Abstract
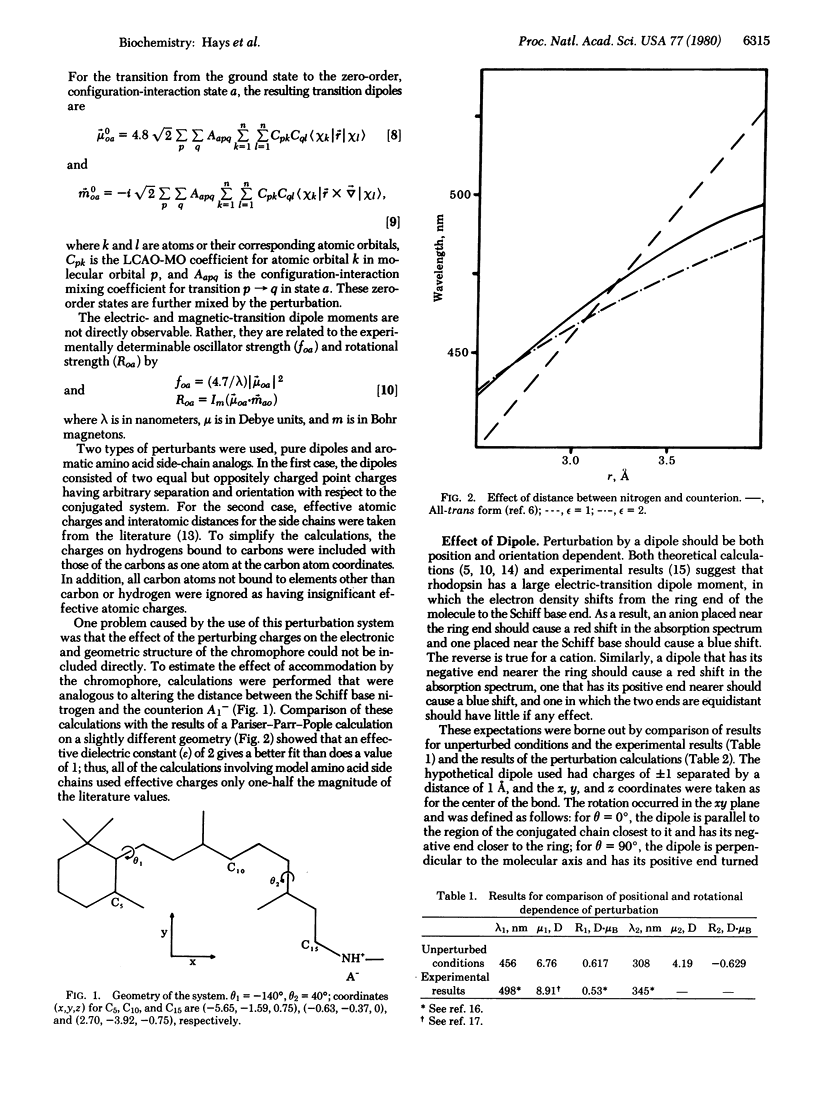
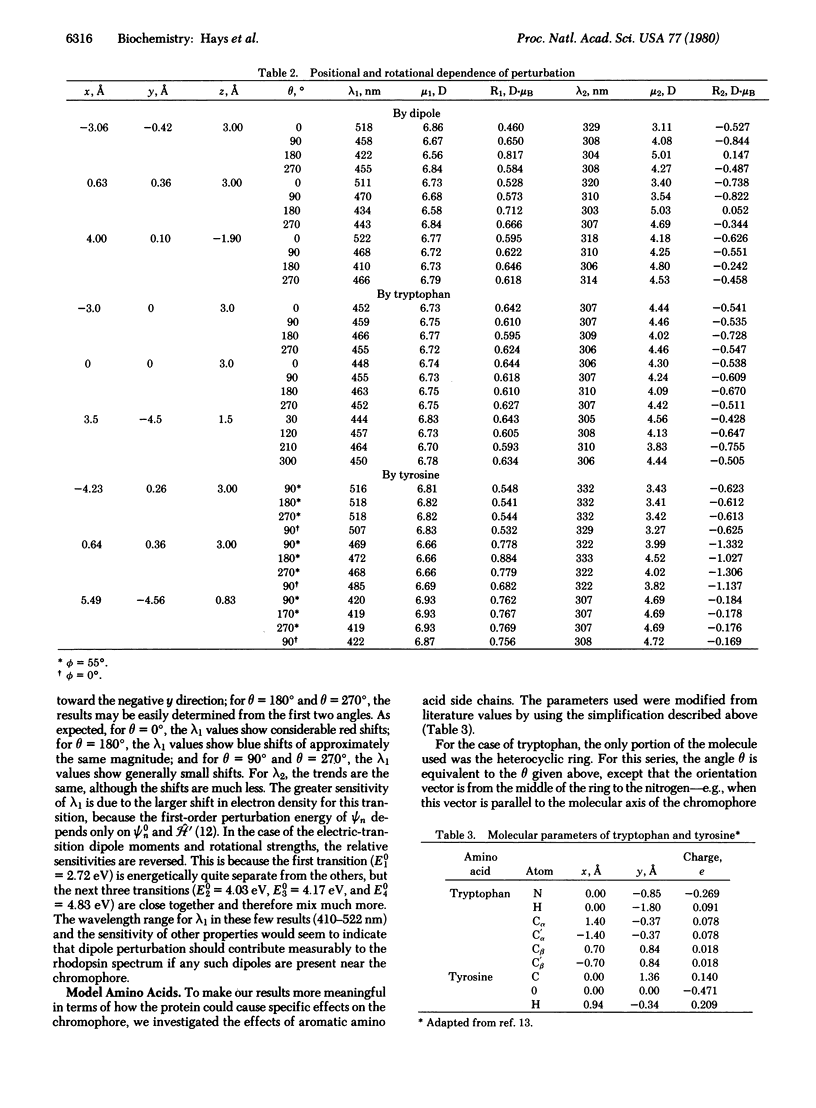
The effects of dipoles and aromatic amino acid side-chain models on the absorption and optical activity of the rhodopsin chromophore were calculated by using perturbation theory, and the results were compared with those of a Pariser-Parr-Pople calculation for the unperturbed system. The interaction was assumed to result from purely electrostatic interactions. It was concluded that the side chains of phenylalanine and tryptophan should have no important effects. However, the charge separation in tyrosine is sufficient to cause substantial electrostatic perturbation; in fact, the effect of tyrosine is large enough to approximately many of the spectral properties of rhodopsin quantitatively. This is encouraging because the use of aromatic amino acid side-chain analogs probably provides a better physical model than the use of isolated full charges, except in the case of the counterion to the protonated Schiff base.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Callender R. H., Doukas A., Crouch R., Nakanishi K. Molecular flow resonance Raman effect from retinal and rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1621–1629. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DELRE G., PULLMAN B., YONEZAWA T. ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF THE ALPHA-AMINO ACIDS OF PROTEINS. I. CHARGE DISTRIBUTIONS AND PROTON CHEMICAL SHIFTS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 24;75:153–182. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90595-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dartnall H. J., Lythgoe J. N. The spectral clustering of visual pigments. Vision Res. 1965 Apr;5(3):81–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(65)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. O., Blatz P. E. N-retinylidene-1-amino-2-propanol: a Schiff base analog for rhodopsin. Vision Res. 1968 Oct;8(10):1367–1375. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(68)90056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirtenstein M. D., Akhtar M. A convenient synthesis of labelled rhodopsin and studies on its active site. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(3):359–366. doi: 10.1042/bj1190359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Greenberg A. D., Dinur U., Ebrey T. G. Visual-pigment spectra: implications of the protonation of the retinal Schiff base. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4593–4599. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irreverre F., Stone A. L., Shichi H., Lewis M. S. Biochemistry of visual pigments. I. Purification and properties of bovine rhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):529–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KROPF A., HUBBARD R. The mechanism of bleaching rhodopsin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Nov 12;74(2):266–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb39550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliger D. S., Milder S. J., Dratz E. A. Solvent effects on the spectra of retinal Schiff bases--I. models for the bathochromic shift of the chromophore spectrum in visual pigments. Photochem Photobiol. 1977 Mar;25(3):277–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1977.tb06911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON R. A., PITT G. A. Studies on rhodopsin. IX. pH and the hydrolysis of indicator yellow. Biochem J. 1955 Jan;59(1):128–134. doi: 10.1042/bj0590128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. C. Energetics of permeation of thin lipid membranes by ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 5;448(2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathies R., Stryer L. Retinal has a highly dipolar vertically excited singlet state: implications for vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2169–2173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oseroff A. R., Callender R. H. Resonance Raman spectroscopy of rhodopsin in retinal disk membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 24;13(20):4243–4248. doi: 10.1021/bi00717a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner A. S., Stryer L. Induced optical activity of the metarhodopsins. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 17;10(17):3250–3254. doi: 10.1021/bi00793a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waleh A., Ingraham L. L. A molecular orbital study of the protein-controlled bathochromic shift in a model of rhodopsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 May;156(1):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshel A. Charge stabilization mechanism in the visual and purple membrane pigments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2558–2562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenfeld J. R., Abrahamson E. W. Visual pigments: their spectra and isomerizations. Photochem Photobiol. 1968 Nov;8(5):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1968.tb05892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



