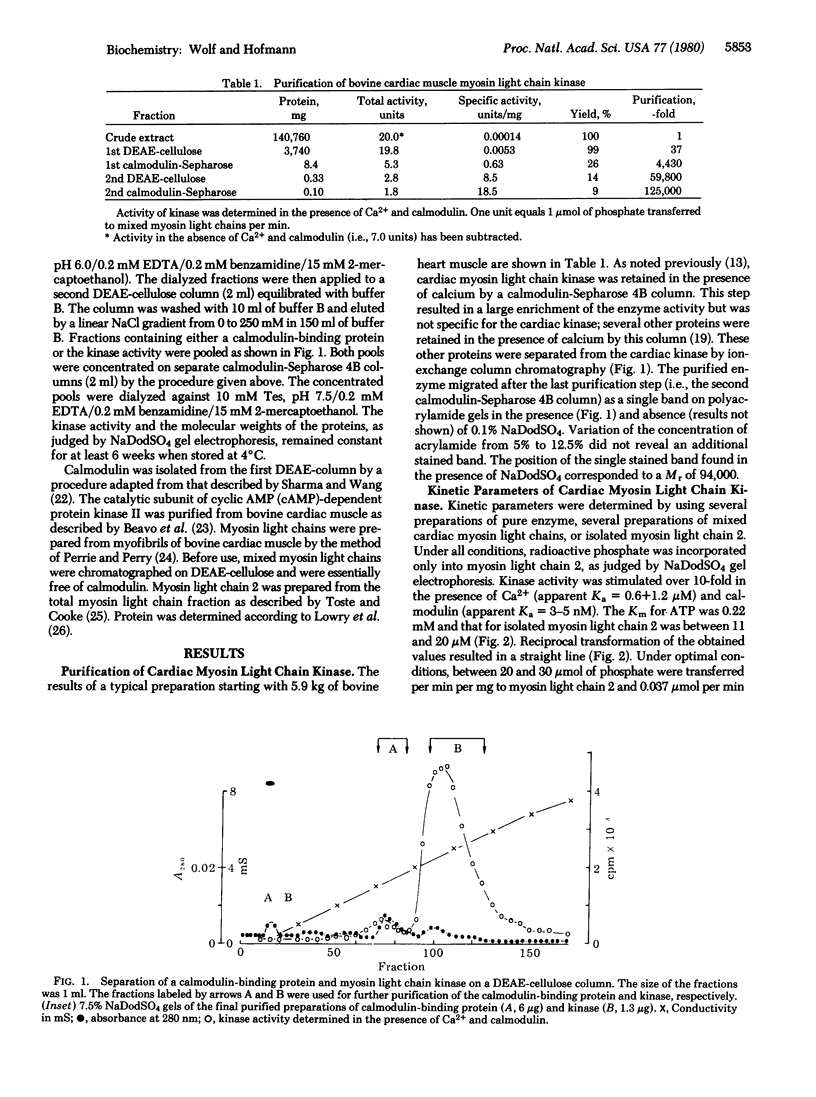
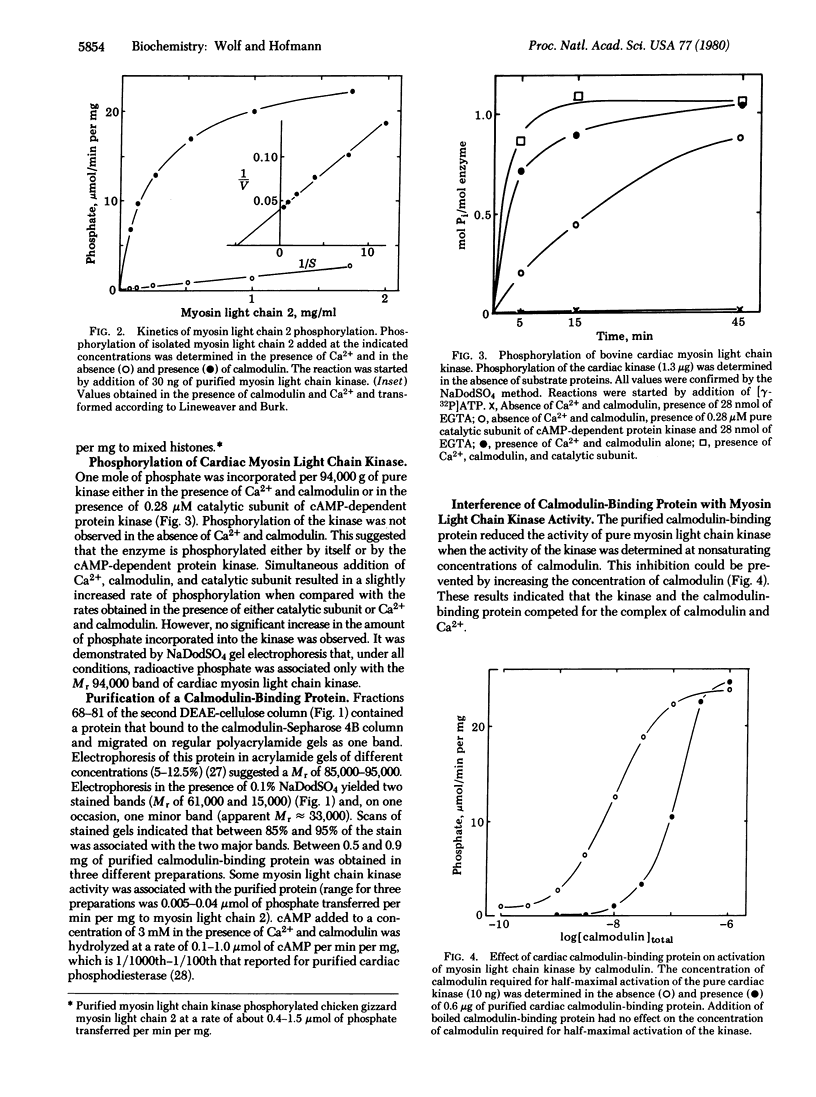
Myosin light chain kinase was purified > 100,000-fold to apparent homogeneity with a yield of 10% from bovine cardiac muscle. Sodium dodecyl sulfate gels of the purified kinase showed one stained band corresponding to a Mr of 94,000. The enzyme was activated > 10-fold in the presence of Ca2+ (apparent Ka = 0.6-1.2 microM) and calmodulin (apparent Ka = 3-5 nM). The purified enzyme had a specific activity of 20-30 mumol of phosphate transferred per min per mg from ATP to cardiac myosin light chain 2. One mole of phosphate was incorporated per 94,000 g of the kinase in the presence of Ca2+ and calmodulin or of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase or of both additions. In addition to myosin light chain kinase, a calmodulin-binding protein of unknown function was purified from bovine cardiac muscle. This protein had a Mr of 85,000, was composed of two dissimilar subunits (Mr of 61,000 and 15,000), and competed with myosin light chain kinase for calmodulin. The protein appears to be closely related to the calmodulin-binding protein I purified from brain.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Conti M. A., Hathaway D. R., Klee C. B. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase by the catalytic subunit of adenosine 3': 5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8347–8350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adelstein R. S., Hathaway D. R. Role of calcium and cyclic adenosine 3':5' monophosphate in regulating smooth muscle contraction. Mechanisms of excitation-contraction coupling in smooth muscle. Am J Cardiol. 1979 Oct 22;44(5):783–787. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(79)90197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barron J. T., Bárány M., Bárány K. Phosphorylation of the 20,000-dalton light chain of myosin of intact arterial smooth muscle in rest and in contraction. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):4954–4956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Preparation of homogeneous cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase(s) and its subunits from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:299–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány K., Bárány M. Phosphorylation of the 18,000-dalton light chain of myosin during a single tetanus of frog muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4752–4754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska R., Aromatorio D., Sherry J. M., Hartshorne D. J. Composition of the myosin light chain kinase from chicken gizzard. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Oct 24;78(4):1263–1272. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91429-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska R., Sherry J. M., Aromatorio D. K., Hartshorne D. J. Modulator protein as a component of the myosin light chain kinase from chicken gizzard. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):253–258. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockerzi V., Speichermann N., Hofmann F. A guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from bovine heart muscle. Purification and phosphorylation of histone I and IIb. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3395–3399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frearson N., Solaro R. J., Perry S. V. Changes in phosphorylation of P light chain of myosin in perfused rabbit heart. Nature. 1976 Dec 23;264(5588):801–802. doi: 10.1038/264801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho H. C., Wirch E., Stevens F. C., Wang J. H. Purification of a Ca2+-activatable cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from bovine heart by specific interaction with its Ca2+-dependent modulator protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Walseth T. F. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-32P]ATP, [alpha-32P]GTP, [32P]cAMP, and [32P]cGMP, and their use in the assay of adenylate and guanylate cyclases and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:135–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Krinks M. H. Calcineurin: a calcium- and calmodulin-binding protein of the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6270–6273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Krinks M. H. Purification of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitory protein by affinity chromatography on activator protein coupled to Sepharose. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):120–126. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Perry S. V. Calmodulin and myosin light-chain kinase of rabbit fast skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 1;179(1):89–97. doi: 10.1042/bj1790089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Smillie L. B., Perry S. B. A phosphorylated light-chain component of myosin from skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):151–164. doi: 10.1042/bj1350151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pires E., Perry S. V., Thomas M. A. Myosin light-chain kinase, a new enzyme from striated muscle. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 1;41(2):292–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Walsh D. A., Krebs E. G. Purification and properties of rabbit skeletal muscle adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1986–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K., Wang J. H. Preparation and assay of the Ca2+--dependent modulator protein. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:187–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull J. T., High C. W. Phosphorylation of skeletal muscle contractile proteins in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):1078–1083. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toste A. P., Cooke R. Interactions of contractile proteins with free and immobilized cibacron Blue F3GA. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jun;95(2):317–328. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90734-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan P. F., Butt V. S. The action of o-dihydric phenols in the hydroxylation of p-coumaric acid by a phenolase from leaves of spinach beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Biochem J. 1970 Aug;119(1):89–94. doi: 10.1042/bj1190089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. P., Vallet B., Autric F., Demaille J. G. Purification and characterization of bovine cardiac calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12136–12144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Waisman D. M. Calmodulin and its role in the second-messenger system. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1979;15:47–107. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152815-7.50006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazawa M., Yagi K. Calcium-binding subunit of myosin light chain kinase. J Biochem. 1977 Jul;82(1):287–289. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




