Abstract
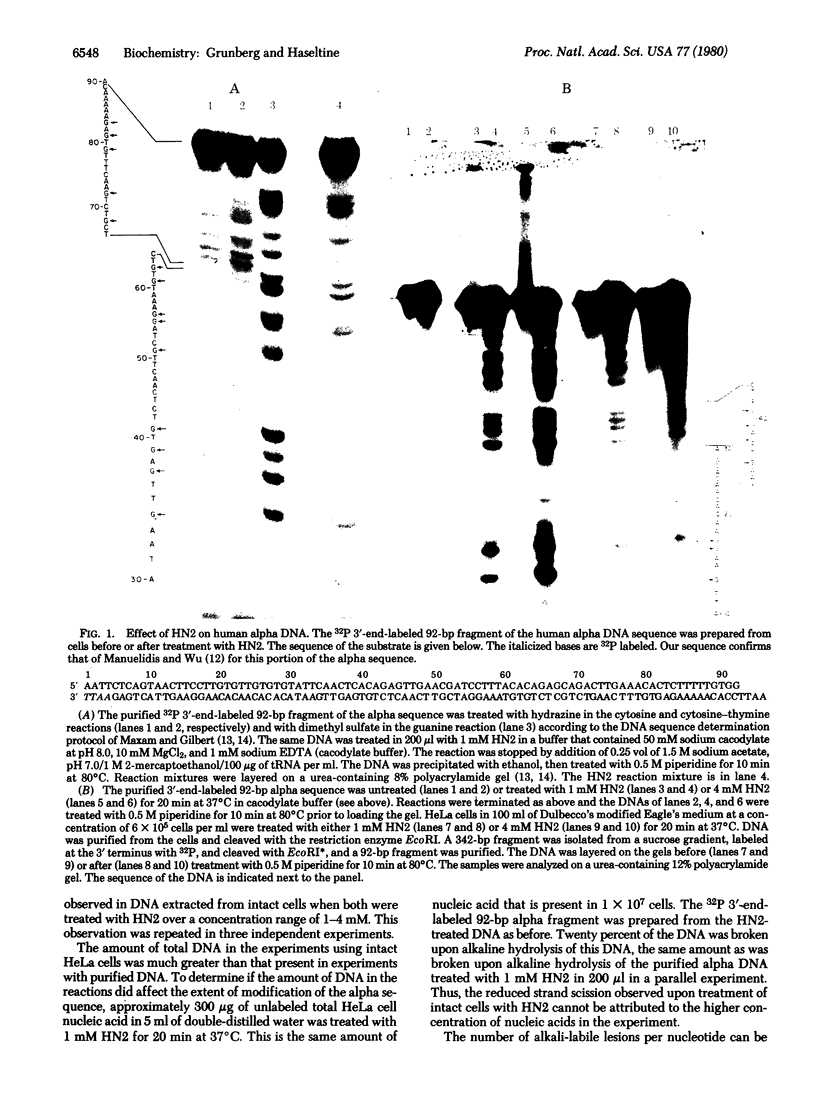
A highly reiterated sequence of human DNA was used to determine the sites of modification of DNA caused by the anti-tumor drug methylbis(2-chloroethyl)amine (HN2, mechlorethamine, nitrogen mustard) upon treatment of cells in culture and of purified DNA. The lengths of the breakage products of the DNA treated with HN2 were compared to the lengths of DNA scission products produced by chemical reactions used for DNA sequence determination. HN2 was found to create alkali-labile lesions at positions of guanine. The distribution of the guanine modifications was the same for DNA extracted from cells treated with HN2 and for purified DNA treated with HN2. However, the extent of damage was at least 2-fold greater when purified DNA was used as the substrate. Several nitrogen mustard analogues also produced alkali-labile lesions at positions of guanine.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FOLEY G. E., LAZARUS H., FARBER S., UZMAN B. G., BOONE B. A., MCCARTHY R. E. CONTINUOUS CULTURE OF HUMAN LYMPHOBLASTS FROM PERIPHERAL BLOOD OF A CHILD WITH ACUTE LEUKEMIA. Cancer. 1965 Apr;18:522–529. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196504)18:4<522::aid-cncr2820180418>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDER R. H., MARTIN-GUZMAN G., JONES J., GOLDSTEIN N. O., ROTENBERG S., RUTMAN R. J. EXPERIMENTAL CHEMOTHERAPY STUDIES. 3. PROPERTIES OF DNA FROM ASCITES CELLS TREATED IN VIVO WITH NITROGEN MUSTARD. Cancer Res. 1964 Jul;24:964–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Lindan C. P., D'Andrea A. D., Johnsrud L. The use of DNA fragments of defined sequence for the study of DNA damage and repair. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):235–248. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley P. D., Brookes P. Interstrand cross-linking of DNA by difunctional alkylating agents. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):143–160. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J., Brown F. L., Musich P. R. Subunit structure of chromatin and the organization of eukaryotic highly repetitive DNA: recurrent periodicities and models for the evolutionary origins of repetitive DNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):637–655. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Repeating restriction fragments of human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Nov;3(11):3063–3076. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.11.3063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Wu J. C. Homology between human and simian repeated DNA. Nature. 1978 Nov 2;276(5683):92–94. doi: 10.1038/276092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Reaction of nucleosome DNA with dimethyl sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2133–2137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery J. A., Struck R. F. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of pre-activated analogs of cyclophosphamide (NSC-26271). Cancer Treat Rep. 1976 Apr;60(4):381–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polisky B., Greene P., Garfin D. E., McCarthy B. J., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. Specificity of substrate recognition by the EcoRI restriction endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3310–3314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torkelson A. R., LaBudde J. A., Weikel J. H., Jr The metabolic fate of cyclophosphamide. Drug Metab Rev. 1974;3(1):131–165. doi: 10.3109/03602537408993740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]