Abstract
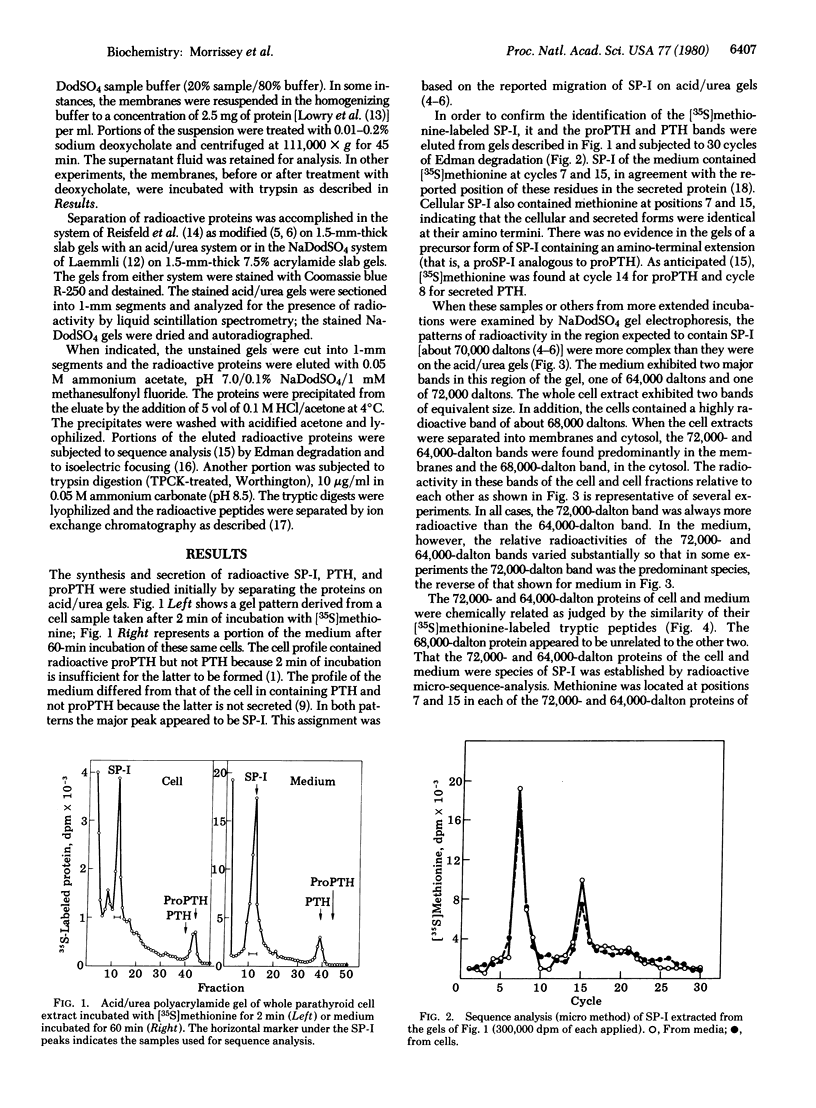
Examination of whole cell extracts and subcellular fractions of dispersed porcine parathyroid cells incubated with [35S]methionine indicates that two species of secretory protein-I, 72,000 and 64,000 daltons, respectively, are synthesized. Two secretory protein-I species of molecular weights equivalent to those in the cell but with slightly different isoelectric points were secreted; calcium suppressed the secretion of both of these. The secretory protein-I of cell and medium were shown to be related to each other and to previously identified secreted secretory protein-I by comparison of their 35S-labeled tryptic peptides and location of methionine in positions 7, 15, and 32 of the peptide chains. Both of the cellular species appeared to be enclosed within membranes similar to those containing parathyroid hormone and its immediate biosynthetic precursor because they were associated with the membrane fraction of the cell, were not digested when the membranes were exposed to trypsin, and were extracted from these membranes, as were parathyroid hormone and proparathyroid hormone, with dilute sodium deoxycholate. We did not find an amino-terminal precursor form of secretory protein-I in an incubation as short as 2 min with [35S]methionine, whereas [35S]proparathyroid hormone was readily detected, indicating that processing of secretory protein-I involves a direct conversion of the pre-protein to the secretory protein-I. Posttranslational glycosylation or deletion of carboxy-terminal region of the secretory protein-I species might account for the differences in molecular weights and isoelectric points of the cellular and secreted forms.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. M., Hurwitz S., Aurbach G. D. Preparation of viable isolated bovine parathyroid cells. Endocrinology. 1976 Dec;99(6):1582–1588. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-6-1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu L. K., Huang W. Y., Littledike E. T., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V. Porcine proparathyroid hormone. Identification, biosynthesis, and partial amino acid sequence. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 12;14(16):3631–3635. doi: 10.1021/bi00687a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. V., Hamilton J. W. Newer aspects of parathyroid chemistry and physiology. Cornell Vet. 1976 Jul;66(3):271–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F., Potts J. T., Jr Biosynthesis of parathyroid hormone (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Sep 21;299(12):635–644. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197809212991205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper B., Habener J. F., Rich A., Potts J. T., Jr Parathyroid secretion: discovery of a major calcium-dependent protein. Science. 1974 Apr 12;184(4133):167–169. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4133.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keutmann H. T., Aurbach G. D., Dawson B. F., Niall H. D., Deftos L. J., Potts J. T., Jr Isolation and characterization of the bovine parathyroid isohormones. Biochemistry. 1971 Jul 6;10(14):2779–2787. doi: 10.1021/bi00790a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
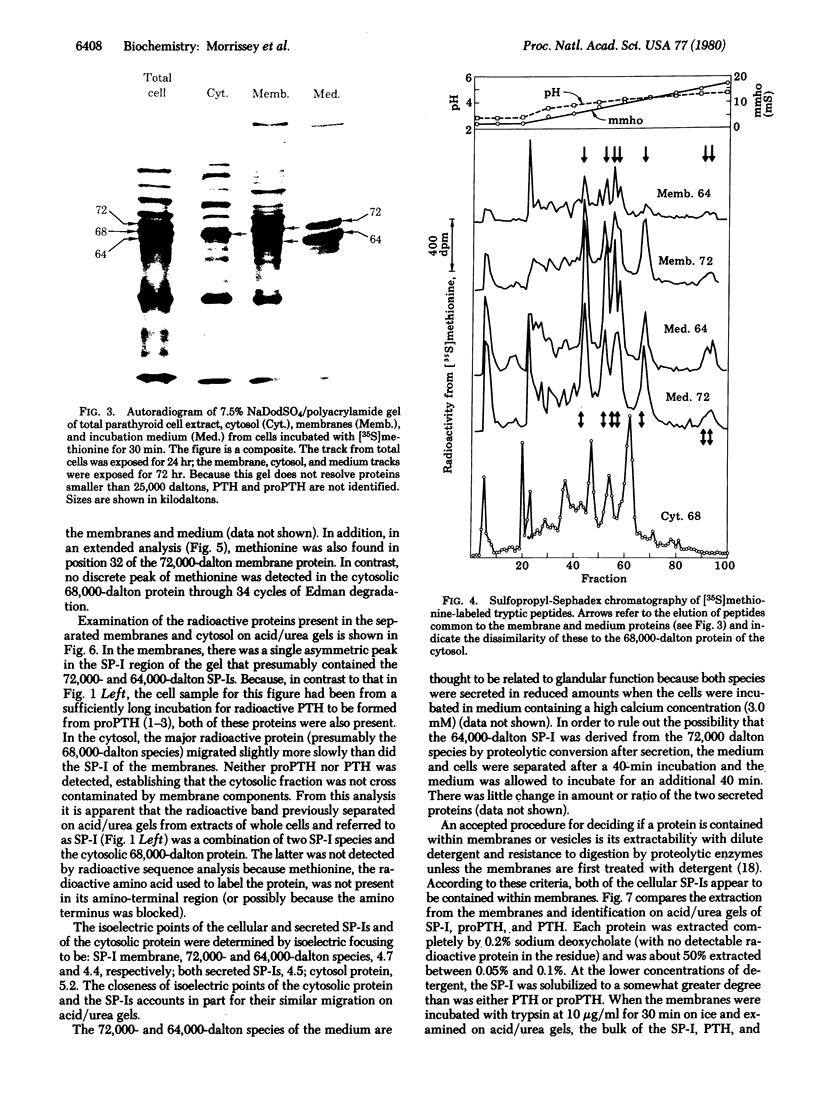
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Chu L. L., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V. Studies on the subcellular localization of proparathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone in the bovine parathyroid gland: separation of newly synthesized from mature forms. Endocrinology. 1973 Dec;93(6):1387–1397. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-6-1387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Cohn D. V. The intracellular pathway for parathormone biosynthesis and secretion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978 Nov-Dec;(137):244–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V. The mode of conversion of proparathormone to parathormone by a particulate converting enzymic activity of the parathyroid gland. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):2012–2017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Hamilton J. W., Shofstall R. E., Cohn D. V. Isolation and characterization of porcine parathyroid cathepsin B. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4423–4427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majzoub J. A., Kronenberg H. M., Potts J. T., Jr, Rich A., Habener J. F. Identification and cell-free translation of mRNA coding for a precursor of parathyroid secretory protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7449–7455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
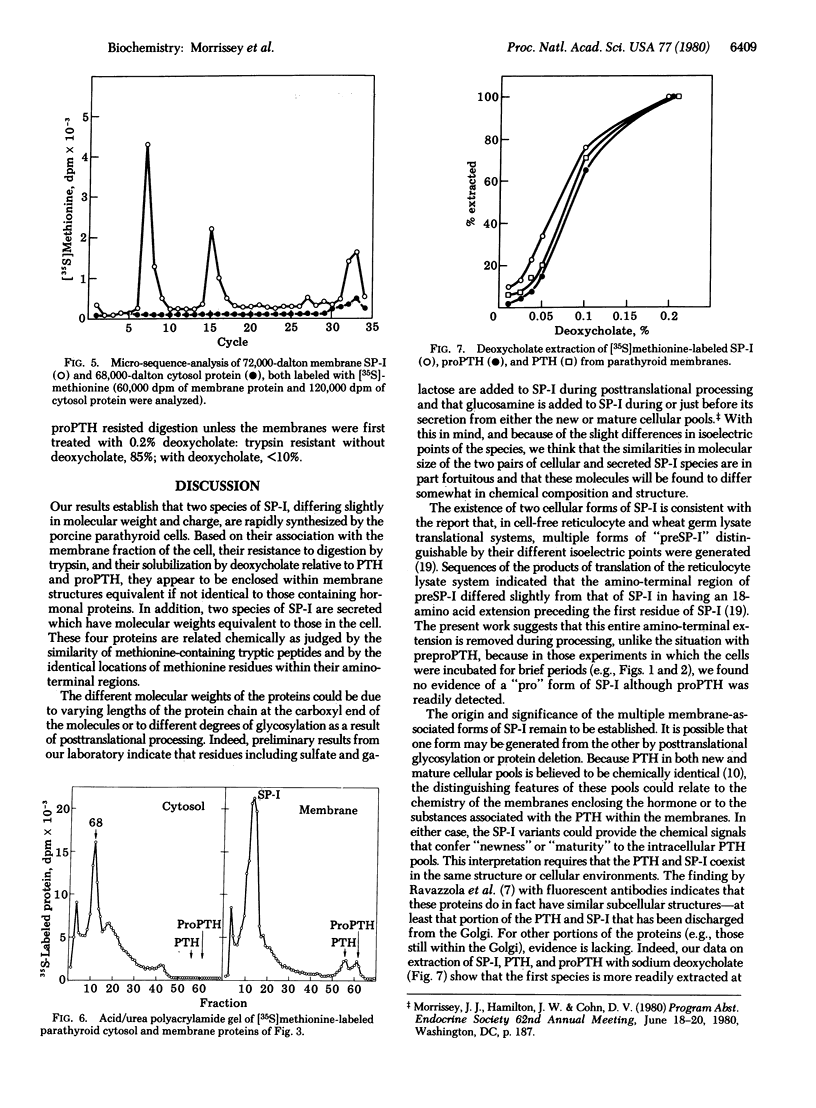
- Morrissey J. J., Cohn D. V. Regulation of secretion of parathormone and secretory protein-I from separate intracellular pools by calcium, dibutyryl cyclic AMP, and (1)-isoproterenol. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jul;82(1):93–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. J., Cohn D. V. Secretion and degradation of parathormone as a function of intracellular maturation of hormone pools. Modulation by calcium and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):521–528. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. J., Cohn D. V. The effects of calcium and magnesium on the secretion of parathormone and parathyroid secretory protein by isolated porcine parathyroid cells. Endocrinology. 1978 Dec;103(6):2081–2090. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-6-2081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. J., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V. The secretion of parathormone and glycosylated proteins by parathyroid cells in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jun 29;82(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90326-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravazzola M., Orci L., Habener J. F., Potts J. T., Jr Parathyroid secretory protein: Immunocytochemical localisation within cells that contain parathyroid hormone. Lancet. 1978 Aug 12;2(8085):371–372. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92967-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]