Abstract
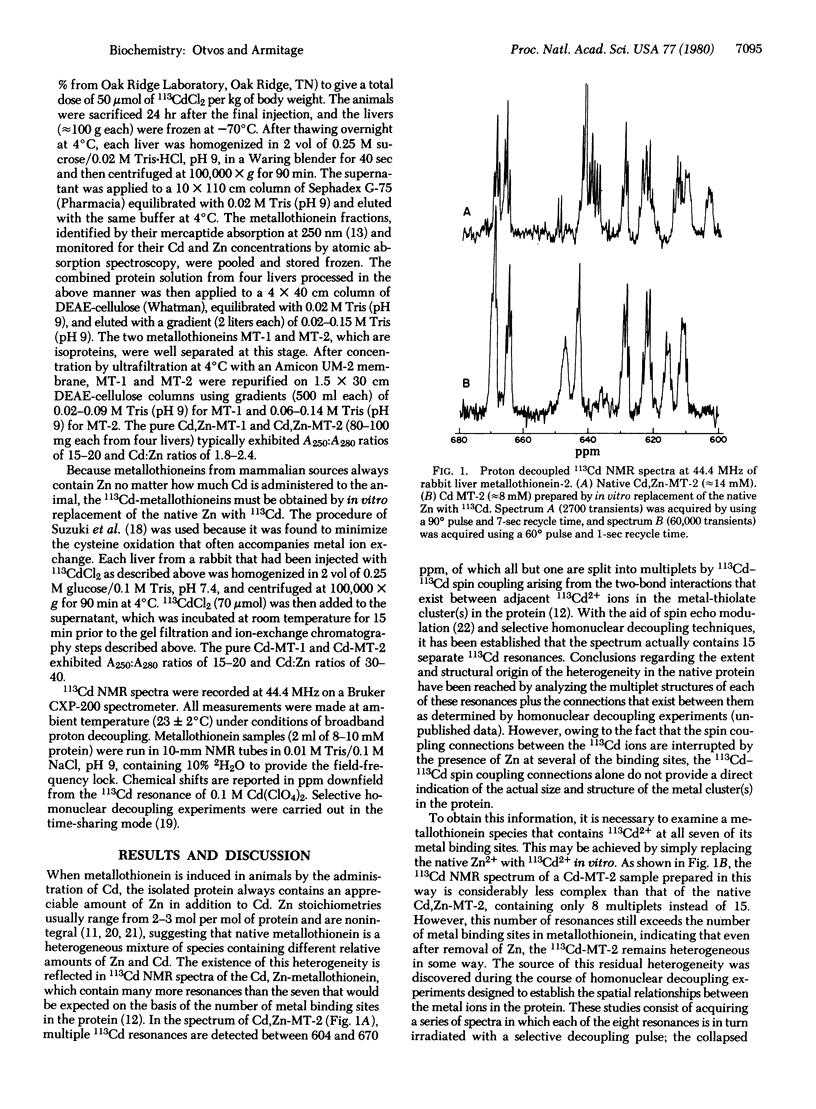
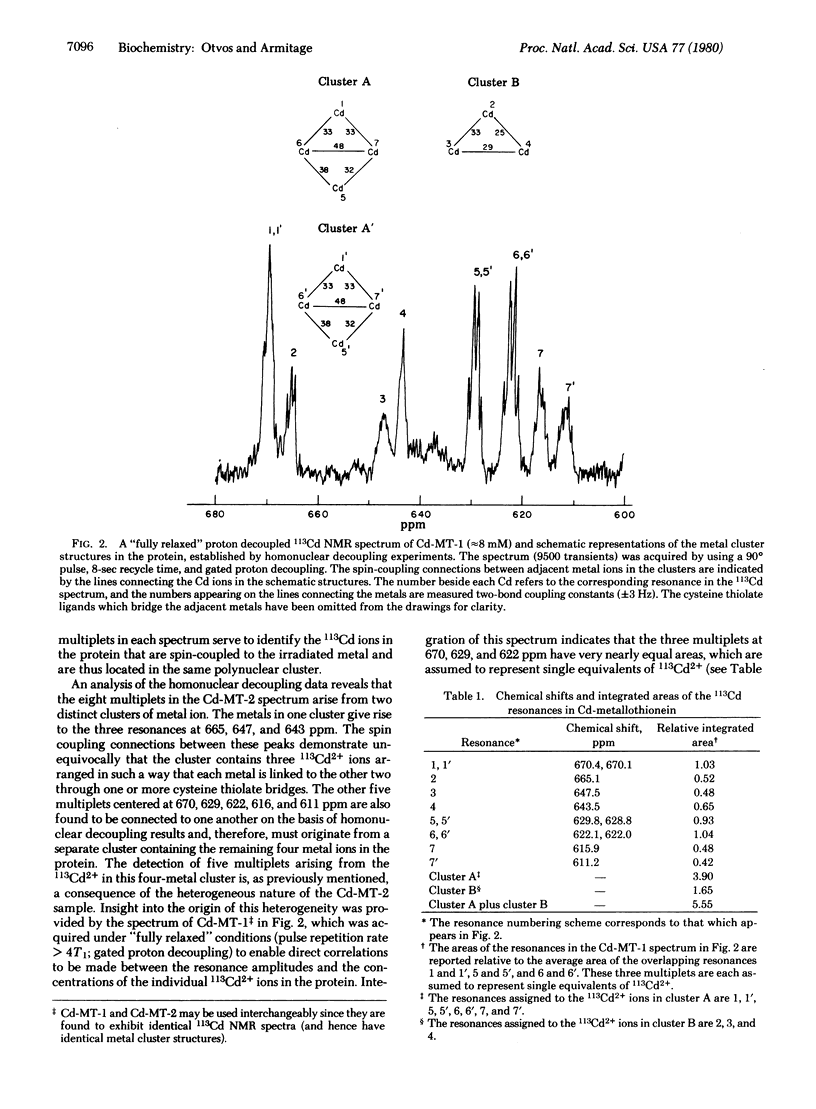
Cadmium-113 nuclear magnetic resonance (113Cd NMR) has been used to determine the structures of the multiple cadmium binding sites in the two major isoproteins of rabbit liver metallothionein. The isotopically 113Cd-labeled metallothionein used in these studies was isolated from the livers of rabbits that had been subjected to repeated injections of 113CdCl2. The native protein isolated from these livers contains an appreciable amount of Zn in addition to Cd, ranging from 2-3 mol per mol of protein out of a total metal content of 7 mol per mol of protein. The 113Cd NMR spectrum of Cd, Zn-containing metallothionein is quite complex, reflecting the fact that the native protein is a heterogeneous mixture of species containing different relative amounts of Zn and Cd. Replacement of the native Zn with 113Cd in vitro gave a protein whose 113Cd NMR spectrum was much simpler, containing eight distinct multiplets with chemical shifts ranging from 611-670 ppm. The origin of the multiplet structures has been shown to be 113Cd-113Cd scalar coupling arising from two-bond interactions between 113Cd ions linked to one another by bridging cysteine thiolate ligands. The size and structures of the metal clusters in the protein were determined by the application of selective homonuclear 113Cd decoupling techniques. Analysis of these data showed that rabbit liver metallothionein contains two separate metal clusters, one containing four Cd2+ ions and the other containing three. These two clusters, whose structures are the same in both isoproteins, have been designated “cluster A” and “cluster B,” respectively. Structures for the clusters are proposed that account for the 113Cd spin coupling data and the participation of all 20 of the cysteine residues in metal ligation, 11 in cluster A and 9 in cluster B. The appearance in the spectrum of eight multiplets rather than the seven that would be expected on the basis of the number of metal binding sites in the protein is an indication of some residual heterogeneity in the 113Cd-labeled metallothionein sample. The origin of this heterogeneity is suggested to be the presence of a protein species that lacks metal ions at its cluster B binding sites.
Keywords: 113Cd NMR, homonuclear decoupling, isoproteins
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bremner I., Young B. W. Isolation of (copper, zinc)-thioneins from the livers of copper-injected rats. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):517–520. doi: 10.1042/bj1570517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler R. H., Kägi J. H. Human hepatic metallothioneins. FEBS Lett. 1974 Feb 15;39(2):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. D., Dobson C. M., Williams R. J., Wright P. E. Pulse methods for the simplification of protein NMR spectra. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):96–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80160-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang I. Y., Yoshida A. Mouse liver metallothioneins. Complete amino acid sequence of metallothionein-I. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8217–8221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGI J. H., VALLEE B. L. Metallothionein: a cadmium and zinc-containign protein from equine renal cortex. II. Physico-chemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1961 Sep;236:2435–2442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissling M. M., Kägi H. R. Primary structure of human hepatic metallothionein. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80594-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima Y., Berger C., Vallee B. L., Kägi J. H. Amino-acid sequence of equine renal metallothionein-1B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3413–3417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi J. H., Himmelhoch S. R., Whanger P. D., Bethune J. L., Vallee B. L. Equine hepatic and renal metallothioneins. Purification, molecular weight, amino acid composition, and metal content. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3537–3542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowski J. K., Trojanowska B., Wiśniewska-Knypl J. M., Bolanowska W. Mercury binding in the kidney and liver of rats repeatedly exposed to mercuric chloride: induction of metallothionein by mercury and cadmium. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;27(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(74)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén L., Deutsch H. F. Preparation and properties of the major copper-binding component in human fetal liver. Its identification as metallothionein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):519–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squibb K. S., Cousins R. J. Control of cadmium binding protein synthesis in rat liver. Environ Physiol Biochem. 1974;4(1):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squibb K. S., Cousins R. J., Feldman S. L. Control of zinc-thionein synthesis in rat liver. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):223–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1640223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K. T., Takenaka S., Kubota K. Fate and comparative toxicity of metallothioneins with differing Cd/Zn ratios in rat kidney. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1979;8(1):85–95. doi: 10.1007/BF01055143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunoo H., Kino K., Nakajima H., Hata A., Huang I. Y., Yoshida A. Mouse liver metallothioneins. Purification, molecular weight, amino acid composition, and metal content. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4172–4174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weser U., Rupp H., Donay F., Linnemann F., Voelter W., Voetsch W., Jung G. Characterization of Cd, Zn-thionein (metallothionein) isolated from rat and chicken liver. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 1;39(1):127–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winge D. R., Premakumar R., Rajagopalan K. V. Studies on the zinc content of Cd-induced thionein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jun;188(2):466–475. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(78)80031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



