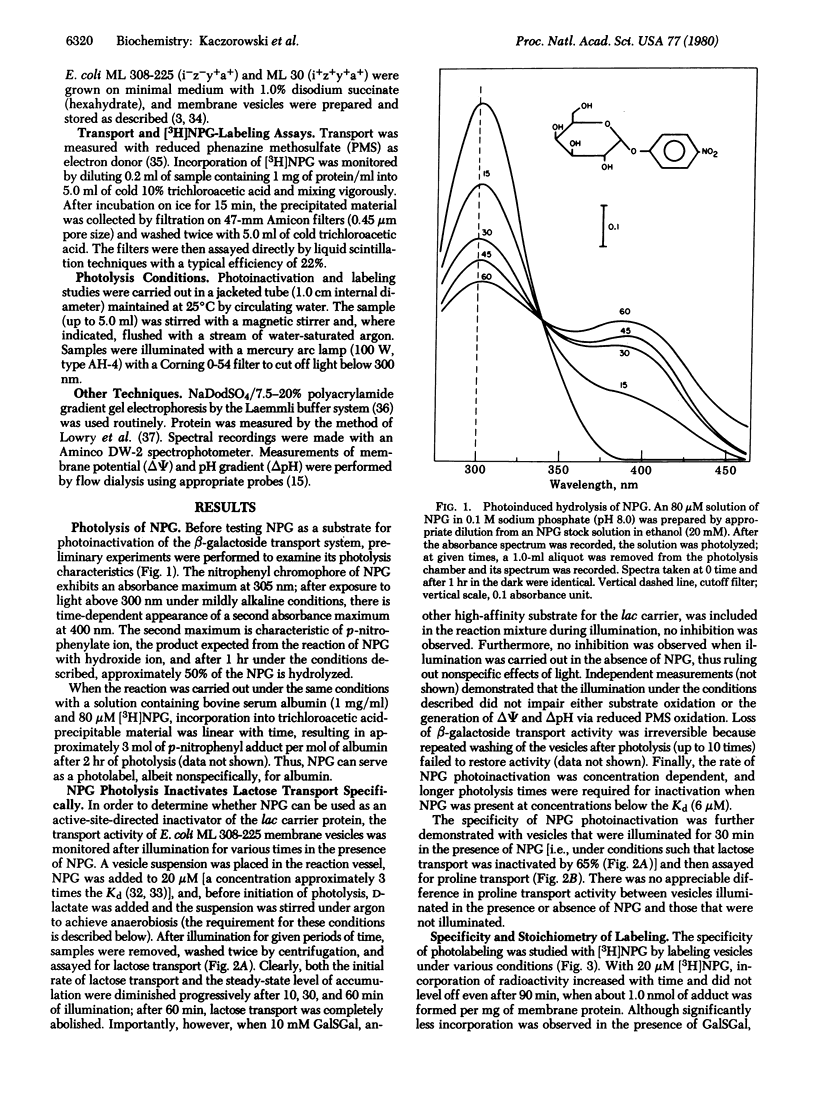
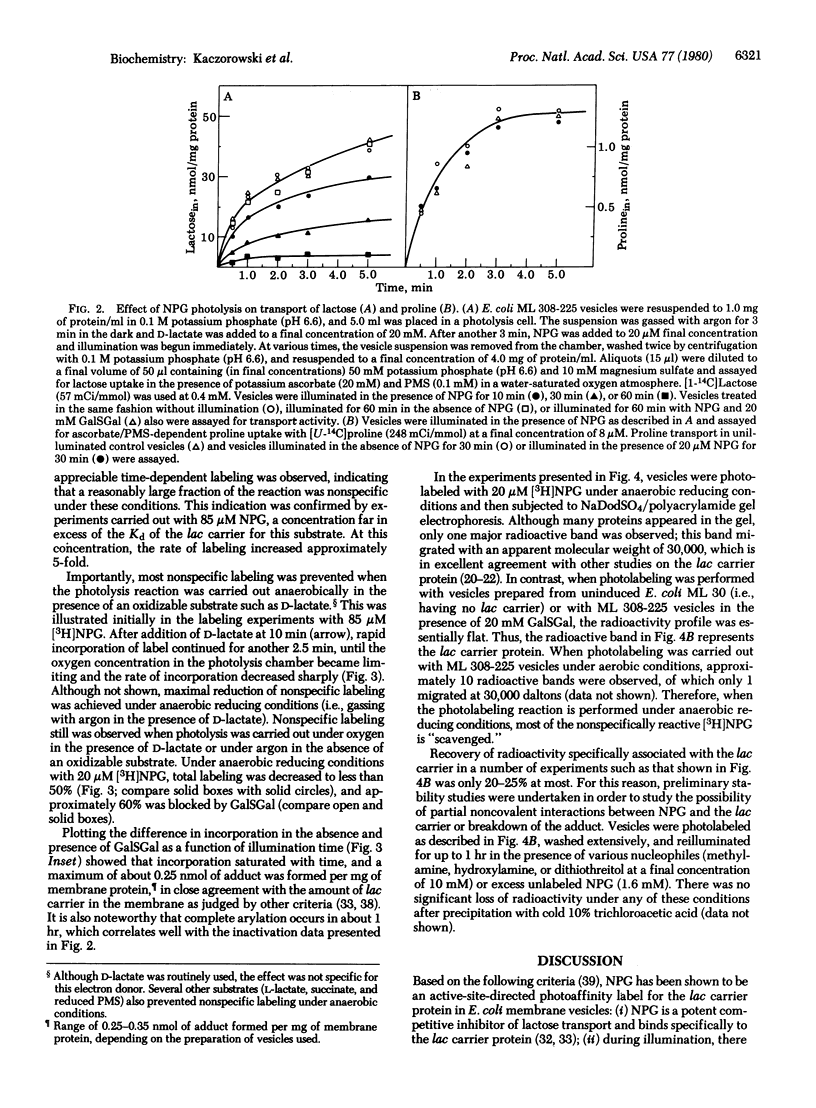
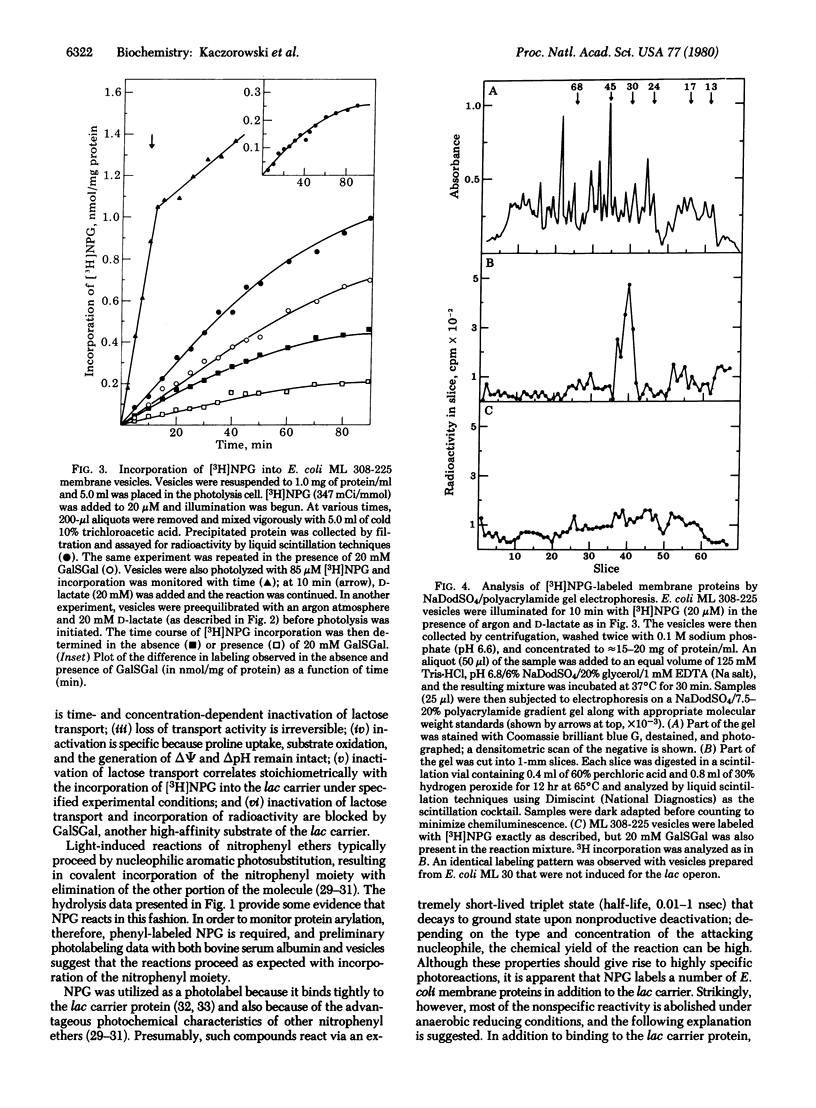
Abstract
4-Nitrophenyl-alpha-D-galactopyranoside (NPG) was used as a photoaffinity reagent to specifically inactivate the beta-galactoside transport system in Escherichia coli ML 308-225 membrane vesicles. Photolysis of NPG produced time-dependent, irreversible loss of transport activity with corresponding incorporation of [3H]NPG into the membrane. Both processes were blocked by beta-D-galactopyranosyl 1-thio-beta-D-galactopyranoside, a high-affinity substrate of the lac carrier protein and inactivation of lactose transport was specific because NPG photolysis did not affect proline uptake or the ability of the vesicles to generate an electrochemical proton gradient. Arylation of the lac carrier protein was stoichiometric and resulted in the formation of 0.25 nmol of NPG adduct per mg of membrane protein. All attempts to regenerate transport activity by reillumination in the presence of externally added nucleophiles failed, indicating that arylation is functionally irreversible. When vesicles labeled with [3H]NPG under defined experimental conditions were solubilized and analyzed by gel electrophoresis, only one radioactive peak with an apparent molecular weight of 30,000 was observed, confirming that the reaction is highly specific. The results demonstrate that NPG is an active-site-directed photoaffinity label for the lac carrier protein.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. The biotin transport system. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:613–617. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhry V., Westheimer F. H. Photoaffinity labeling of biological systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:293–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Kennedy E. P. Specific labeling and partial purification of the M protein, a component of the beta-galactoside transport system of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):891–899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover G. I. Amino acid transport proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:607–613. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groman E. V., Schultz R. M., Engel L. L. Catalytic competence: a direct criterion for affinity labeling. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:54–58. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S. An ecf mutation in Escherichia coli pleiotropically affecting energy coupling in active transport but not generation or maintenance of membrane potential. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8582–8588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelenc P. C., Cantor C. R., Simon S. R. High yield photoreagents for protein crosslinking and affinity labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3564–3568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. H., Kennedy E. P. Characterization of the membrane protein component of the lactose transport system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5981–5987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Molecular biology and energetics of membrane transport. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Dec;89(4):575–593. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:698–709. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport studies in bacterial membrane vesicles. Science. 1974 Dec 6;186(4167):882–892. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4167.882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., Kaback H. R. Mechanism of lactose translocation in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. 1. Effect of pH on efflux, exchange, and counterflow. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3691–3697. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., Robertson D. E., Kaback H. R. Mechanism of lactose translocation in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. 2. Effect of imposed delata psi, delta pH, and Delta mu H+. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3697–3704. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy E. P., Rumley M. K., Armstrong J. B. Dierect measurement of the binding of labeled sugars to the lactose permease M protein. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Keilin's respiratory chain concept and its chemiosmotic consequences. Science. 1979 Dec 7;206(4423):1148–1159. doi: 10.1126/science.388618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins R. E., Langdon R. G. Maltosyl isothiocyanate: an affinity label for the glucose transporter of the human erythrocyte membrane. 1. Inhibition of glucose transport. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1199–1205. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Teather R. M., Simoni R. D., Aichele G., Wilhelm U. Lactose carrier protein of Escherichia coli. Transport and binding of 2'-(N-dansyl)aminoethyl beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside and p-nitrophenyl alpha-d-galactopyranoside. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):1–11. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Antigenic architecture of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1422–1426. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Immunochemical analysis of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1413–1422. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Molecular structure of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3148–3152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Patel L., Kaback H. R. Effect of diethylpyrocarbonate on lactose/proton symport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6221–6225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical proton gradient in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):848–854. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The relationship between the electrochemical proton gradient and active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):854–859. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. pH-dependent changes in proton:substrate stoichiometries during active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4270–4275. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical gradient of protons and its relationship to active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reenstra W. W., Patel L., Rottenberg H., Kaback H. R. Electrochemical proton gradient in inverted membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 8;19(1):1–9. doi: 10.1021/bi00542a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick G., Kaback H. R. Photoinactivation of the beta-galactoside transport system in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles with an impermeant azidophenylgalactoside. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6847–6851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick G., Kaback H. R., Weil R. Photoinactivation of the beta-galactoside transport system in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles with 2-nitro-4-azidophenyl-1-thio-beta-D-galactopyranoside. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1371–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick G., Schildiner S., Kaback H. R. Equilibrium between two forms of the lac carrier protein in energized and nonenergized membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5126–5131. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., Kaback H. R., Kohn L. D. Localization of D-lactate dehydrogenase in native and reconstituted Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4291–4296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Kaback H. R. Sodium-dependent methyl 1-thio-beta-D-galactopyranoside transport in membrane vesicles isolated from Salmonella typhimurium. Biochemistry. 1977 May 17;16(10):2130–2136. doi: 10.1021/bi00629a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarejo M. Evidence for two lac Y gene derived protein products in the E. coli membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 13;93(1):16–23. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80239-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


