Abstract
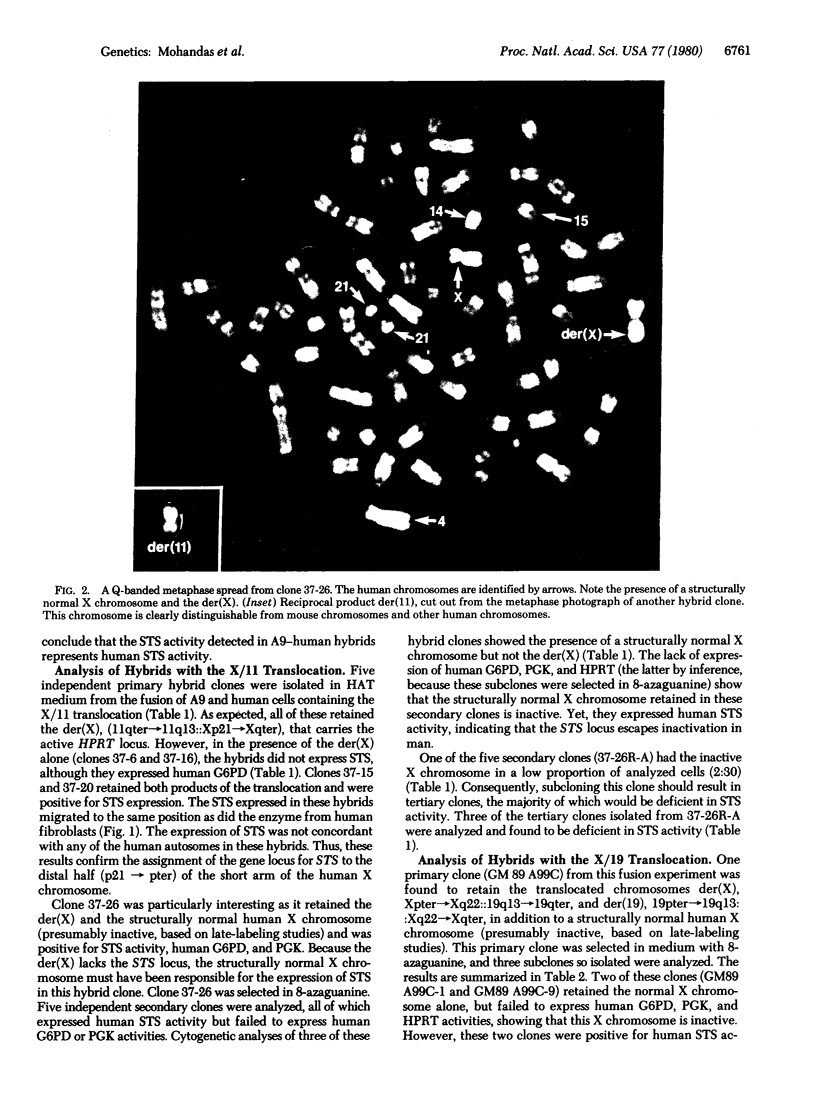
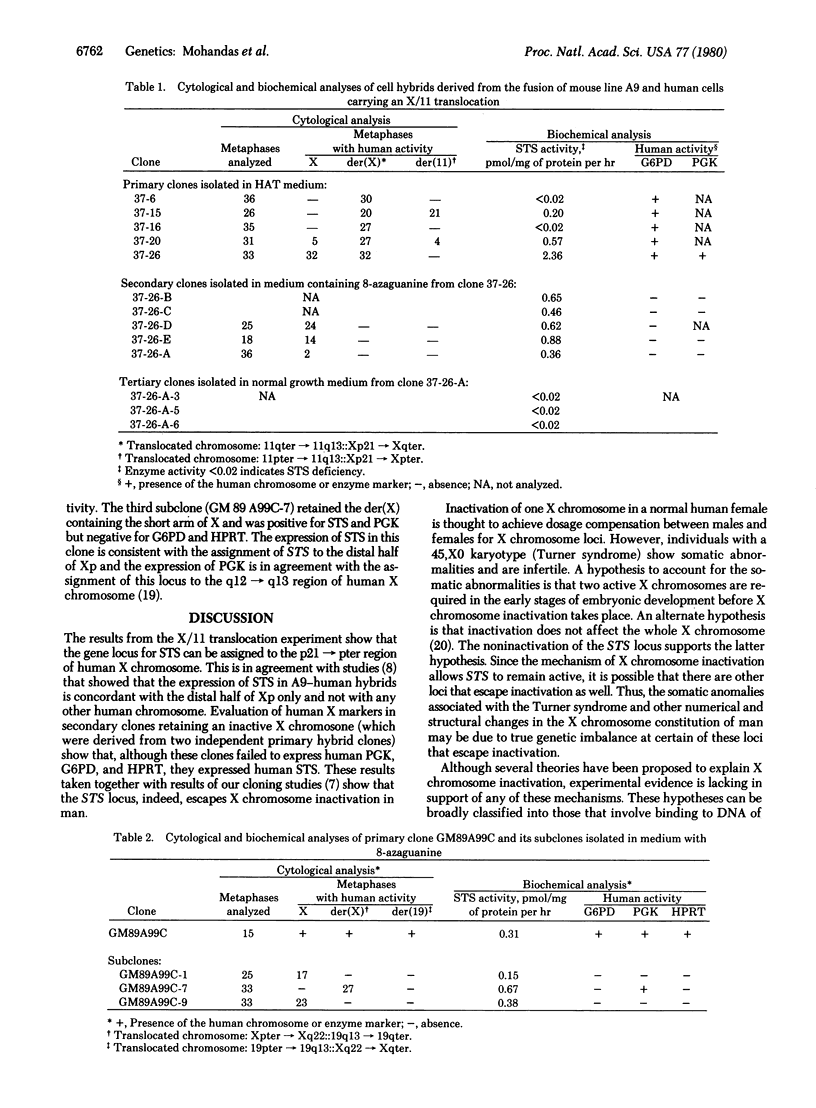
Somatic cell hybrid clones were derived from the fusion of hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT; EC 2.4.2.8)-deficient mouse cells and two different human fibroblast strains, each carrying an X chromosome-autosome translocation. One of these had an X/11 translocation [46,X,t(X;11)(p21;q13)] and the other had an X/19 translocation [46,X,t(X;19)(q22;q13)]. The structurally normal human X chromosome is the late-replicating (genetically inactive) chromosome in these two cell strains; the rearranged X chromosome is early replicating (genetically active). One primary hybrid clone carrying both the translocated X chromosome and the structurally normal X chromosome was isolated in hypoxanthine/aminopterin/thymidine medium from each of these two cell fusion experiments. These clones were then selected in medium containing 8-azaguanine to achieve the loss of the active human HPRT locus. Five subclones from the cell hybrid with the X/11 translocation failed to express two known human X-chromosome markers [glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD; EC 1.1.1.49) and phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK; EC 2.7.2.3)] but did express human microsomal steroid sulfatase (STS; sterol-sulfate sulfohydrolase, EC 3.1.6.2). Three of these were cytogenetically analyzed and found to contain a structurally normal human X chromosome but not the X/11 translocation. Two subclones were isolated in 8-azaguanine from the hybrid with the X/19 translocation. Cytogenetic analysis of these two clones showed the presence of a structurally normal human X chromosome; the X/19 translocation was not present. They did not express human G6PD, PGK, or HPRT but did express human STS. These results indicate that human STS is expressed from a locus on the inactive human X chromosome and support our earlier finding that the STS locus escapes X-inactivation in man.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler E. Electrophoresis of phosphoglycerate kinase. Biochem Genet. 1969 Apr;3(2):189–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00520353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R. Hypothesis on differentiation and the inheritance of gene superstructure. Nature. 1973 Sep 7;245(5419):23–25. doi: 10.1038/245023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington G. J., Bernard H. P., Ruddle F. H. Human serum albumin phenotype activation in mouse hepatoma--human leukocyte cell hybrids. Science. 1974 Sep 6;185(4154):859–862. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4154.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON-SMITH M. A. KARYOTYPE-PHENOTYPE CORRELATIONS IN GONADAL DYSGENESIS AND THEIR BEARING ON THE PATHOGENESIS OF MALFORMATIONS. J Med Genet. 1965 Jun;2(2):142–155. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2.2.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J. X-chromosome inactivation and the Xg locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1970 Jul;22(4):460–463. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Andina R. J. Mammalian X-chromosome inactivation. Adv Hum Genet. 1976;7:99–140. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0659-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellkuhl B., Grzeschik K. H. Partial reactivation of a human inactive X chromosome in human-mouse somatic cell hybrids. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):527–530. doi: 10.1159/000131016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON M. F. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature. 1961 Apr 22;190:372–373. doi: 10.1038/190372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F. Possible mechanisms of X chromosome inactivation. Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 25;232(34):229–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio232229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F. X-chromosome inactivation and developmental patterns in mammals. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1972 Jan;47(1):1–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1972.tb00969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J., Sparkes R. S., Sparkes M. C. Regional assignment of the steroid sulfatase-X-linked ichthyosis locus: implications for a noninactivated region on the short arm of human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5779–5783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Sparkes M. C., Shulkin J. D. Assignment of the human gene for galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase to chromosome 9: studies with Chinese hamster-human somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5628–5631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller C. R., Westerveld A., Migl B., Franke W., Ropers H. H. Regional assignment of the gene locus for steroid sulfatase. Hum Genet. 1980;54(2):201–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00278972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S. Conservation of ancient linkage groups in evolution and some insight into the genetic regulatory mechanism of x-inactivation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:155–164. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D. X inactivation, differentiation, and DNA methylation. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;14(1):9–25. doi: 10.1159/000130315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L. J., Mohandas T., Weiss R., Romeo G. Non-inactivation of an x-chromosome locus in man. Science. 1979 Jun 15;204(4398):1224–1226. doi: 10.1126/science.156396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L. J., Weiss R., Buxman M. M., Vidgoff J., Dimond R. L., Roller J. A., Wells R. S. Enzymatic basis of typical X-linked icthyosis. Lancet. 1978 Oct 7;2(8093):756–757. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92646-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes R. S., Baluda M. C., Townsend D. E. Cellulose acetate electrophoresis of human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Mar;73(3):531–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summitt R. L., Tipton R. E., Wilroy R. S., Jr, Martens P. R., Phelan J. P. X-autosome translocations: a review. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1978;14(6C):219–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A., Miller O. J. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosomes 10, 11, 12, X, and Y. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1979;25(1-4):47–58. doi: 10.1159/000131399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]