Abstract
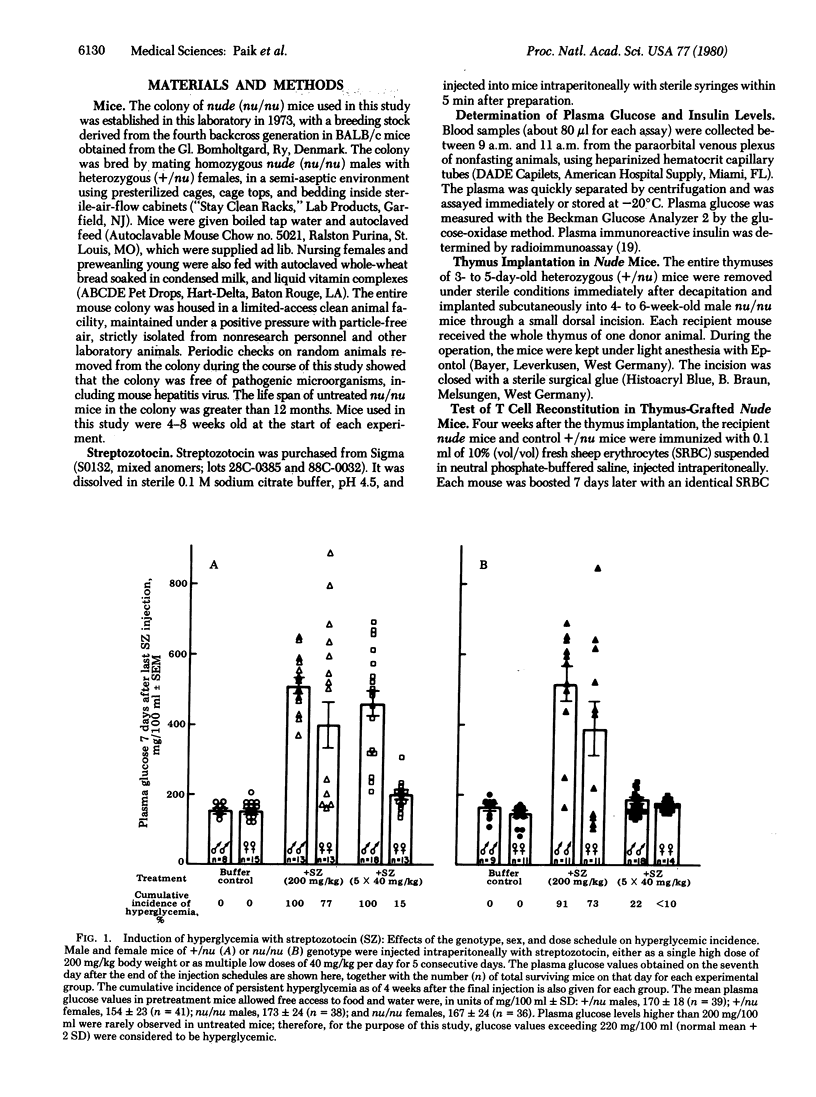
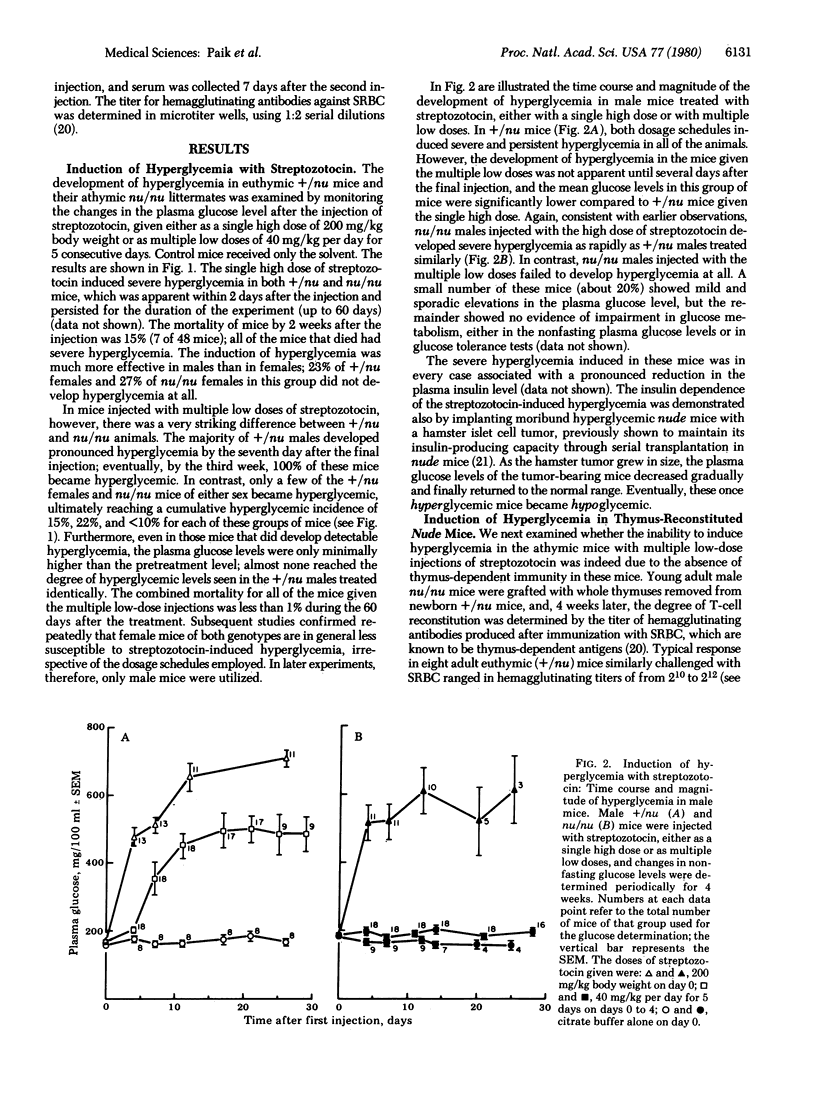
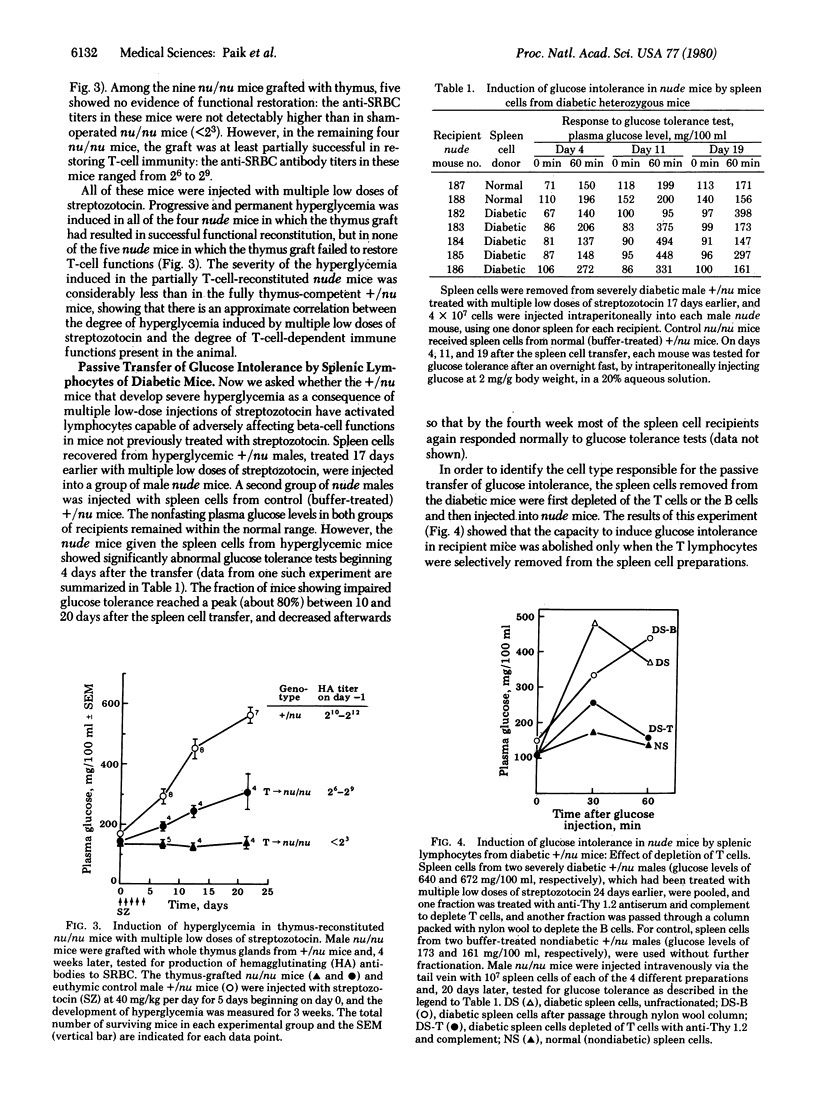
The role of thymic functions in the development of insulin-dependent diabetes was investigated in athymic nude (nu/nu) mice and euthymic heterozygous (+/nu) littermates of BALB/c origin treated with streptozotocin. The injection of a single high dose of streptozotocin (200 mg/kg body weight) induced rapid and permanent hyperglycemia in both nu/nu and +/nu mice. In contrast, the injection of the same total dose divided into multiple "subdiabetogenic" doses (40 mg/kg per day for 5 consecutive days) caused the development of delayed but progressive hyperglycemia only in the thymus-competent +/nu mice. Female mice of either genotype were significantly less susceptible to streptozotocin at both doses. Restoration of thymic immunity in nu/nu mice by thymus grafts also restored the susceptibility to the hyperglycemic effects of multiple low doses of streptozotocin. Moreover, splenic lymphocytes from +/nu mice previously made diabetic with the multiple low-dose injections of streptozotocin induced transient glucose intolerance in nu/nu mice. The ability of the diabetic spleen cells to transfer the diabetic state was abolished when the splenic lymphocytes were depleted of the T cells but not when they were depleted of B cells. These results provide direct proof that thymus-dependent functions play an obligatory etiologic role in the development of diabetes in mice treated with repeated subdiabetogenic doses of streptozotocin. These observations also add to the growing evidence that autoimmune amplification mechanisms may be critically involved in the etiology of juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus in humans.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beattie G., Lannom R., Lipsick J., Kaplan N. O., Osler A. G. Streptozotocin-induced diabetes in athymic and conventional BALB/c mice. Diabetes. 1980 Feb;29(2):146–150. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.2.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschard K., Madsbad S., Rygaard J. Passive transfer of diabetes mellitus from man to mouse. Lancet. 1978 Apr 29;1(8070):908–910. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90684-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschard K., Rygaard J. Is the diabetogenic effect of streptozotocin in part thymus-dependent? Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1978 Feb;86(1):23–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb02552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschard K., Rygaard J., Lung E. The inability of a diabetogenic virus to induce diabetes mellitus in athymic (nude) mice. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Aug;84(4):299–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschard K., Rygaard J., Madsbad S. Passive transfer in diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1979 Aug 11;2(8137):303–303. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschard K., Rygaard J. Passive transfer of streptozotocin induced diabetes mellitus with spleen cells. Studies of synogeneic and allogeneic transfer to normal and athymic nude mice. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Dec;85C(6):469–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb03670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschard K., Rygaard J. T-lymphocytes transfer streptozotocin induced diabetes mellitus in mice. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1978 Dec;86C(6):277–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb02591.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craighead J. E. Current views on the etiology of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1978 Dec 28;299(26):1439–1445. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197812282992605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craighead J. E. The role of viruses in the pathogenesis of pancreatic disease and diabetes mellitus. Prog Med Virol. 1975;19:161–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble D. R., Taylor K. W., Cumming H. Coxsackie viruses and diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1973 Nov 3;4(5887):260–262. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5887.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gepts W. Pathologic anatomy of the pancreas in juvenile diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1965 Oct;14(10):619–633. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.10.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. W., Maclaren N. K. Insulin-dependent diabetes: a disease of autoaggression. Science. 1976 Apr 2;192(4234):64–66. doi: 10.1126/science.769160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindred B., Loor F. Activity of host-derived T cells which differentiate in nude mice grafted with co-isogenic or allogeneic thymuses. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1215–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lendrum R., Walker G., Gamble D. R. Islet-cell antibodies in juvenile diabetes mellitus of recent onset. Lancet. 1975 Apr 19;1(7912):880–882. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91683-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Rossini A. A., Guberski D. L., Appel M. C., Williams R. M. Spontaneous diabetes mellitus: reversal and prevention in the BB/W rat with antiserum to rat lymphocytes. Science. 1979 Dec 21;206(4425):1421–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.388619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Rossini A. A. Streptozotocin-induced pancreatic insulitis: new model of diabetes mellitus. Science. 1976 Jul 30;193(4251):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.180605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsick J., Beattie G., Osler A. G., Kaplan N. O. Passive transfer of lymphocytes from diabetic man to athymic mouse. Lancet. 1979 Jun 16;1(8129):1290–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92246-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L. Virus-induced diabetes mellitus. Arch Virol. 1977;54(1-2):1–17. doi: 10.1007/BF01314374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera T., Jenson A. B., Yoon J. W., Notkins A. L. Virus-induced diabetes mellitus: reovirus infection of pancreatic beta cells in mice. Science. 1978 Aug 11;201(4355):529–531. doi: 10.1126/science.208156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossini A. A., Appel M. C., Williams R. M., Like A. A. Genetic influence of the streptozotocin-induced insulitis and hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 1977 Oct;26(10):916–920. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.10.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossini A. A., Like A. A., Chick W. L., Appel M. C., Cahill G. F., Jr Studies of streptozotocin-induced insulitis and diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2485–2489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein P., Suciu-Foca N., Nicholson J. F. Genetics of juvenile diabetes mellitus. A recessive gene closely linked to HLA D and with 50 per cent penetrance. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 10;297(19):1036–1040. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711102971905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serra A. S., Farndon J. R., Shenton B. K., Johnston I. D. Passive transfer of lymphocytes from diabetic man to athymic mouse. Lancet. 1979 Jun 16;1(8129):1292–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin S. I., Baum S. G., Fleischer N., Rosen O. M. Retention of endocrine function by an insulin-secreting pancreatic islet cell tumour from Syrain hamster through serial transplantation in nude mice. J Cell Sci. 1975 Jul;18(2):199–206. doi: 10.1242/jcs.18.2.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurneyssen O., Jansen F. K., Vialettes B., Vague P., Selam J. L., Mirouze J. Passive transfer of lymphocytes from diabetic man to athymic mouse. Lancet. 1979 Jun 16;1(8129):1291–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. W., Austin M., Onodera T., Notkins A. L. Isolation of a virus from the pancreas of a child with diabetic ketoacidosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 May 24;300(21):1173–1179. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197905243002102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. W., Lesniak M. A., Fussganger R., Notkins A. L. Genetic differences in susceptibility of pancreatic beta cells to virus-induced diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1976 Nov 11;264(5582):178–180. doi: 10.1038/264178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


