Abstract
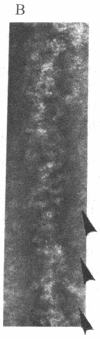
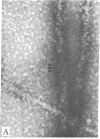
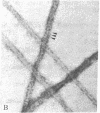
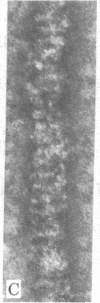
Adenylate deaminase (AMP deaminase; AMP aminohydrolase, EC 3.5.4.6), a tetrameric enzyme found at particularly high concentrations in skeletal muscle, has previously been shown to bind strongly to the subfragment-2-portion of myosin in vitro and to the ends of the A band in vivo. It is shown here that when adenylate deaminase is dialyzed with skeletal myosin during formation of synthetic filaments at pH 7.0 it decorates the filament at 14.3-nm intervals, presumably in the region of exposed backbone between crossbridge levels. Optical diffraction of the aggregates reveals both enhancement of reflections arising from underlying myosin organization and other reflections arising from adenylate deaminase arrangement on the filament surface. Adenylate deaminase can thus be used as a specific label in the study of myosin presence and organization.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby B., Frieden C. Adenylate deaminase. Kinetic and binding studies on the rabbit muscle enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8728–8735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby B., Frieden C., Bischoff R. Immunofluorescent and histochemical localization of AMP deaminase in skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):361–373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby B., Frieden C. Interaction of AMP-aminohydrolase with myosin and its subfragments. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1869–1872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffee C. J., Solano C. Rat muscle 5'-adenylic acid aminohydrolase. Role of K+ and adenylate energy charge in expression of kinetic and regulatory properties. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1606–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretz J. F. Structural studies of synthetic filaments prepared from column-purified myosin. Biophys J. 1979 Sep;27(3):423–432. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85226-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos C., Offer G., Starr R., Bennett P. Interaction of C-protein with myosin, myosin rod and light meromyosin. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 5;97(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien E. J., Bennett P. M., Hanson J. Optical diffraction studies of myofibrillar structure. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 May 27;261(837):201–208. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1971.0051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offer G., Moos C., Starr R. A new protein of the thick filaments of vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Extractions, purification and characterization. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):653–676. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley K. L., Suelter C. H. Univalent cations as allosteric activators of muscle adenosine 5'-phosphate deaminase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1980–1981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomozawa Y., Wolfenden R. Binding of guanosine triphosphate and adenosine triphosphate by rabbit muscle adenosine monophosphate deaminase. Biochemistry. 1970 Aug 18;9(17):3400–3404. doi: 10.1021/bi00819a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. J., Lowenstein J. M. Adenylate deaminase from rat muscle. Regulation by purine nucleotides and orthophosphate in the presence of 150 mM KCl. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8994–8999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]