Abstract
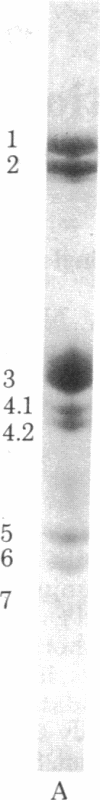
Oligosaccharide chains on the surfce of human erythrocytes were labeled with the probe eosin 5-thiosemicarbazide. The probe was conjugated to aldehydes produced by oxidation of sialic acid and galactose residues. The probe is associated mostly with glycophorin A after sialic acid labeling, whereas multiple components, including band 3 and lipids, are labeled after galactose oxidation. Fast molecular motion was studied by measuring steady-state and picosecond time-resolved fluorescence depolarization. Slower motions were investigated by observing flash-induced transient dichroism. It was found that both eosin-labeled sialic acid and galactose residues exhibit a rapid motion with correlation time of approximately 3 nsec. This motion is assigned to independent motion of the probe, possibly in conjunction with a short segment of the oligosaccharide chain. The order parameter of the fast motion is 0.8.-0.9, demonstrating that its angular amplitude is highly restricted. For eosin-labeled sialic acid, the order parameter in the microsecond time range is 0.2-0.3. It is deduced that a second, slower rotational motion is present, which is assigned to a cooperative motion of the oligosaccharide chains. The correlation time of this motion is in the range 10(-7)-(10-5) sec. Some eosin-labeled galactose residues may have a similar slow motion, but most appear to be remarkably immobile over the time range 10(-8)-10(-3) sec.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Low P. S. Covalent labelling of specific membrane carbohydrate residues with fluorescent probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 10;597(2):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin R. H., Chan S. S., Jovin T. M. Rotational diffusion of cell surface components by time-resolved phosphorescence anisotropy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5650–5654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beddard G. S., Fleming G. R., Porter G., Searle G. F., Synowiec J. A. The fluorescence decay kinetics of in vivo chlorophyll measured using low intensity excitation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 11;545(1):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Bürkli A., Busslinger M., Schneider G., Parish G. R. Rotational diffusion of band 3 proteins in the human erythrocyte membrane. Nature. 1976 Sep 30;263(5576):389–393. doi: 10.1038/263389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J. Measurement of protein rotational diffusion in membranes by flash photolysis. Methods Enzymol. 1978;54:47–61. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)54007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Schneider G. A spectroscopic technique for measuring slow rotational diffusion of macromolecules. 2: Determination of rotational correlation times of proteins in solution. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3657–3661. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Surface modulation in cell recognition and cell growth. Science. 1976 Apr 16;192(4236):218–226. doi: 10.1126/science.769162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Andersson L. C. Selective radioactive labeling of cell surface sialoglycoproteins by periodate-tritiated borohydride. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5888–5894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi H., Cleve H. Solubilization and comparative analysis of mammalian erythrocyte membrane glycoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Apr 28;47(2):459–464. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90736-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P. Determination of lipid order parameters and rotational correlation times from fluorescence depolarization experiments. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):359–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80564-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C. The complex carbohydrates of mammalian cell surfaces and their biological roles. Essays Biochem. 1975;11:1–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. Structural order of lipids and proteins in membranes: evaluation of fluorescence anisotropy data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6361–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Kawato S., Ikegami A. A theory of fluorescence polarization decay in membranes. Biophys J. 1977 Dec;20(3):289–305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85550-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavalette D., Amand B., Pochon F. Rotational relaxation of 70S ribosomes by a depolarization method using triplet probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1407–1411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. M., Grant C. W. Headgroup dynamics of an integral membrane glycoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):856–863. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91906-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Furthmayr H., Tomita M. The red cell membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:667–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C., Boxer D., Garland P. Phosphorescence depolarization and the measurement of rotational motion of proteins in membranes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 1;108(1):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Transmembrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. I. Cytoplasmic influence over surface components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 13;457(1):57–108. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E., Cherry R. J. Dimeric association of band 3 in the erythrocyte membrane demonstrated by protein diffusion measurements. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):493–494. doi: 10.1038/277493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE H. G., OKLANDER M. IMPROVED PROCEDURE FOR THE EXTRACTION OF LIPIDS FROM HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:428–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R., Bangerter F. W. On the labelling of oxidized cell surface membranes by acyl hydrazides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 2;557(2):354–362. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90333-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. Cross-linking the major proteins of the isolated erythrocyte membrane. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 14;66(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90481-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett R. B., Carraway K. L. Proteolytic digestion of erythrocytes, resealed ghosts, and isolated membranes. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 18;11(15):2897–2903. doi: 10.1021/bi00765a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G. Rotational Brownian motion and polarization of the fluorescence of solutions. Adv Protein Chem. 1953;8:415–459. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P., Hof L. Introduction of a fluorescent label into the carbohydrate moiety of glycoconjugates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 18;65(4):1298–1302. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80371-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilchek M., Spiegel S., Spiegel Y. Fluorescent reagents for the labeling of glycoconjugates in solution and on cell surfaces. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 27;92(4):1215–1222. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90416-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yguerabide J. Nanosecond fluorescence spectroscopy of macromolecules. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:498–578. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]