Abstract
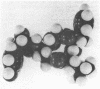
A conformationally restricted analog of [Leu5]enkephalin was synthesized by cyclization of the COOH-terminal carboxyl group of leucine to the gamma-amino moiety of alpha, gamma-diaminobutyric acid (A2bu) substituted in position 2 of the peptide. Relative to [Leu5]enkephalin, the cyclic analog with D configuration in position 2, H-Tyr-cyclo(-N gamma-D-A2bu-Gly-Phe-Leu-), was 17.5 times more potent in the guinea pig ileum assay and twice as potent in the rat brain receptor binding assay, whereas its diastereomer H-Tyr-cyclo(-N gamma-L-A2bu-Gly-Phe-Leu-) showed low activity. The cyclic D isomer was also slightly more active than the open-chain reference compound [D-Nva2, Leu5]enkephalinamide in both assays, and it proved to be highly resistant to degradation by brain "enkephalinases." The steric constraints introduced in H-Tyr-cyclo(-N gamma-D-A2bu-Gly-Phe-Leu-) were shown to prevent the realization of most of the conformational features ascribed to linear enkephalin in solution or in the crystalline state and permitted an assessment of proposed models of the conformation of enkephalin when it is bound to the receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal N. S., Hruby V. J., Katz R., Klee W., Nirenberg M. Synthesis of leucine enkephalin derivatives: structure-function studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 May 9;76(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91677-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belleau B., Malek G. A new convenient reagent for peptide syntheses. J Am Chem Soc. 1968 Mar 13;90(6):1651–1652. doi: 10.1021/ja01008a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury A. F., Smyth D. G., Snell C. R. Biosynthetic origin and receptor conformation of methionine enkephalin. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):165–166. doi: 10.1038/260165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Perdrisot R., Gacel G., Swerts J. P., Roques B. P., Schwartz J. C. Inhibitory potency of various peptides on enkephalinase activity from mouse striatum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):130–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90593-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin F. A., Balasubramanian T. M., Barry C. D., Marshall G. R. Elucidation of the receptor-bound conformation of the enkephalins. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(1):27–39. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin F. A., Marshall G. R. Proposal for the biologically active conformation of opiates and enkephalin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5179–5183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynbaum A., Kastin A. J., Coy D. H., Marks N. Breakdown of enkephalin and endorphin analogs by brain extracts. Brain Res Bull. 1977 Nov-Dec;2(6):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(77)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson D., Sharpe R., Szelke M. Methionine enkephalin and isosteric analogues. Part II.: Receptor conformation of methionine enkephalin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1980 Feb;15(2):122–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. R., Gibbons W. A., Garsky V. Proton magnetic resonance studies of conformation and flexibility of enkephalin peptides. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):779–782. doi: 10.1038/262779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Swerts J. P., Guyon A., Roques B. P., Schwartz J. C. High-affinity enkephalin-degrading peptidase in brain is increased after morphine. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):523–526. doi: 10.1038/276523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Wilson H. A., Snyder S. H. Differential effects of protein-modifying reagents on receptor binding of opiate agonists and antagonists. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 May;11(3):340–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Pert A., Chang J. K., Fong B. T. (D-Ala2)-Met-enkephalinamide: a potent, long-lasting synthetic pentapeptide analgesic. Science. 1976 Oct 15;194(4262):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.968485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Garbay-Jaureguiberry C., Oberlin R., Anteunis M., Lala A. K. Conformation of Met5-enkephalin determined by high field PMR spectroscopy. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):778–779. doi: 10.1038/262778a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller P. W., Lipton A., Horrobin D. F., Bodanszky M. Unsulfated C-terminal 7-peptide of cholecystokinin: a new ligand of the opiate receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 29;85(4):1332–1338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller P. W., St-Hilaire J. Synthesis, in vitro opiate activity, and intramolecular tyrosine--tryptophan distances of [4-tryptophan]enkephalin analogues. A reassessment of conformational models of enkephalin in solution. J Med Chem. 1980 Mar;23(3):290–294. doi: 10.1021/jm00177a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller P. W., Yam C. F., Lis M. Evidence for topographical analogy between methionine-enkephalin and morphine derivatives. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1831–1838. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller P. W., Yam C. F., Prosmanne J. Synthesis, opiate receptor affinity, and conformational parameters of [4-tryptophan]enkephalin analogues. J Med Chem. 1978 Nov;21(11):1110–1116. doi: 10.1021/jm00209a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioiri T., Ninomiya K., Yamada S. Diphenylphosphoryl azide. A new convenient reagent for a modified Curtus reaction and for the peptide synthesis. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Aug 23;94(17):6203–6205. doi: 10.1021/ja00772a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Childers S. R., Snyder S. H. The opiate receptor binding interactions of 3H-methionine enkephalin, an opioid peptide. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Feb 1;47(3):319–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Griffin J. F. Conformation of [Leu5]enkephalin from X-ray diffraction: features important for recognition at opiate receptor. Science. 1978 Mar 17;199(4334):1214–1216. doi: 10.1126/science.204006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam C. M. Stereochemical criteria for polypeptides and proteins. V. Conformation of a system of three linked peptide units. Biopolymers. 1968 Oct;6(10):1425–1436. doi: 10.1002/bip.1968.360061006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]