Abstract
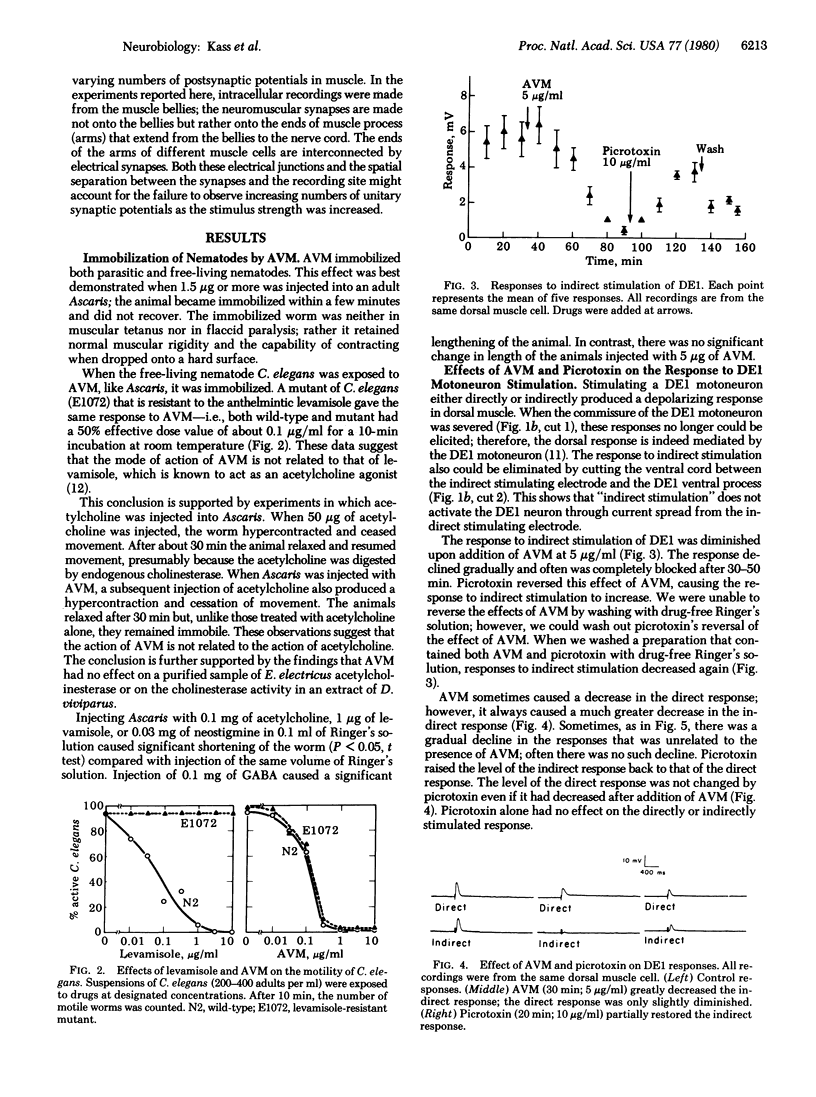
Avermectin B1a (AVM) is an antiparasitic agent that paralyzes nematodes without causing hypercontraction or flaccid paralysis. Using selective stimulation techniques, we have shown that AVM blocks transmission between interneuron(s) and excitatory motorneurons in the ventral nerve cord of Ascaris. It also inhibits transmissin between inhibitory motoneurons and muscle but has little effect on excitatory neuromuscular transmission. Picrotoxin can reverse the AVM-induced block of interneuron-excitatory motoneuron transmission but has no effect on the inhibitory motoneuronal synapse in either the presence or absence of AVM. Our results provide an explanation of how AVM may cause paralysis of nematodes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg R. W., Miller B. M., Baker E. E., Birnbaum J., Currie S. A., Hartman R., Kong Y. L., Monaghan R. L., Olson G., Putter I. Avermectins, new family of potent anthelmintic agents: producing organism and fermentation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):361–367. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Castillo J., De Mello W. C., Morales T. Inhibitory action of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on Ascaris muscle. Experientia. 1964 Mar 15;20(3):141–143. doi: 10.1007/BF02150701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egerton J. R., Ostlind D. A., Blair L. S., Eary C. H., Suhayda D., Cifelli S., Riek R. F., Campbell W. C. Avermectins, new family of potent anthelmintic agents: efficacy of the B1a component. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):372–378. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre P. Some pharmacodynamic effects of the nematocides: methyridine, tetramisole and pyrantel. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;22(1):26–36. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1970.tb08380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz L. C., Wang C. C., Gorio A. Avermectin B1a irreversibly blocks postsynaptic potentials at the lobster neuromuscular junction by reducing muscle membrane resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2062–2066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. W., Chaiet L., Cole D. J., Cole L. J., Flor J. E., Goegelman R. T., Gullo V. P., Joshua H., Kempf A. J., Krellwitz W. R. Avermectins, new family of potent anthelmintic agents: isolation and chromatographic properties. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):368–371. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostlind D. A., Cifelli S., Lang R. Insecticidal activity of the anti-parasitic avermectins. Vet Rec. 1979 Aug 25;105(8):168–168. doi: 10.1136/vr.105.8.168-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pong S. S., Wang C. C., Fritz L. C. Studies on the mechanism of action of avermectin B1a: stimulation of release of gamma-aminobutyric acid from brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1980 Feb;34(2):351–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb06604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pong S. S., Wang C. C. The specificity of high affinity binding of avermectin B1a to mammalian brain. Neuropharmacology. 1980 Mar;19(3):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(80)90155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton A. O., Fishpool R. M., Southgate E., Donmoyer J. E., Walrond J. P., Moses J. E., Kass I. S. Structure and physiological activity of the motoneurons of the nematode Ascaris. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3493–3497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Brand T. The biochemistry of helminths. Z Parasitenkd. 1974;45(2):109–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00348531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



