Abstract
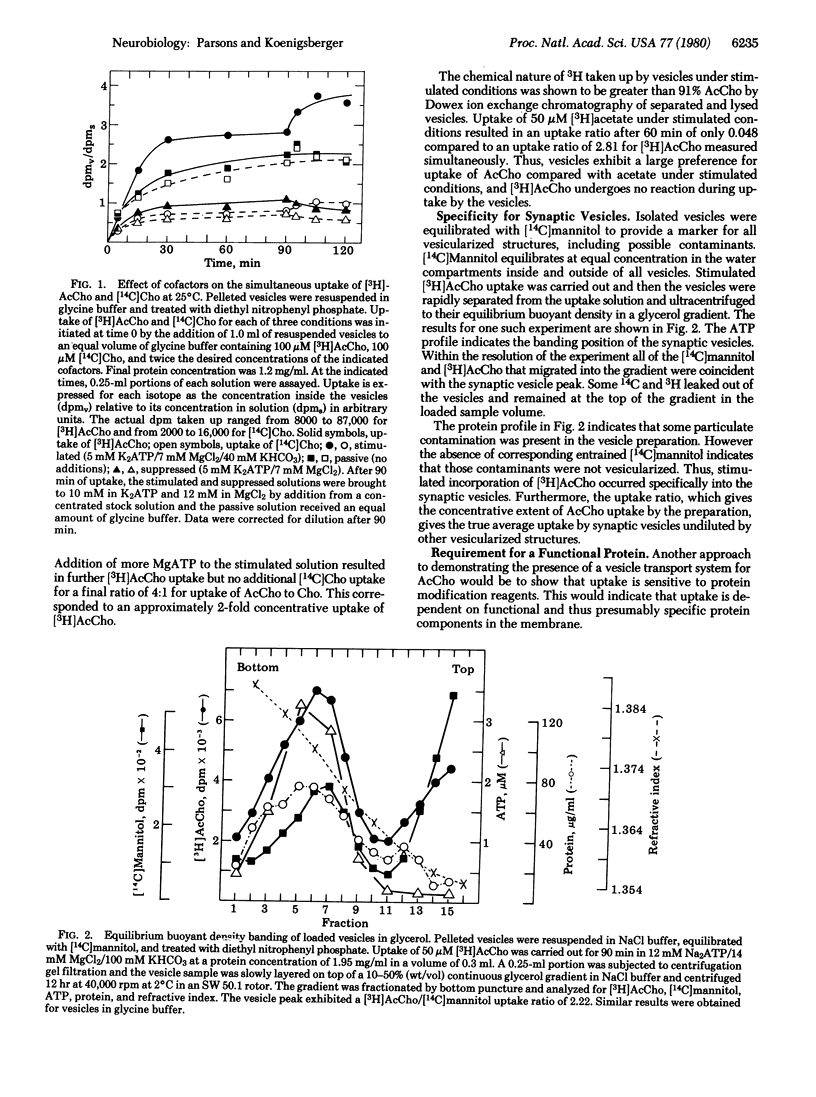
The specificity of acetylcholine uptake by synaptic vesicles isolated from the electric organ of Torpedo californica was studied. In the absence of cofactors, [3H]acetylcholine was taken up identically to[14C]choline in the same solution (passive uptake), and the equilibrium concentration achieved inside the vesicles was equal to the concentration outside. In the presence of MgATP, [3H]acetylcholine and [14C]choline in the same solution were taken up identically, except only about half as much of each was taken up (suppressed uptake). [3H]Acetylcholine uptake was stimulated by MgATP and HCO3- about 4-fold relative to suppressed uptake, for a net concentrative uptake of about 2:1 (stimulated uptake). Uptake of [14C]choline in the same solution remained at the suppressed level. [3H]Acetylcholine taken up under stimulated conditions migrated with vesicles containing [14C]mannitol on analytical glycerol density gradients during centrifugation. Vesicle were treated with nine protein modification reagents under mild conditions. Two reagents had no effect on, dithiothreitol potentiated, and six reagents strongly inhibited subsequent stimulated uptake of [3H]acetylcholine. The results indicate that uptake of acetylcholine is conditionally specific for the transported substrate, is carried out by the synaptic vesicles rather than a contaminant of the preparation, and requires a functional protein system containing a critical sulfhydryl group.
Full text
PDF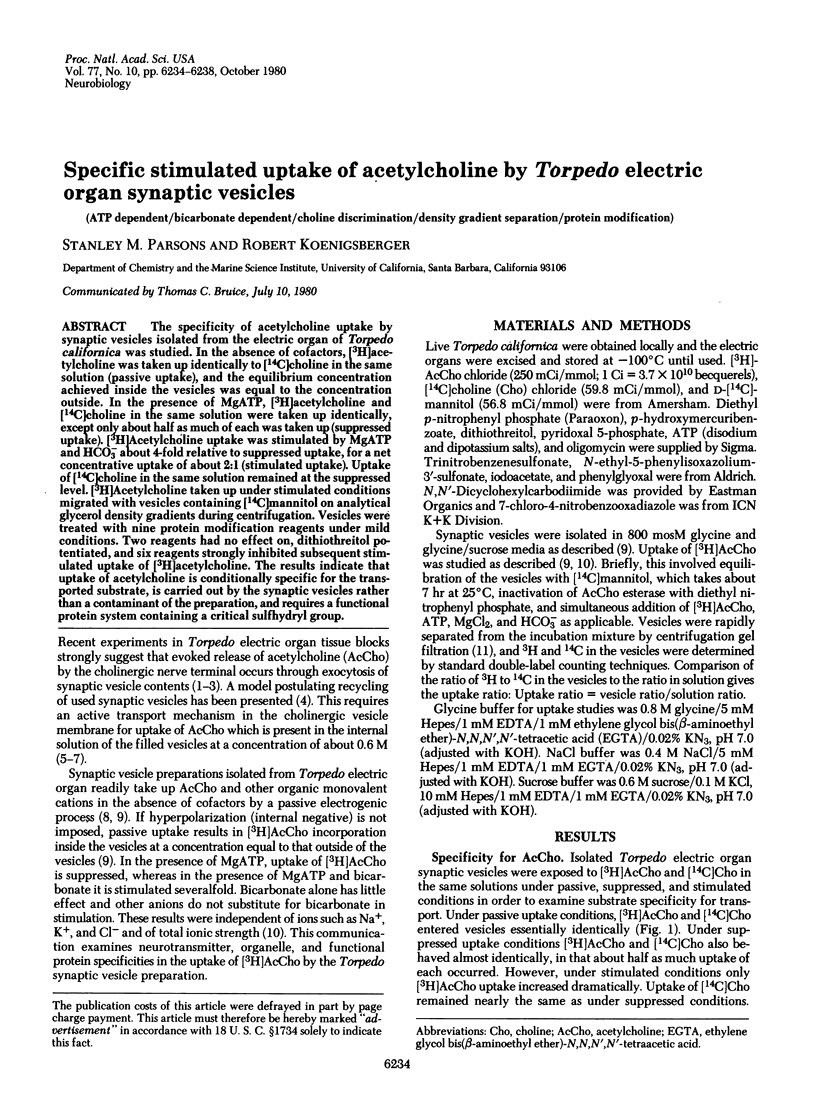



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breer H., Morris S. J., Whittaker V. P. Adenosine triphosphatase activity associated with purified cholinergic synaptic vesicles of Torpedo marmorata. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):313–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter R. S., Parsons S. M. Electrogenic behavior of synaptic vesicles from Torpedo californica. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):326–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson G. E., Shimada M., Blass J. P. Alterations in acetylcholine synthesis and cyclic nucleotides in mild cerebral hypoxia. J Neurochem. 1978 Oct;31(4):757–760. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb00107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halaris A. E., DeMet E. M. Active uptake of [3H]5-HT by synaptic vesicles from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1978 Sep;31(3):591–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenigsberger R., Parsons S. M. Bicarbonate and magnesium ion-ATP dependent stimulation of acetylcholine uptake by Torpedo electric organ synaptic vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):305–312. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80221-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Murrin L. C. Sodium-dependent, high affinity choline uptake. J Neurochem. 1978 Jan;30(1):15–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luqmani Y. A., Sudlow G., Whittaker V. P. Homocholine and acetylhomocholine: false transmitters in the cholinergic electromotor system of Torpedo. Neuroscience. 1980;5(1):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. W., Florini J. R. A rapid method for desalting small volumes of solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Sep;55(1):328–330. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa K., Dowe G. H., Morris S. J., Whittaker V. P. The lipid and protein content of cholinergic synaptic vesicles from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata purified to constant composition: implications for vesicle structure. Brain Res. 1979 Feb 9;161(3):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90674-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilar G., Vaca K. Regulation of acetylcholine synthesis in cholinergic nerve terminals. Prog Brain Res. 1979;49:97–106. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64625-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Pazoles C. J., Creutz C. E., Zinder O. The chromaffin granule and possible mechanisms of exocytosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;58:159–197. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61475-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebois R. V., Reynolds E. E., Toll L., Howard B. D. Storage of dopamine and acetylcholine in granules of PC12, a clonal pheochromocytoma cell line. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1240–1248. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothlein J. E., Parsons S. M. Specificity of association of a Ca2+/Mg2+ ATPase with cholinergic synaptic vesicles from Torpedo electric organ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jun 13;88(3):1069–1076. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91517-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suszkiw J. B., Zimmermann H., Whittaker V. P. Vesicular storage and release of acetylcholine in Torpedo electroplaque synapses. J Neurochem. 1978 Jun;30(6):1269–1280. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb10455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro T., Stadler H. Chemical composition of cholinergic synaptic vesicles from Torpedo marmorata based on improved purification. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct 16;90(3):479–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toll L., Gundersen C. B., Jr, Howard B. D. Energy utilization in the uptake of catecholamines by synaptic vesicles and adrenal chromaffin granules. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 4;136(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. A., Carlson S. S., Kelly R. B. Chemical and physical characterization of cholinergic synaptic vesicles. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1199–1206. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman H., Denston C. R. Recycling of synaptic vesicles in the cholinergic synapses of the Torpedo electric organ during induced transmitter release. Neuroscience. 1977;2(5):695–714. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann H., Denston C. R. Separation of synaptic vesicles of different functional states from the cholinergic synapses of the Torpedo electric organ. Neuroscience. 1977;2(5):715–730. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


