Abstract
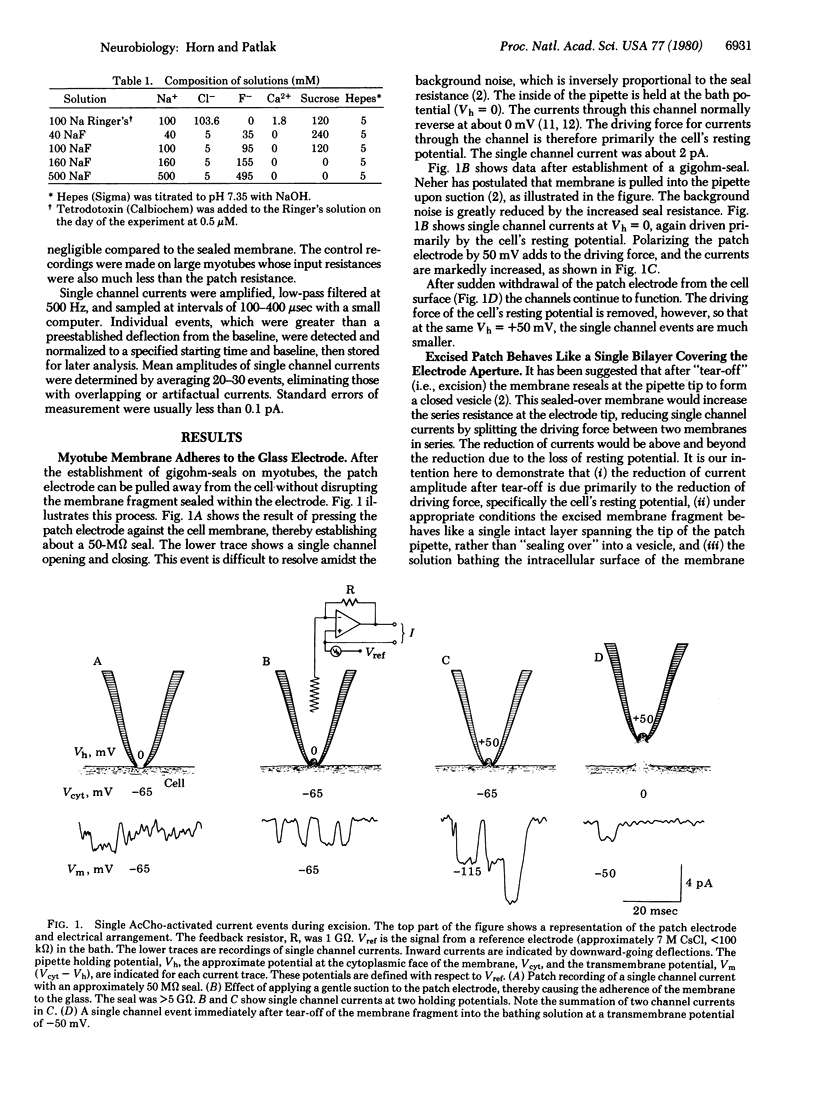
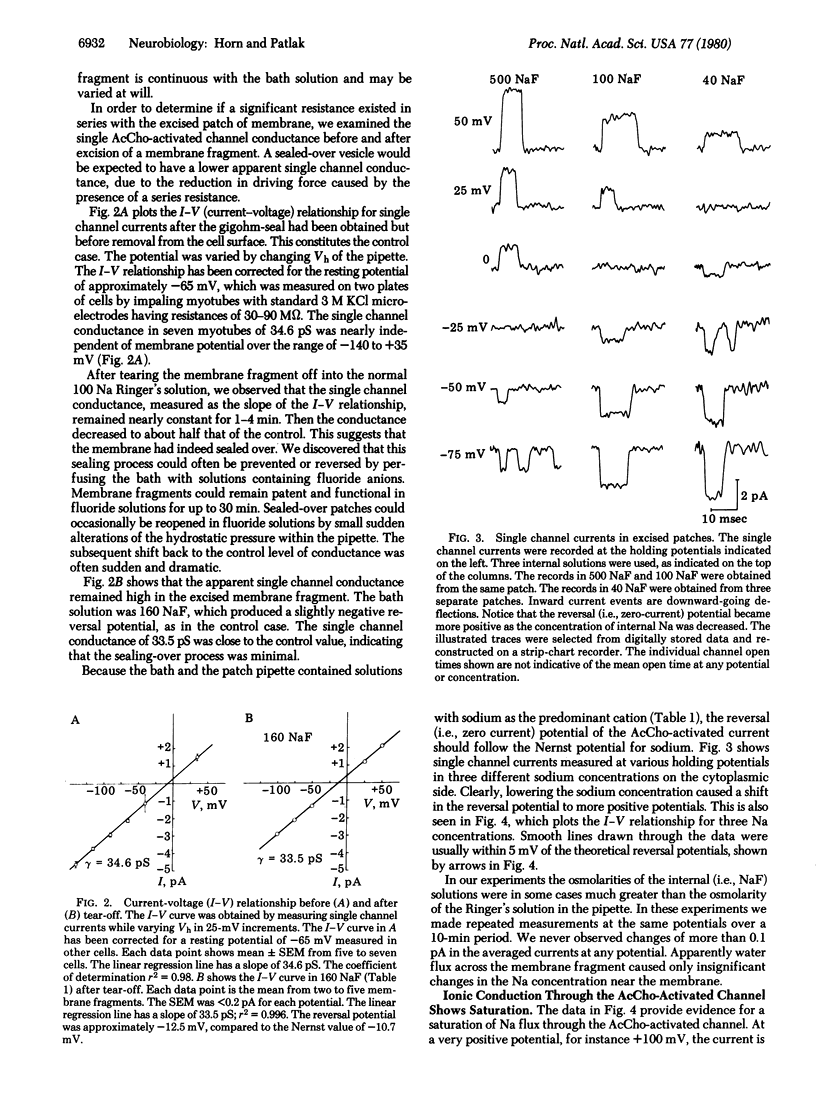
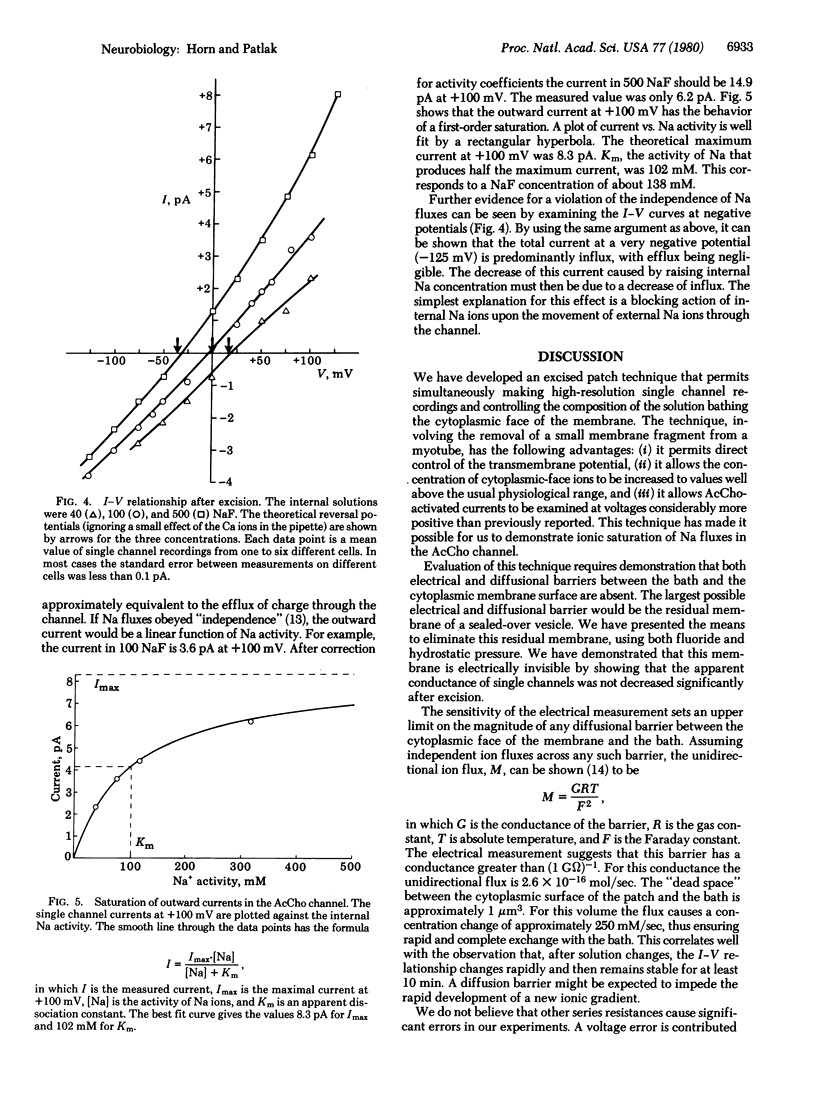
The currents through single acetylcholine-activated channels were measured on membrane fragments that had been torn from rat muscle myotubes with patch pipettes. The membrane fragments were sealed into the pipette by using the "gigohm-seal" technique of Neher, which also permitted voltage clamp of the membrane via the patch electrode. Membrane patches were excited by sudden withdrawal of the electrode from the cell. Substitution of fluoride for chloride ions in the bathing solution could prevent or reverse the tendency for the membrane at the electrode tip to seal over into a closed vesicle. The single membrane layer at the electrode tip could remain functional for up to 30 min. The apparent single channel conductance was minimally affected by excision. The current-voltage relationships for the single channel currents show that the inside (i.e., cytoplasmic surface) of the membrane fragment was exposed to the bathing solution. In symmetric Na solutions the current-voltage curve was nearly linear and reversed at approximately 0 mV. In other bathing solutions from 40 to 500 mM NaF, the observed zero current potential was close to that predicted by the Nernst equation. We present evidence that internal Na interacts with the channel, causing both saturation of outward current and block of inward current. At + 100 mV the apparent dissociation constant for internal Na was 138 mM.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. Replacement of the axoplasm of giant nerve fibres with artificial solutions. J Physiol. 1962 Nov;164:330–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Ionic selectivity of Na and K channels of nerve membranes. Membranes. 1975;3:255–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Brodwick M. S. Acetylcholine-induced current in perfused rat myoballs. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Mar;75(3):297–321. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.3.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Lecar H. Single postsynaptic channel currents in tissue cultured muscle. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):863–864. doi: 10.1038/282863a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Shakhovalov Y. A. Separation of sodium and calcium currents in the somatic membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):545–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Akaike N., Brown A. M. Properties of internally perfused, voltage-clamped, isolated nerve cell bodies. J Gen Physiol. 1978 May;71(5):489–507. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.5.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. A. Ion-concentration dependence of the reversal potential and the single channel conductance of ion channels at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:417–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder T. M., Quastel D. M. A voltage-clamp study of the permeability change induced by quanta of transmitter at the mouse end-plate. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:535–558. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):799–802. doi: 10.1038/260799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B., Steinbach J. H. The extracellular patch clamp: a method for resolving currents through individual open channels in biological membranes. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Jul 18;375(2):219–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00584247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J., Neher E. Single Na+ channel currents observed in cultured rat muscle cells. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):447–449. doi: 10.1038/287447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



