Abstract
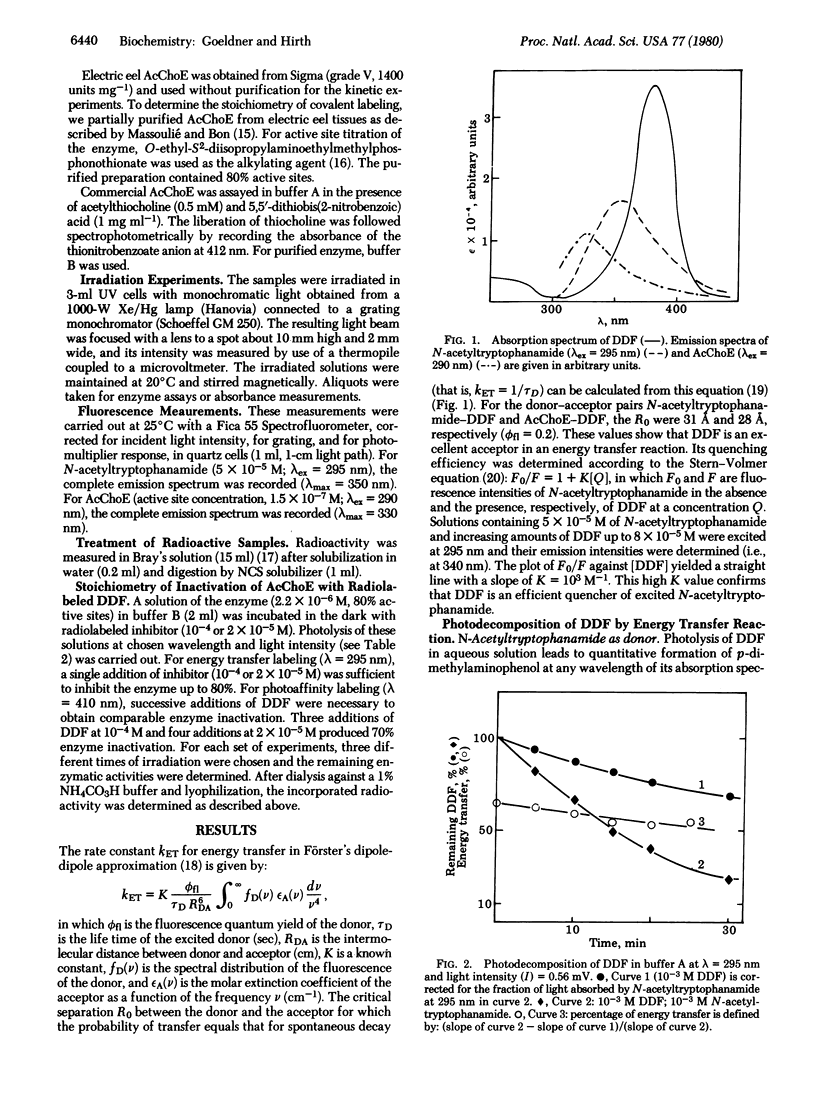
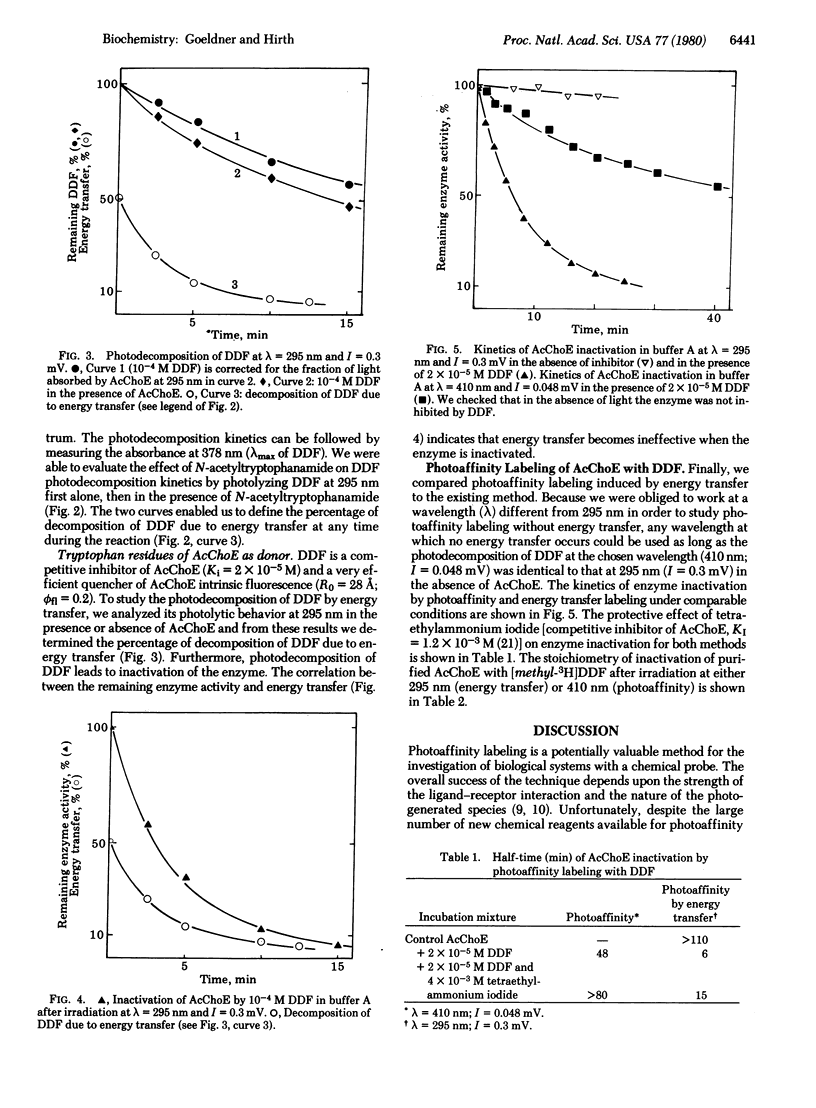
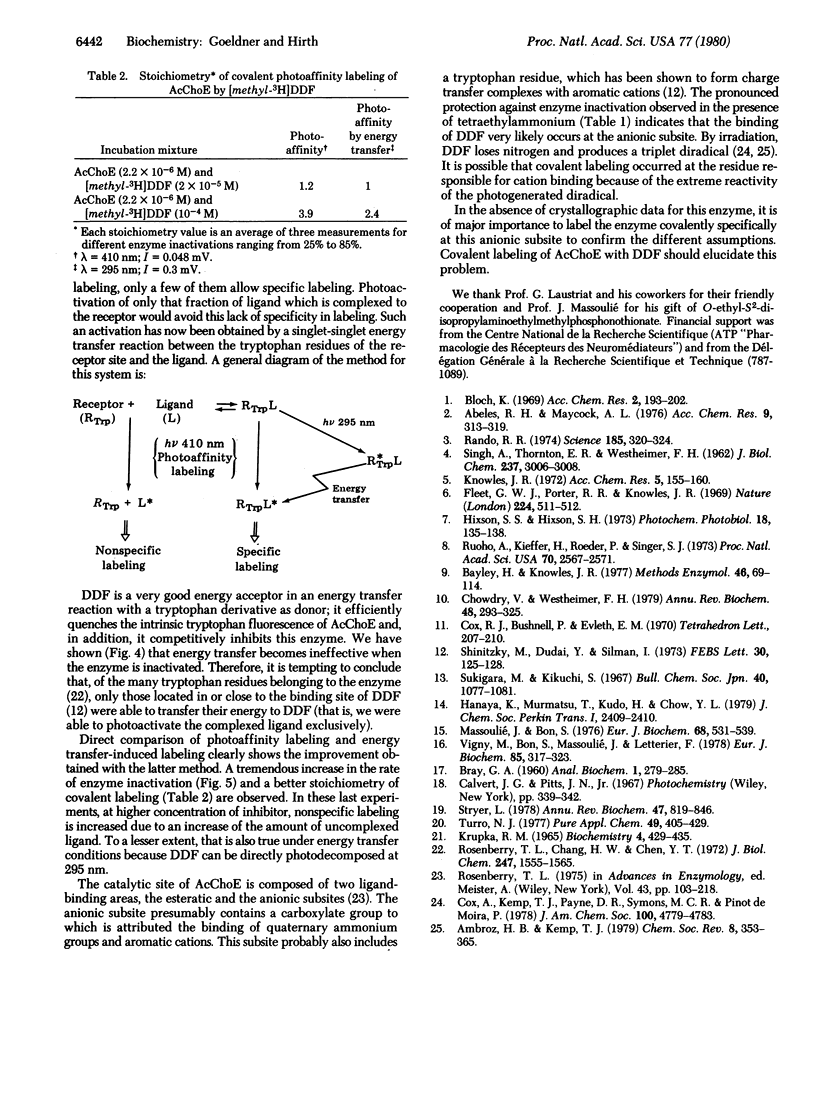
p-Dimethylaminobenzene diazonium fluoroborate belongs to a class of potential photoaffinity labeling reagents which, by irradiation, produces a highly reactive electrophilic species. In addition, it can be photodecomposed by photoexcited tryptophan derivatives (e.g., N-acetyltryptophanamide and tryptophan residues belonging to acetylcholinesterase) by an energy transfer reaction. This substance is a competitive inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (acetylcholine acetylhydrolase, EC 3.1.1.7) and is able to inactivate the enzyme either by photoaffinity labeling after irradiation at 410 nm or by an energy transfer reaction after irradiation at 295 nm. The efficiency of this method is demonstrated by an increase of the rate of enzyme inactivation as well as by a decrease of nonselective labeling with a radioactive inhibitor p-[methyl-3H]-dimethylaminobenzene diazonium fluoroborate.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayley H., Knowles J. R. Photoaffinity labeling. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:69–114. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhry V., Westheimer F. H. Photoaffinity labeling of biological systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:293–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson S. S., Hixson S. H. Photochemical labeling of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase with an azide analog of NAD+. Photochem Photobiol. 1973 Aug;18(2):135–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1973.tb06403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRUPKA R. M. ACETYLCHOLINESTERASE: STRUCTURAL REQUIREMENTS FOR BLOCKING DEACETYLATION. Biochemistry. 1965 Mar;4:429–435. doi: 10.1021/bi00879a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Bon S. Affinity chromatography of acetylcholinesterase. The importance of hydrophobic interactions. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep 15;68(2):531–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10841.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R. Chemistry and enzymology of kcat inhibitors. Science. 1974 Jul 26;185(4148):320–324. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4148.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L. Acetylcholinesterase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;43:103–218. doi: 10.1002/9780470122884.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L., Chang H. W., Chen Y. T. Purification of acetylcholinesterase by affinity chromatography and determination of active site stoichiometry. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1555–1565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoho A. E., Kiefer H., Roeder P. E., Singer S. J. The mechanism of photoaffinity labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2567–2571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGH A., THORNTON E. R., WESTHEIMER F. H. The photolysis of diazoacetylchymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1962 Sep;237:3006–3008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky Meir, Dudai Yadin, Silman Israel. Spectral evidence for the presence of tryptophan in the binding site of acetylcholinesterase. FEBS Lett. 1973 Feb 15;30(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80633-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Fluorescence energy transfer as a spectroscopic ruler. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:819–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigny M., Bon S., Massoulié J., Leterrier F. Active-site catalytic efficiency of acetylcholinesterase molecular forms in Electrophorus, torpedo, rat and chicken. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):317–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


