Abstract
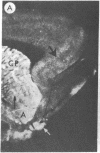
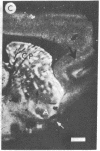
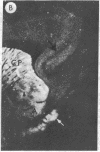
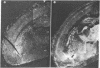
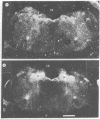
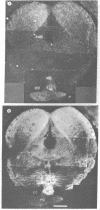
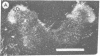
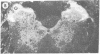
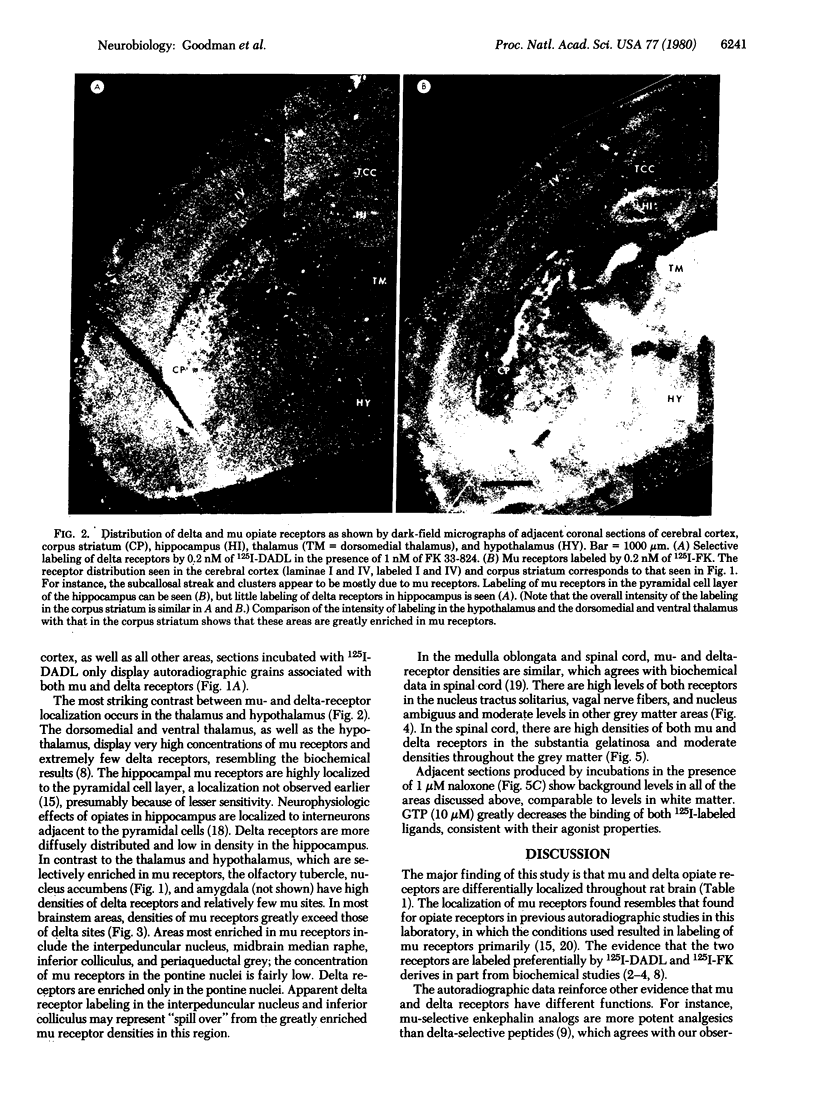
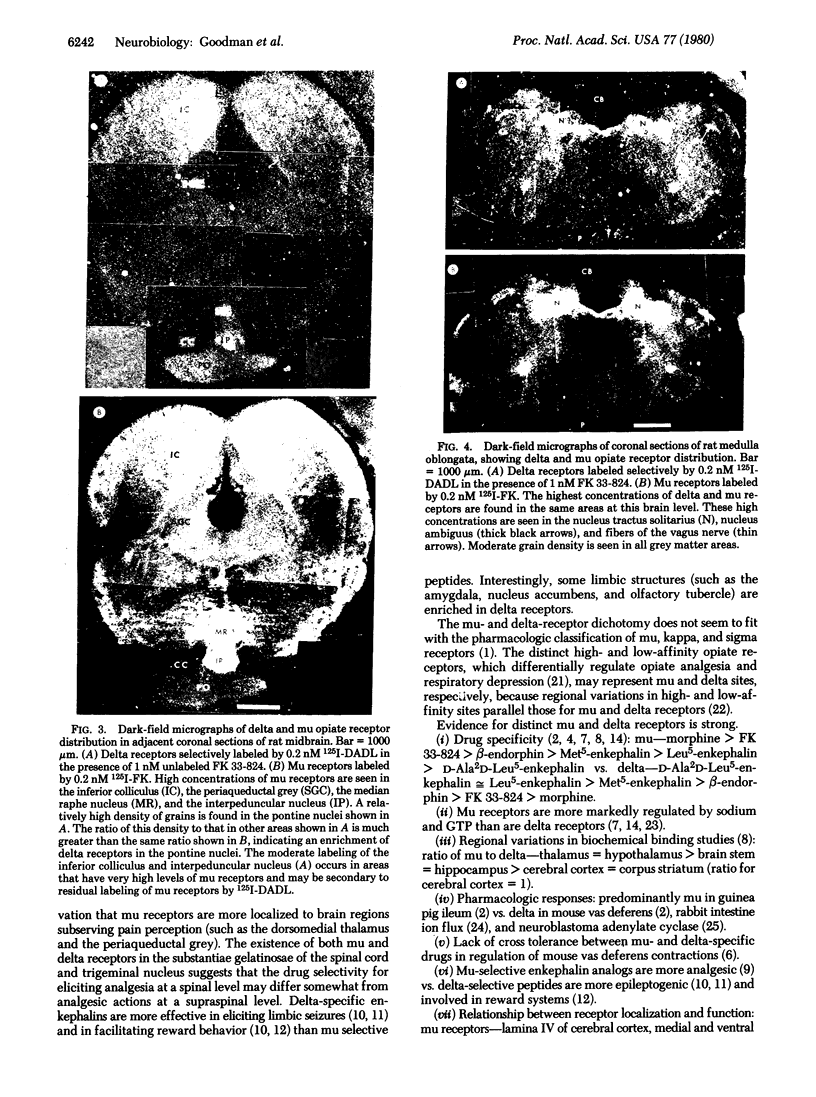
We have observed two discrete populations of opiate receptors that are differently localized in rat brain. Morphine-like (mu) receptors, labeled by 125I-labeled [D-Ala-2MePhe4Met(O)5-ol]enkephalin, are concentrated selectively in lamina IV of the cerebral cortex, certain thalamic nuclei, and the periaqueductal grey, while delta receptors, labeled by 125I-labeled [D-Ala2-D-Leu5]enkephalin, are more diffused, having high densities in cerebral cortex, corpus striatum, amygdala, and olfactory tubercle. Because of similarities in their localizations, we propose that mu and delta receptors are respectively the physiologic receptors for [Met]- and [Leu]enkephalin neurons. These distributions reflect the different physiological functions attributed to mu and delta receptors and thus represent discrete functions of [Met]- and [Leu]enkephalin neurons.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. III. The telencephalon. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 14;134(3):393–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90817-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Cooper B. R., Hazum E., Cuatrecasas P. Multiple opiate receptors: different regional distribution in the brain and differential binding of opiates and opioid peptides. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;16(1):91–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Multiple opiate receptors. Enkephalins and morphine bind to receptors of different specificity. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2610–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers S. R., Creese I., Snowman A. M., Synder S. H. Opiate receptor binding affected differentially by opiates and opioid peptides. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Apr 1;55(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90142-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields H. L., Emson P. C., Leigh B. K., Gilbert R. F., Iversen L. L. Multiple opiate receptor sites on primary afferent fibres. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):351–353. doi: 10.1038/284351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenk H., Urca G., Liebeskind J. C. Epileptic properties of leucine- and methionine-enkephalin: comparison with morphine and reversibility by naloxone. Brain Res. 1978 May 26;147(2):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90843-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz A., Bläsig J., Emrich H. M., Cording C., Pirée S., Kölling A., von Zerssen D. Is there some indication from behavioral effects of endorphins for their involvement in psychiatric disorders? Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1978;18:333–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachur J. F., Miller R. J., Field M. Control of guinea pig intestinal electrolyte secretion by a delta-opiate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2753–2756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee W. A., Nirenberg M. Mode of action of endogenous opiate peptides. Nature. 1976 Oct 14;263(5578):609–612. doi: 10.1038/263609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Childers S., Snyder S. H. Met- and Leu-enkephalin immunoreactivity in separate neurones. Nature. 1979 Nov 22;282(5737):407–410. doi: 10.1038/282407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Eades C. G., Thompson J. A., Huppler R. E., Gilbert P. E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):517–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J., Chang K. J., Leighton J., Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of iodinated enkephalin analogues with opiate receptors. Life Sci. 1978 Feb;22(5):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90284-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Childers S. R., Snyder S. H. Opiate analgesia: evidence for mediation by a subpopulation of opiate receptors. Science. 1980 May 2;208(4443):514–516. doi: 10.1126/science.6245448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson L. E., Kosterlitz H. W. Specific protection of the binding sites of D-Ala2-D-Leu5-enkephalin (delta-receptors) and dihydromorphine (mu-receptors). Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Aug 31;205(1160):425–432. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R., Wüster M., Krenss H., Herz A. Selective development of tolerance without dependence in multiple opiate receptors of mouse vas deferens. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):242–243. doi: 10.1038/285242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Childers S. R., Snyder S. H. The opiate receptor binding interactions of 3H-methionine enkephalin, an opioid peptide. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Feb 1;47(3):319–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Goodman R. R. Multiple neurotransmitter receptors. J Neurochem. 1980 Jul;35(1):5–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb12483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein L., Belluzzi J. D. Brain endorphins: possible role in reward and memory formation. Fed Proc. 1979 Oct;38(11):2468–2472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenius L. Opioid peptides and opiates differ in receptor selectivity. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1977;2(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0306-4530(77)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urca G., Frenk H., Liebeskind J. C., Taylor A. N. Morphine and enkephalin: analgesic and epileptic properties. Science. 1977 Jul 1;197(4298):83–86. doi: 10.1126/science.867056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. A new method for receptor autoradiography: [3H]opioid receptors in rat brain. Brain Res. 1979 Dec 28;179(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90442-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieglgänsberger W., French E. D., Siggins G. R., Bloom F. E. Opioid peptides may excite hippocampal pyramidal neurons by inhibiting adjacent inhibitory interneurons. Science. 1979 Jul 27;205(4404):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.451610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]