Abstract
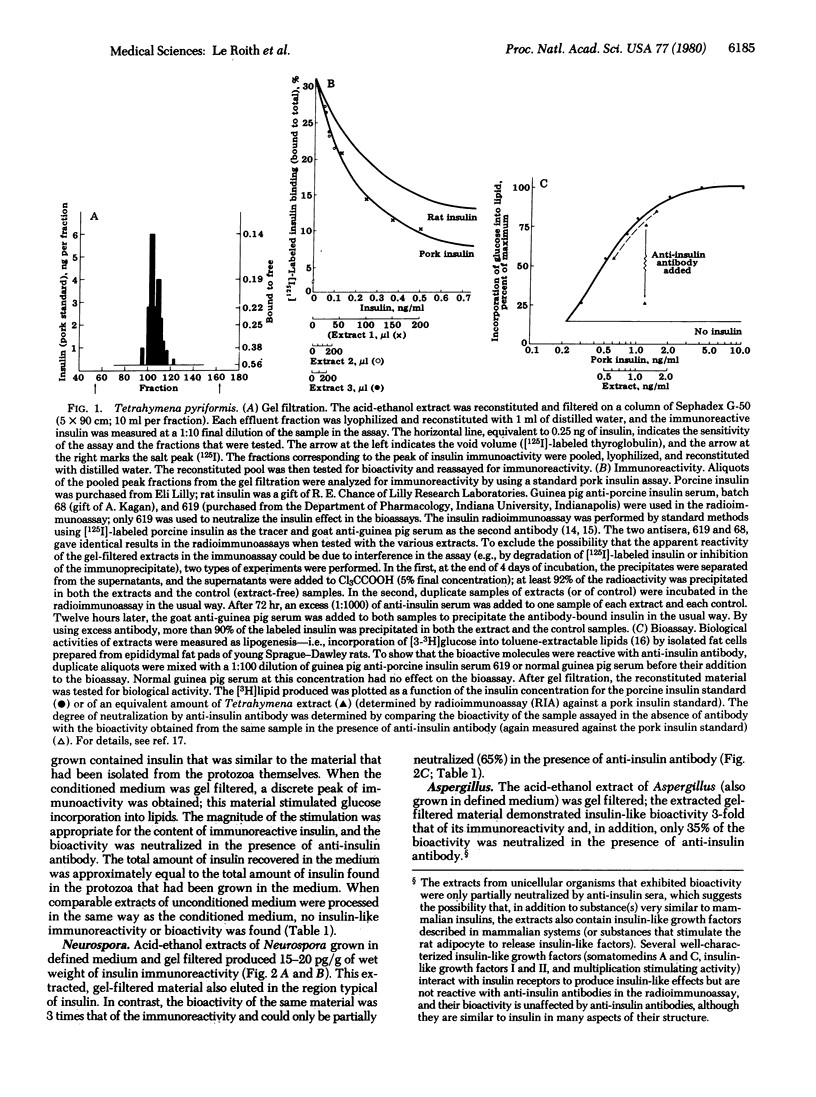
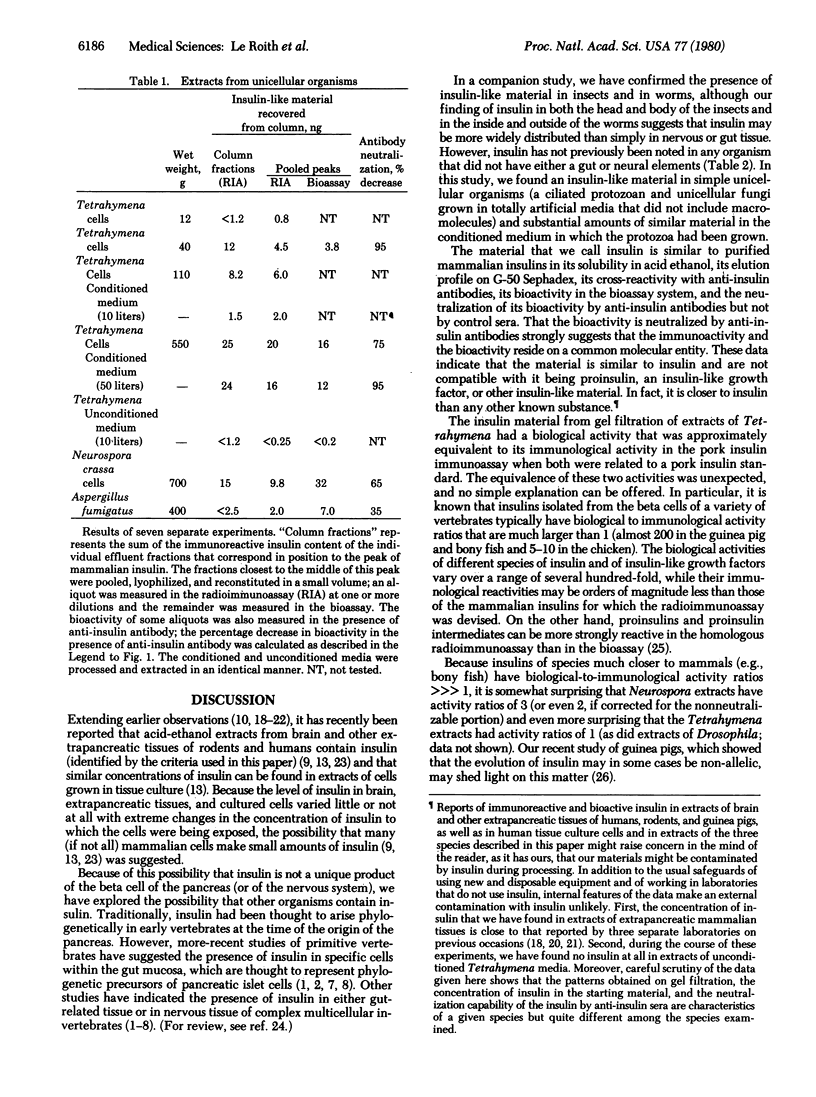
Tetrahymena pyriformis, Neurospora crassa, and Aspergillus fumigatus that had been grown in simple defined media were extracted with acid ethanol by a classic method for recovering insulin from pancreas. After filtration of the extracts on Sephadex G-50, distinct peaks of insulin immunoreactivity were recovered in the region typical of insulin. The gel-filtered material from the Tetrahymena had reactivity in the pork insulin radioimmunoassay about equal to its reactivity in the insulin bioassay (stimulation of lipogenesis in isolated rat adipocytes), and the gel-filtered material from neurospora had an immunoreactivity-to-bioactivity ratio of about 1:3. The material that stimulated lipogenesis could be neturalized by anti-insulin sera (i.e., 75-95% of the Tetrahymena material and 60% of the Neurospora material). Bioactive and immunoactive insulin was found in the conditioned medium equal in amount to that in the cells. The findings suggest that insulin did not arise evolutionarily in the intestinal or neural tissues of primitive vertebrates or complex invertebrates but rather has its molecular origins at least as far back as the simplest unicellular eukaryotes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner J. T. Aggregation and differentiation in the cellular slime molds. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:75–92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csaba G., Lantos T. Effect of insulin on the glucose uptake of protozoa. Experientia. 1975 Sep 15;31(9):1097–1098. doi: 10.1007/BF02326980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csaba G., Sudár F., Nagy S. U., Dobozy O. Localization of hormone receptors in Tetrahymena. Protoplasma. 1977;91(2):179–189. doi: 10.1007/BF01276732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. K., Falkmer S., Mehrotra B. K., Wilson S. Insulin assays and light microscopical studies of digestive organs in protostomian and deuterostomian species and in coelenterates. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1971 Oct;17(2):388–401. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(71)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duve H., Thorpe A., Lazarus N. R. Isolation of material displaying insulin-like immunological biological activity from the brain of the blowfly Calliphora vomitoria. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):221–227. doi: 10.1042/bj1840221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emdin S. O., Falkmer S. Phylogeny of insulin. Some evolutionary aspects of insulin production with particular regard to the biosynthesis of insulin in Myxine glutinosa. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1977;(270):15–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1977.tb15117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng J., Yalow R. S. Insulin recoverable from tissues. Diabetes. 1980 Feb;29(2):105–109. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch H. A., Van Noorden S., Pearse A. G. Cytochemical and immunofluorescence investigations of insulin-like producing cells in the intestine of Mytilus edulis L. (Bivalvia). Cell Tissue Res. 1976 Jan 27;165(3):365–369. doi: 10.1007/BF00222439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Kahn C. R., Gorden P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Radioreceptor assay of insulin: Comparison of plasma and pancreatic insulins and proinsulins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Sep;41(3):438–445. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-3-438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havrankova J., Roth J., Brownstein M. J. Concentrations of insulin and insulin receptors in the brain are independent of peripheral insulin levels. Studies of obese and streptozotocin-treated rodents. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):636–642. doi: 10.1172/JCI109504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havrankova J., Schmechel D., Roth J., Brownstein M. Identification of insulin in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5737–5741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Ljungdahl A., Lundberg J. M., Schultzberg M. Peptidergic neurones. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):515–521. doi: 10.1038/284515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janakidevi K., Dewey V. C., Kidder G. W. The biosynthesis of catecholamines in two genera of protozoa. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jun 10;241(11):2576–2578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D., Manoil C., Dworkin M. Myxobacteria: cell interactions, genetics, and development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:595–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legros F., Uytdenhoef P., Dumont I., Hanson B., Jeamart J., Massant B., Conard V. Specific binding of insulin to the unicellular alga Acetabularia mediterranea. Protoplasma. 1975;86(1-3):119–134. doi: 10.1007/BF01275626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibson L. Endocrinology evolution and evolutionary endocrinology. Perspect Biol Med. 1979 Autumn;23(1):25–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston V. W., Livingston A. M. Some cultural, immunological, and biochemical properties of Progenitor cryptocides. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jun;36(6):569–582. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1974.tb01602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruo T., Cohen H., Segal S. J., Koide S. S. Production of choriogonadotropin-like factor by a microorganism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneses P., De Los Angeles Ortíz M. A protein extract from Drosophila melanogaster with insulin-like activity. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1975 Jun 1;51(2):483–485. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(75)90398-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody A. J., Stan M. A., Stan M., Gliemann J. A simple free fat cell bioassay for insulin. Horm Metab Res. 1974 Jan;6(1):12–16. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plisetskaya E., Kazakov V. K., Soltitskaya L., Leibson L. G. Insulin-producing cells in the gut of freshwater bivalve molluscs Anodonta cygnea and Unio pictorum and the role of insulin in the regulation of their carbohydrate metabolism. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1978 Jun;35(2):133–145. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(78)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig J. L., Havrankova J., Lesniak M. A., Brownstein M., Roth J. Insulin is ubiquitous in extrapancreatic tissues of rats and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):572–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. S., Bhathena S. J., Nompleggi D., Penhos J. C., Recant L. Studies on persistent circulating immunoreactive glucagon (IRG) and immunoreactive insulin (IRI) found in eviscerated rats with a functional liver. Diabetologia. 1978 Mar;14(3):177–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00429778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Markese J., Kramer K. J., Speirs R. D., Childs C. N. Glucagon-like and insulin-like hormones of the insect neurosecretory system. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 15;156(3):515–520. doi: 10.1042/bj1560515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNGER R. H., LOCHNERJDE V., EISENTRAUT A. M. IDENTIFICATION OF INSULIN AND GLUGACON IN A BRONCHOGENIC METASTASIS. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Sep;24:823–831. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-9-823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uvnäs B., Uvnäs-Wallensten K. "Insulinergic" nerves to the skeletal muscles of the cat? Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Jul;103(3):346–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto Y., Wolfsen A. R., Odell W. D. Human chorionic gonadotropin-like substance in nonendocrine tissues of normal subjects. Science. 1977 Aug 5;197(4303):575–577. doi: 10.1126/science.195341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



