Abstract
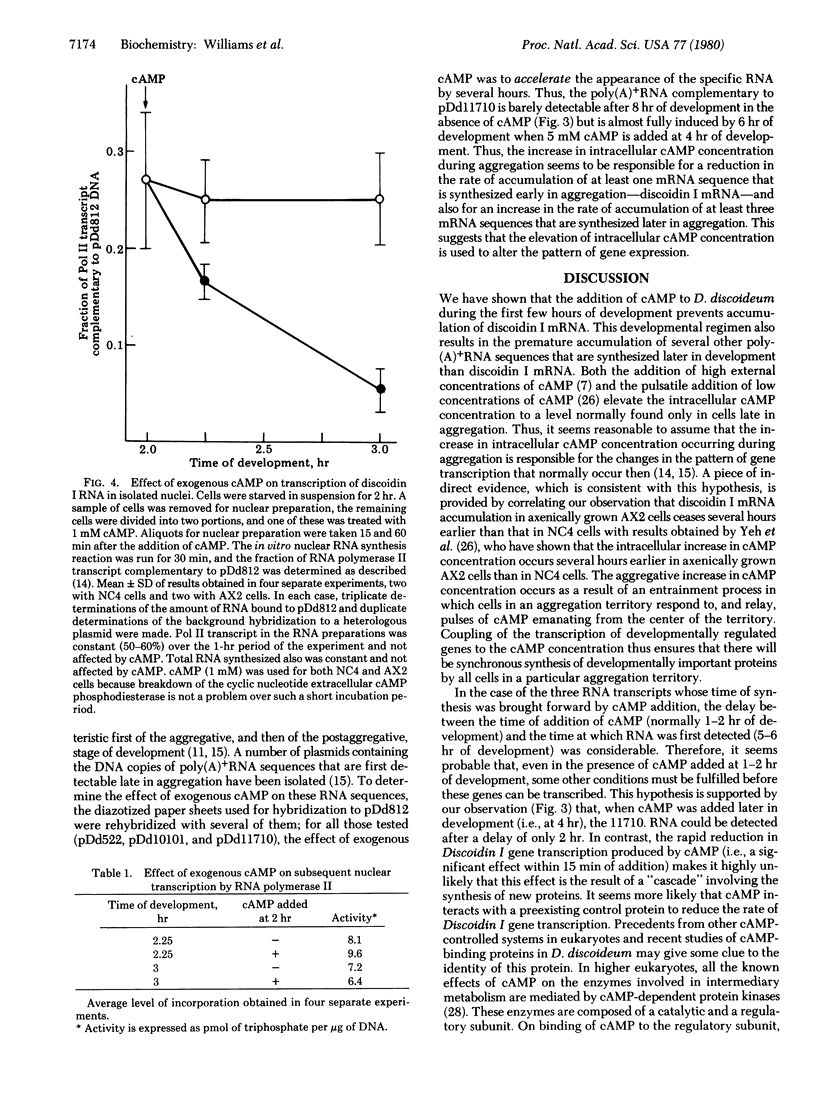
The plasmid pDd812 contains the DNA copy of an mRNA sequence from Dictyostelium discoideum that undergoes first an increase and then a decrease in concentration during the first few hours of differentiation. We have recently shown that the mRNA sequence complementary to pDd812 encodes discoidin I, a developmentally regulated lectin that may play a role in cellular cohesion. By using pDd812 as a hybridization probe, we found that addition of cyclic AMP during the first few hours of development inhibited the accumulation of discoidin I mRNA. By measuring the rate of transcription in isolated nuclei, we showed that, at least in part, this inhibition results from a rapid and specific reduction in the rate of transcription of the discoidin I gene. Addition of cyclic AMP during the first few hours of development inhibited the accumulation of discoidin I mRNA. By measuring the rate of transcription in isolated nuclei, we showed that, at least in part, this inhibition results from a rapid and specific reduction in the rate of transcription of the discoidin I gene. Addition of cyclic AMP during the first few hours of development inhibited the accumulation of discoidin I mRNA. By measuring the rate of transcription in isolated nuclei, we showed that, at least in part, this inhibition results from a rapid and specific reduction in the rate of transcription of the discoidin I gene. Addition of high external concentrations of cAMP is known to increase the intracellular concentration to a level normally found later in development. This natural increase in cAMP concentration occurs at the time during development when transcription of the discoidin I gene ceases. We suggest, therefore, that changes in the intracellular concentration of cAMP act at the level of transcription to control gene expression during development. This hypothesis is supported by our observation that several poly(A)+RNA sequences that normally accumulate after transcription of the discoidin I gene has ceased are synthesized prematurely in cells exposed to exogenous cAMP.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Rosbash M. Polynucleotide sequences in eukaryotic DNA and RNA that form ribonuclease-resistant complexes with polyuridylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 5;85(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. T., Barkley D. S., Hall E. M., Konijn T. M., Mason J. W., O'Keefe G., 3rd, Wolfe P. B. Acrasin, Acrasinase, and the sensitivity to acrasin in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1969 Jul;20(1):72–87. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(69)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. T. Induction of stalk cell differentiation by cyclic AMP in the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):110–113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. M., Reitherman R. W., Rosen S. D., Barondes S. H. Cell surface location of discoidin, a developmentally regulated carbohydrate-binding protein from Dictyostelium discoideum. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Oct 1;95(1):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90618-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darmon M., Brachet P., Da Silva L. H. Chemotactic signals induce cell differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3163–3166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Fromm H., Huesgen A., Wick U. Control of cell-contact sites by cyclic AMP pulses in differentiating Dictyostelium cells. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):547–549. doi: 10.1038/255547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A., Firtel R. A., Lodish H. F. Synthesis of messenger and ribosomal RNA precursors in isolated nuclei of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 15;82(2):213–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R. R., Garrod D., Tilly R. Requirement for cell differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature. 1978 Jan 5;271(5640):58–60. doi: 10.1038/271058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C. Induction of phosphodiesterase by cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in differentiating Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7134–7138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn T. M., Van De Meene J. G., Bonner J. T., Barkley D. S. The acrasin activity of adenosine-3',5'-cyclic phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1152–1154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G. Protein kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1972;5:99–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landfear S. M., Lodish H. F. A role for cyclic AMP in expression of developmentally regulated genes in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1044–1048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma G. C., Firtel R. A. Regulation of the synthesis of two carbohydrate-binding proteins in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3924–3932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolskee J. P., Lodish H. F. Half-lives of messenger RNA species during growth and differentiation of Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1980 Jan;74(1):37–49. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmsdorf H. J., Gerisch G. Specific binding proteins for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Differ. 1978 Oct;7(5):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(78)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray J., Shinnick T., Lerner R. A mutation altering the function of a carbohydrate binding protein blocks cell-cell cohesion in developing Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature. 1979 May 17;279(5710):215–221. doi: 10.1038/279215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen S. D., Kafka J. A., Simpson D. L., Barondes S. H. Developmentally regulated, carbohydrate-binding protein in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2554–2557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. Developmentally regulated cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases in Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90328-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J., Town C., Gross J. Cyclic AMP and the control of aggregative phase gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1978 Nov;67(1):54–64. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu C. H., Lerner R. A., Ma G., Firtel R. A., Loomis W. F. Developmentally regulated proteins of the plasma membrane of Dictyostelium discoideum. The carbohydrate-binding protein. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 15;100(2):157–178. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Williams J. G. Quantitative analysis of specific labelled RNA'S using DNA covalently linked to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):195–203. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Coffino P. Two-dimensional gel analysis of cyclic AMP effects in cultured S49 mouse lymphoma cells: protein modifications, inductions and repressions. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):719–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Town C., Gross J. The role of cyclic nucleotides and cell agglomeration in postaggregative enzyme synthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1978 Apr;63(2):412–420. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang A. S., Coukell M. B. Direct evidence for extracellular adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase induction and phosphodiesterase inhibitor repression by exogenous adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in Dictyostelium purpureum. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr 2;95(2):419–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace L. J., Frazier W. A. Photoaffinity labeling of cyclic-AMP- and AMP-binding proteins differentiating Dictyostelium discoideum cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4250–4254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Lloyd M. M. Changes in the abundance of polyadenylated RNA during slime mould development measured using cloned molecular hybridization probes. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):19–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Lloyd M. M., Devine J. M. Characterization and transcription analysis of a cloned sequence derived from a major developmentally regulated mRNA of D. discoideum. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh R. P., Chan F. K., Coukell M. B. Independent regulation of the extracellular cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase-inhibitor system and membrane differentiation by exogenous cyclic AMP in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1978 Oct;66(2):361–374. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]