Abstract
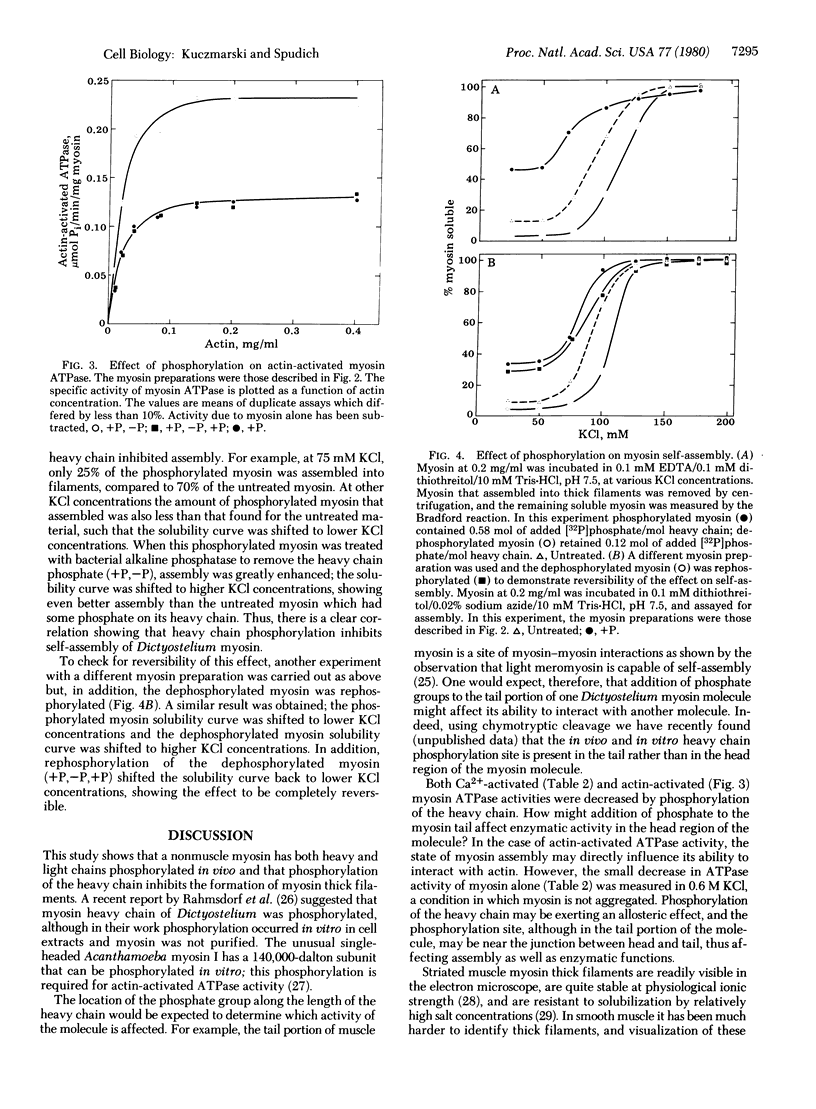
Dictyostelium myosin is composed of two heavy chains and two pairs of light chains in a 1:1:1 stoichiometry. Myosin purified from amoebae grown in medium containing [32P]phosphate had two of the subunits labeled (0.2-0.3 mol of phosphate per mol of 210,000-dalton heavy chains and approximately 0.1 mol of phosphate per mol of 18,000-dalton light chain). Kinase activities specific for the 210,000-dalton and for the 18,000-dalton subunits have been identified in extracts of Dictyostelium amoebae, and the heavy chain kinase has been purified 50-fold. This kinase phosphorylated Dictyostelium myosin to a maximum of 0.5-1.0 mol of phosphate per mol of heavy chain. Heavy chain phosphate, but not light chain phosphate, can be removed with bacterial alkaline phosphatase. Actin-activated myosin ATPase increased 80% when phosphorylated myosin was dephosphorylated to a level of approximately 0.06 mol of phosphate per mol of heavy chain. This effect could be reversed by rephosphorylating the myosin. The ability of myosin to self-assemble into thick filaments was inhibited by heavy chain phosphorylation. For example, in 80-100 mM KCl, only 10-20% of the myosin was assembled into thick filaments when the heavy chains were fully phosphorylated. Removal of the heavy chain phosphate resulted in 70-90% thick filament formation. This effect on self-assembly could be reversed by rephosphorylating the dephosphorylated myosin. These findings suggest that heavy chain phosphorylation may regulate cell contractile events by altering the state of myosin assembly.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Conti M. A. Phosphorylation of platelet myosin increases actin-activated myosin ATPase activity. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):597–598. doi: 10.1038/256597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess D. R., Schroeder T. E. Polarized bundles of actin filaments within microvilli of fertilized sea urchin eggs. J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):1032–1037. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson L., Nyström L. E., Sundkvist I., Markey F., Lindberg U. Actin polymerizability is influenced by profilin, a low molecular weight protein in non-muscle cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M., Spudich J. A. Biochemical and structural studies of actomyosin-like proteins from non-muscle cells. Isolation and characterization of myosin from amoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):209–222. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M., Spudich J. A. Nonmuscle contractile proteins: the role of actin and myosin in cell motility and shape determination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:797–822. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edds K. T. Isolation and characterization of two forms of a cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):109–115. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke J., Kessin R. A defined minimal medium for axenic strains of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara K., Pollard T. D. Fluorescent antibody localization of myosin in the cytoplasm, cleavage furrow, and mitotic spindle of human cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 Dec;71(3):848–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Carlson K., Rosenbaum J. L. Simple method for quantitive densitometry of polyacrylamide gels using fast green. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jun;35(2):359–370. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDIES ON THE STRUCTURE OF NATURAL AND SYNTHETIC PROTEIN FILAMENTS FROM STRIATED MUSCLE. J Mol Biol. 1963 Sep;7:281–308. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa T., Takahashi S., Hayashi H., Hatano S. Fragmin: a calcium ion sensitive regulatory factor on the formation of actin filaments. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2677–2683. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellewell S. B., Taylor D. L. The contractile basis of ameboid movement. VI. The solation-contraction coupling hypothesis. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):633–648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. The mechanism of muscular contraction. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1356–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. E., Rice R. V. Ultrastructural studies on the contractile mechanism of smooth muscle. J Cell Biol. 1969 Sep;42(3):683–694. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D. Biochemistry of actomyosin-dependent cell motility (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):588–599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta H., Korn E. D. Acanthamoeba cofactor protein is a heavy chain kinase required for actin activation of the Mg2+-ATPase activity of Acanthamoeba myosin I. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8329–8332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta H., Korn E. D. Purification from Acanthamoeba castellanii of proteins that induce gelation and syneresis of F-actin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):399–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mockrin S. C., Spudich J. A. Calcium control of actin-activated myosin adenosine triphosphatase from Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2321–2325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Smillie L. B., Perry S. B. A phosphorylated light-chain component of myosin from skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):151–164. doi: 10.1042/bj1350151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmsdorf H. J., Malchow D., Gerisch G. Cyclic AMP-induced phosphorylation in Dictyostelium of a polypeptide comigrating with myosin heavy chains. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 15;88(2):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholey J. M., Taylor K. A., Kendrick-Jones J. Regulation of non-muscle myosin assembly by calmodulin-dependent light chain kinase. Nature. 1980 Sep 18;287(5779):233–235. doi: 10.1038/287233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. E. The contractile ring. II. Determining its brief existence, volumetric changes, and vital role in cleaving Arbacia eggs. J Cell Biol. 1972 May;53(2):419–434. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobieszek A., Small J. V. Myosin-linked calcium regulation in vertebrate smooth muscle. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 25;102(1):75–92. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A. Biochemical and structural studies of actomyosin-like proteins from non-muscle cells. II. Purification, properties, and membrane association of actin from amoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):6013–6020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Onishi H., Takahashi K., Watanabe S. Structure and function of chicken gizzard myosin. J Biochem. 1978 Dec;84(6):1529–1542. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter J. A., Adelstein R. S. Macrophage myosin. Regulation of actin-activated ATPase, activity by phosphorylation of the 20,000-dalton light chain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8781–8785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyemura D. G., Brown S. S., Spudich J. A. Biochemical and structural characterization of actin from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9088–9096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Groeschel-Stewart U. Antibody to myosin: the specific visualization of myosin-containing filaments in nonmuscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4561–4564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yerna M. J., Dabrowska R., Hartshorne D. J., Goldman R. D. Calcium-sensitive regulation of actin-myosin interactions in baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):184–188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]