Abstract
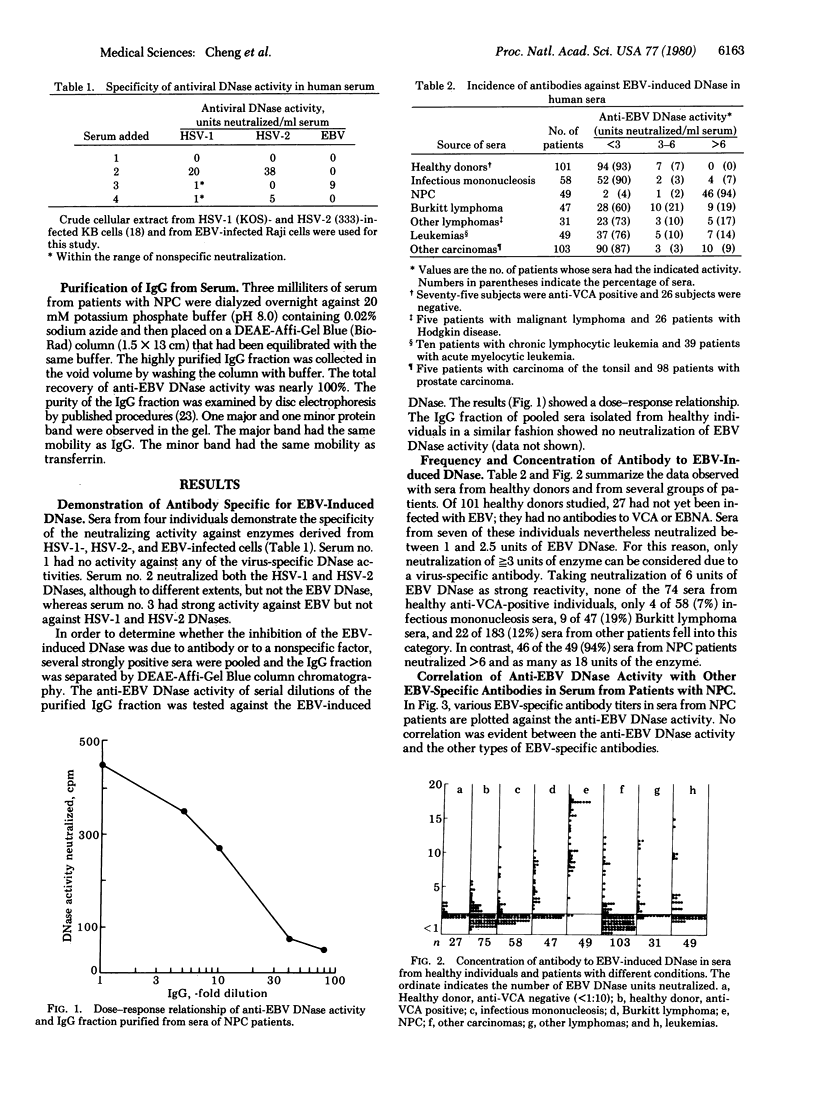
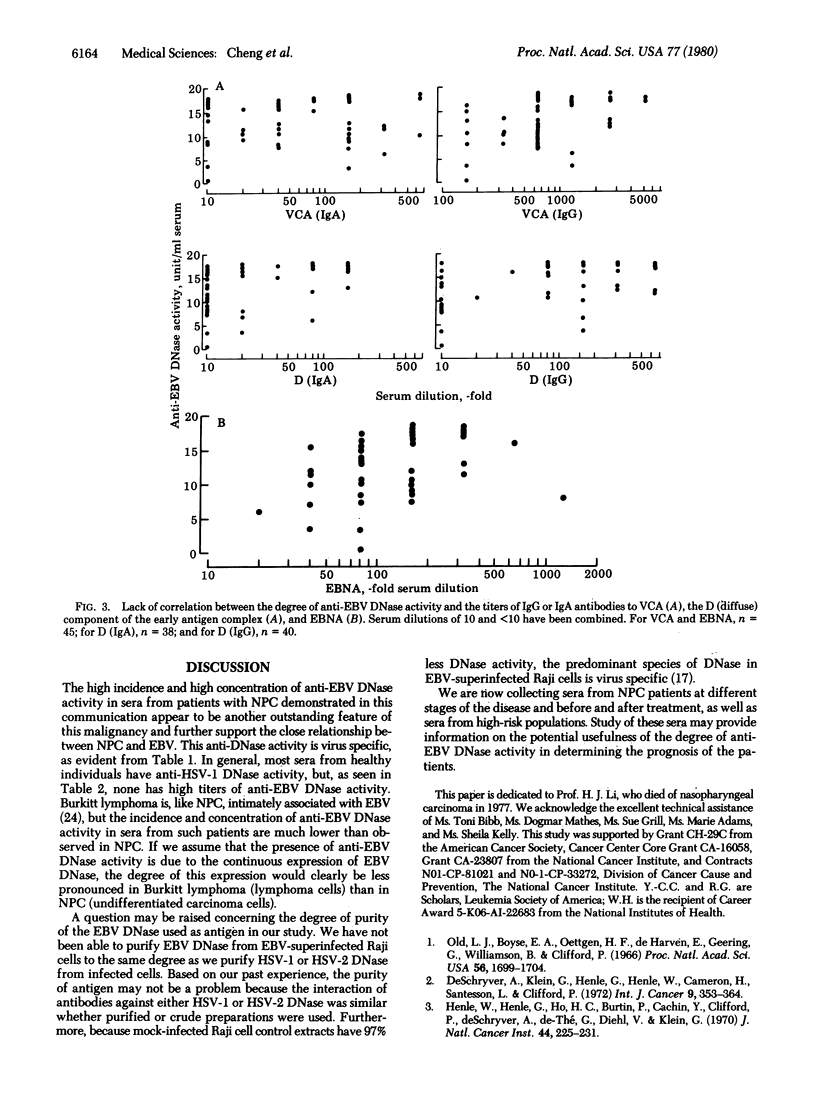
Sera from healthy individuals and patients with infectious mononucleosis, Burkitt lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, or other malignancies were examined for their capacity to neutralize Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-induced DNase activity. Sera were found that neutralized the EBV DNase but not herpes simplex virus type 1 or type 2 DNases, and vice versa. Sera from 46 of the 49 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma examined (94%) neutralized > 6 units of EBV DNase per ml of serum. In contrast, only 19% of 47 patients with Burkitt lymphoma, 12% of 183 patient with other malignancies, 4% of 58 patients with infectious mononucleosis, and none of 101 healthy individuals had such levels of neutralizing activity. The neutralizing factor was found in the IgG fraction derived from nasopharyngeal carcinoma sera. There was no correlation between the concentration of these antibodie and the titers of IgG ad IgA antibodies to the EBV capsid antigen, the early antigen complex, or the EBV-associated nuclear antigen.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson-Anvret M., Forsby N., Klein G., Henle W. Relationship between the Epstein-Barr virus and undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma: correlated nucleic acid hybridization and histopathological examination. Int J Cancer. 1977 Oct 15;20(4):486–494. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caradonna S. J., Cheng Y. C. Uracil DNA-glycosylase. Purification and properties of this enzyme isolated from blast cells of acute myelocytic leukemia patients. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2293–2300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Chen J. Y., Hoffmann P. J., Glaser R. Studies on the activity of DNase associated with the replication of the Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):334–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90524-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Schryver A., Klein G., Henle G., Henle W., Cameron H. M., Santesson L., Clifford P. EB-virus associated serology in malignant disease: antibody levels to viral capsid antigens (VCA), membrane antigens (MA) and early antigens(EA) in patients with various neoplastic conditions. Int J Cancer. 1972 Mar 15;9(2):353–364. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910090214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R., Nonoyama M., Szymanowski R. T., Graham W. Human nasopharyngeal carcinomas positive for Epstein-Barr virus DNA in North America. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Jun;64(6):1317–1319. doi: 10.1093/jnci/64.6.1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgA serum antibodies as an outstanding feature of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W., Klein G. Demonstration of two distinct components in the early antigen complex of Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells. Int J Cancer. 1971 Sep 15;8(2):272–282. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910080212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Guerra A., Henle G. False negative and prozone reactions in tests for antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen. Int J Cancer. 1974 Jun 15;13(6):751–754. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G. E., Horwitz C. A. Epstein-Barr virus specific diagnostic tests in infectious mononucleosis. Hum Pathol. 1974 Sep;5(5):551–565. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(74)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Ho H. C., Burtin P., Cachin Y., Clifford P., de Schryver A., de-Thé G., Diehl V., Klein G. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, other head and neck neoplasms, and control groups. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Jan;44(1):225–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Ho H. C., Henle G., Kwan H. C. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-related antigens in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Comparison of active cases with long-term survivors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Aug;51(2):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Ho J. H., Henle G., Chau J. C., Kwan H. C. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: significance of changes in Epstein-Barr virus-related antibody patterns following therapy. Int J Cancer. 1977 Nov 15;20(5):663–672. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang D. P., Ho H. C., Henle W., Henle G., Saw D., Lui M. Presence of EBNA in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and control patient tissues related to EBV serology. Int J Cancer. 1978 Sep 15;22(3):266–274. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang D. P., Ho J. H., Henle W., Henle G. Demonstration of Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells from fresh biopsies. Int J Cancer. 1974 Nov 15;14(5):580–588. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910140504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B. C., Lindahl T., Fialkow P. J., Singh S., Stehlin J. S. Direct evidence for the presence of Epstein-Barr virus DNA and nuclear antigen in malignant epithelial cells from patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of the nasopharynx. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4737–4741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Huang C. H., Pagano J. S., Klein G., Singh S. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus detected in tissue of Burkitt's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3265–3268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J., Boyse E. A., Oettgen H. F., Harven E. D., Geering G., Williamson B., Clifford P. Precipitating antibody in human serum to an antigen present in cultured burkitt's lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1699–1704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., zur Hausen H., Becker V. EB viral genomes in epithelial nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 22;244(138):245–247. doi: 10.1038/newbio244245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de-Thé G., Ho J. H., Ablashi D. V., Day N. E., Macario A. J., Martin-Berthelon M. C., Pearson G., Sohier R. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. IX. Antibodies to EBNA and correlation with response to other ebv antigens in chinese patients. Int J Cancer. 1975 Nov 15;16(5):713–721. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Schulte-Holthausen H., Klein G., Henle W., Henle G., Clifford P., Santesson L. EBV DNA in biopsies of Burkitt tumours and anaplastic carcinomas of the nasopharynx. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1056–1058. doi: 10.1038/2281056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


