Abstract
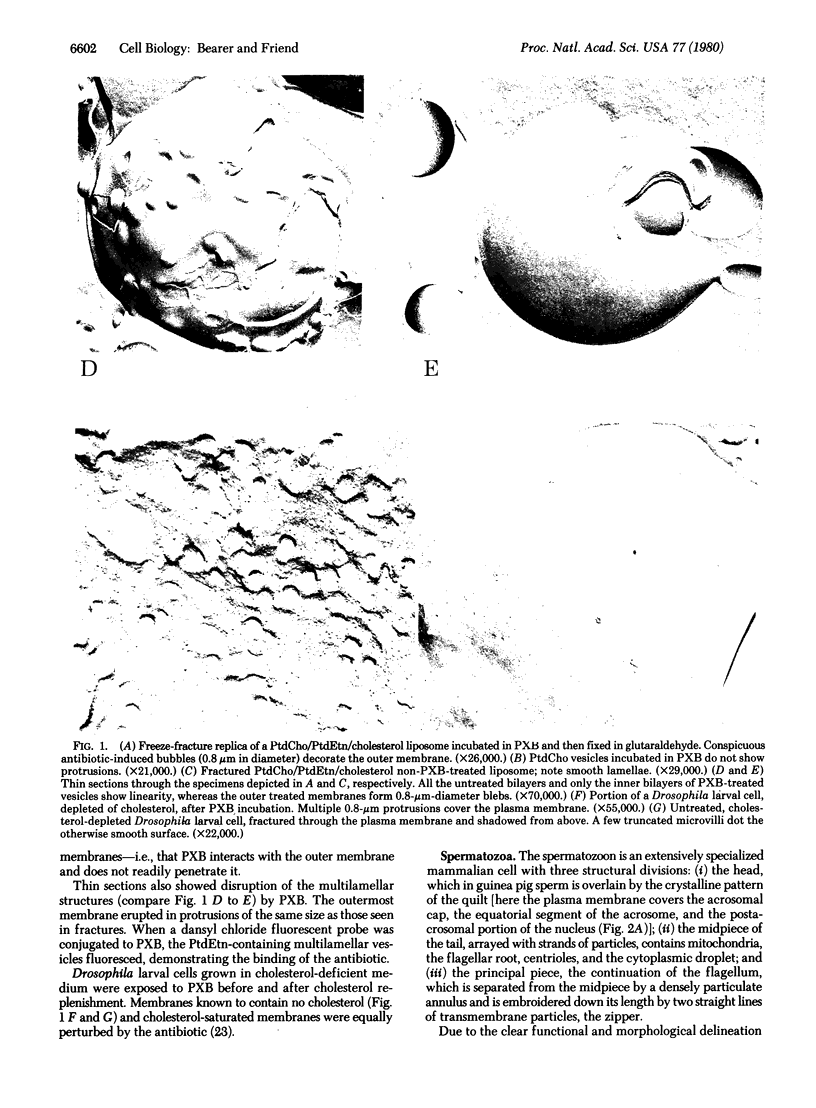
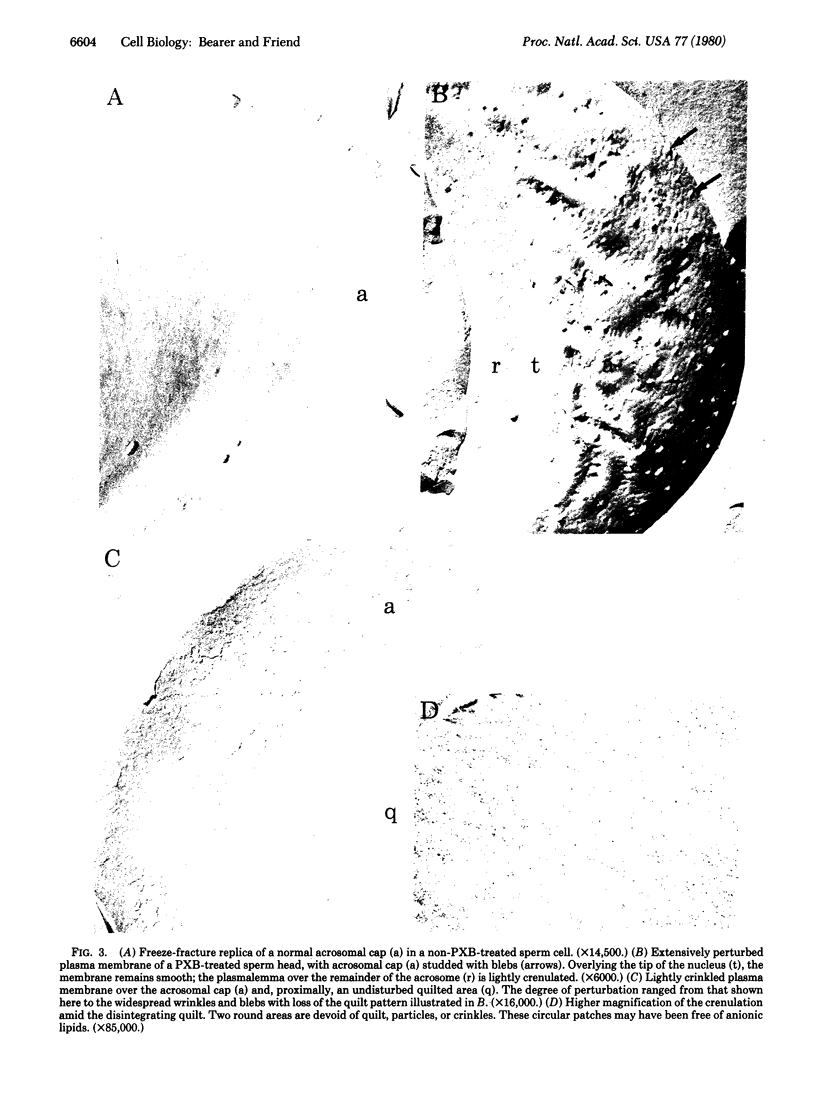
Polymyxin B was used to explore distribution of anionic phospholipids in sperm plasma membranes by electron microscopy of freeze-fracture replicas. After exposure to Hepes/Tris-buffered polymyxin at 4 mM, phosphatidylcholine liposomes showed no perturbations nor did they fluoresce with dansylated incubation. When phosphatidylethanolamine was included in the liposomes, they became perturbed and fluoresced. Plasma membranes of Drosophila larval cells, containing or lacking cholesterol, were also disrupted by polymyxin. The cell membranes of guinea pig sperm were likewise disrupted but in specific functional areas. Fusional membrane domains showed protrusions; the stable membrane of the flagellum revealed diffuse bubbling. Regions of well-defined particle arrays and the postacrosomal segment maintained smooth contours. By fluorescence microscopy, we detected the same heterogeneous binding of the polymyxin dansyl derivative.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bader J., Teuber M. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes. 1. Binding to the O-antigenic lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella typhimurium. Z Naturforsch C. 1973 Jul-Aug;28(7):422–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Beckers F., Zimmermann U. Reversible electrical breakdown of lipid bilayer membranes: a charge-pulse relaxation study. J Membr Biol. 1979 Jul 16;48(2):181–204. doi: 10.1007/BF01872858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Fröhlich O., Läuger P., Montal M. Electrical capacity of black lipid films and of lipid bilayers made from monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 3;394(3):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Mashak E. M., Tocanne J. F. Polymyxin B-phosphatidylglycerol interactions. A monolayer (pi, delta V) study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 28;596(2):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Friend D. S., Goerke J. Membrane sterol heterogeneity. Freeze-fracture detection with saponins and filipin. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Sep;27(9):1247–1260. doi: 10.1177/27.9.479568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. W., Weaver D. E., Clegg E. D. Diacyl, alkenyl, and alkyl ether phospholipids in ejaculated, in utero-, and in vitro-incubated porcine spermatozoa. J Lipid Res. 1980 Feb;21(2):223–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., HsuChen C. C., Sud I. J. Basis for the selectivity of action of the polymyxin antibiotics on cell membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):480–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S., Fawcett D. W. Membrane differentiations in freeze-fractured mammalian sperm. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):641–664. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galla H. J., Sackmann E. Chemically induced lipid phase separation in model membranes containing charged lipids: a spin label study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 2;401(3):509–529. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann W., Galla H. J., Sackmann E. Polymyxin binding to charged lipid membranes. An example of cooperative lipid-protein interaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 16;510(1):124–139. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Inoue K., Nojima S. Effect of polymyxin B on liposomal membranes derived from Escherichia coli lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 14;375(1):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike M., Iida K., Matsuo T. Electron microscopic studies on mode of action of polymyxin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):448–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.448-452.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolber M. A., Haynes D. H. Evidence for a role of phosphatidyl ethanolamine as a modulator of membrane-membrane contact. J Membr Biol. 1979 Jun 29;48(1):95–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01869258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lounatmaa K., Mäkelä P. H., Sarvas M. Effect of polymyxin on the ultrastructure of the outer membrane of wild-type and polymyxin-resistant strain of Salmonella. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1400–1407. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1400-1407.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lounatmaa K., Nanninga N. Effect of polymyxin on the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: freeze-fracture studies. J Bacteriol. 1976 Nov;128(2):665–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.2.665-667.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller I. R., Bach D., Teuber M. Effect of polymyxin B on the structure and the stability of lipid layers. J Membr Biol. 1978 Feb 6;39(1):49–56. doi: 10.1007/BF01872754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. A fluorescent derivative of polymyxin: its preparation and use in studying the site of action of the antibiotic. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Apr;12(2):226–236. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-2-226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal K. S., Swanson P. E., Storm D. R. Disruption of Escherichia coli outer membranes by EM 49. A new membrane active peptide. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 28;15(26):5783–5792. doi: 10.1021/bi00671a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler P. R., Teuber M. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes: morphological changes in the cytoplasm and in the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):95–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott T. W., Voglmayr J. K., Setchell B. P. Lipid composition and metabolism in testicular and ejaculated ram spermatozoa. Biochem J. 1967 Feb;102(2):456–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1020456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixl F., Galla H. J. Cooperative lipid-protein interaction. Effect of pH and ionic strength on polymyxin binding to phosphatidic acid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 2;557(2):320–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90330-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider D. R., Clegg E. D. Alteration of phospholipids in porcine spermatozoa during in vivo uterus and oviduct incubation. J Anim Sci. 1975 Feb;40(2):269–274. doi: 10.2527/jas1975.402269x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm D. R., Rosenthal K. S., Swanson P. E. Polymyxin and related peptide antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:723–763. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. T., Hsang C. C., Day E. P., Ho J. T. Fusion of phosphatidylserine and mixed phosphatidylserine-phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Dependence on calcium concentration and temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F., Jr, Papahadjopoulos D. Procedure for preparation of liposomes with large internal aqueous space and high capture by reverse-phase evaporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4194–4198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuber M., Bader J. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes. Binding capacities for polymyxin B of inner and outer membranes isolated from Salmonella typhimurium G30. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Aug;109(1-2):51–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00425112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuber M., Bader J. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes: phosphatidylglycerol- and cardiolipin-induced susceptibility to polymyxin B in Acholeplasma laidlawii B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):26–35. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuber M., Miller I. R. Selective binding of polymyxin B to negatively charged lipid monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 16;467(3):280–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90305-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahn K., Lutsch G., Rockstroh T., Zapf K. Morphological and physiological investigations on the action of polymyxin B on Escherichia coli. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;63(2):103–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00412165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagimachi R., Noda Y. D., Fujimoto M., Nicolson G. L. The distribution of negative surface charges on mammalian spermatozoa. Am J Anat. 1972 Dec;135(4):497–519. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001350405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]