Abstract
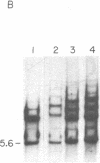
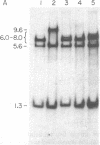
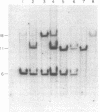
We have found that human and ape ribosomal genes undergo concerted evolution involving genetic exchanges among nucleolus organizers on nonhomologous chromosomes. This conclusion is based upon restriction enzyme analysis of the ribosomal gene families in man and five ape species. Certain structural features were found to differ among (but not within) species even though the ribosomal genes have a multichromosomal distribution. Genetic exchanges among nucleolus organizer regions may be related to the well-known phenomenon of acrocentric chromosome associations observed in man and apes. Length variation in a region of the nontranscribed spacer was found in both chimpanzee species we examined. The nature of this length variation was found to be identical to that previously described in man. The origin of the length variation and its polymorphism within these three species might be explained by unequal alignment and unequal cross-over among the ribosomal genes. An especially surprising finding was a nucleotide sequence polymorphism present in each individual human and ape we examined. Some ribosomal genes of each individual have a HindII site in the 28S gene about 800 base pairs from the EcoRI site in this gene. The remaining 28S genes lack this HindII site. The presence of this polymorphism within individuals of every species we examined suggests that it has been maintained by natural selection.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheim N. Characterization of mouse ribosomal gene fragments purified by molecular cloning. Gene. 1979 Oct;7(2):83–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheim N., Kuehn M. The genetic behaviour of a cloned mouse ribosomal DNA segment mimics mouse ribosomal gene evolution. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):743–763. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheim N., Southern E. M. Heterogeneity of the ribosomal genes in mice and men. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrand J. R., Myers P. A., Roberts R. J. A new restriction endonuclease from Streptomyces albus G. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 5;118(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90249-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Chipchase M., Speirs J. The ribosomal RNA cistrons. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1971;11:351–389. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60332-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. A., Gibson D. Neutral evolution and immunoglobulin diversity. Nature. 1974 Jul 26;250(464):327–328. doi: 10.1038/250327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan P., Reeder R. H., Dawid I. B. Restriction analysis of the nontranscribed spacers of Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Wensink P. C., Jordan E. A comparison of the ribosomal DNA's of Xenopus laevis and Xenopus mulleri: the evolution of tandem genes. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jan 14;63(1):57–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90521-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commerford S. L. Iodination of nucleic acids in vitro. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):1993–2000. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOSKOCIL J., SORM F. Distribution of 5-methylcytosine in pyrimidine sequences of deoxyribonucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jun 11;55:953–959. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90909-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Glover D. M. Differential replication of ribosomal gene repeats in polytene nuclei of Drosophila. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):597–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90267-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. S., Atwood K. C., Warburton D. Chromosomal distribution of rDNA in Pan paniscus, Gorilla gorilla beringei, and Symphalangus syndactylus: comparison to related primates. Chromosoma. 1976 Dec 16;59(2):147–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00328483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. S., Warburton D., Atwood K. C. Location of ribosomal DNA in the human chromosome complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3394–3398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. S., Warburton D., Megraw-Ripley S., Atwood K. C. The chromosomal location of rDNA in the Sumatran orangutan, Pongo pygmaeus albei. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1979;23(3):213–216. doi: 10.1159/000131328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A., Warburton D., Atwood K. C. Localization of rDNA in the chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) chromosome complement. Chromosoma. 1974;46(4):435–441. doi: 10.1007/BF00331631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Campbell J. H., Elgin S. C. The organization, expression, and evolution of antibody genes and other multigene families. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:305–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.001513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Mayer M., Morton N. E. Acrocentric chromosome associations in man. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 Nov;28(6):567–576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan Y. W., Dozy A. M. Polymorphism of DNA sequence adjacent to human beta-globin structural gene: relationship to sickle mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5631–5635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Smith H. O. A restriction enzyme from Hemophilus influenzae. II. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):393–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90150-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkman H. N. Rectification of tandemly repetitious DNA. II. Clustering and periodicity. J Theor Biol. 1979 Nov 21;81(2):275–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(79)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal M., Arnheim N. Length heterogeneity in a region of the human ribosomal gene spacer is not accompanied by extensive population polymorphism. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 25;126(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90281-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurnit D. M. Satellite DNA and heterochromatin variants: the case for unequal mitotic crossing over. Hum Genet. 1979 Mar 12;47(2):169–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00273199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Enhanced autoradiographic detection of 32P and 125I using intensifying screens and hypersensitized film. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Dawid I. B. Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:727–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. A., Tantravahi R., Dev V. G., Miller O. J. Frequency of satellite association of human chromosomes is correlated with amount of Ag-staining of the nucleolus organizer region. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Sep;29(5):490–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OHNO S., TRUJILLO J. M., KAPLAN W. D., KINOSITA R. Nucleolus-organisers in the causation of chromosomal anomalies in man. Lancet. 1961 Jul 15;2(7194):123–126. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92647-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perelson A. S., Bell G. I. Mathematical models for the evolution of multigene families by unequal crossing over. Nature. 1977 Jan 27;265(5592):304–310. doi: 10.1038/265304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Wyler T., Hagenbüchle O. Changes in size and secondary structure of the ribosomal transcription unit during vertebrate evolution. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmickel R. D. Quantitation of human ribosomal DNA: hybridization of human DNA with ribosomal RNA for quantitation and fractionation. Pediatr Res. 1973 Jan;7(1):5–12. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197301000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. H., Brown D. D. Retention of common nucleotide sequences in the ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid of eukaryotes and some of their physical characteristics. Biochemistry. 1971 Jul 6;10(14):2761–2769. doi: 10.1021/bi00790a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tantravahi R., Miller D. A., Dev V. G., Miller O. J. Detection of nucleolus organizer regions in chromosomes of human, chimpanzee, gorilla, orangutan and gibbon. Chromosoma. 1976 Jun 30;56(1):15–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00293725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartof K. D., Dawid I. G. Similarities and differences in the structure of X and Y chromosome rRNA genes of Drosophila. Nature. 1976 Sep 2;263(5572):27–30. doi: 10.1038/263027a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartof K. D. Evolution of transcribed and spacer sequences in the ribosomal RNA genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):607–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartof K. D. Redundant genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:355–385. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanyushin B. F., Tkacheva S. G., Belozersky A. N. Rare bases in animal DNA. Nature. 1970 Mar 7;225(5236):948–949. doi: 10.1038/225948a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER P. M., MCLAREN A. SPECIFIC DUPLEX FORMATION IN VITRO OF MAMMALIAN DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:394–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton D., Henderson A. S., Atwood K. C. Localization of rDNA and Giemsa-banded chromosome complement of white-handed gibbon, Hylobates lar. Chromosoma. 1975;51(1):35–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00285805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B., Brown D. D., Reeder R. H. The molecular basis for length heterogeneity in ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 25;105(4):461–486. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Isolation and sequence organization of human ribosomal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 5;128(3):289–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. II. Heteroduplex mapping of cloned and uncloned rDNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):769–782. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B., Tartof K. D. X and Y chromosomal ribosomal DNA of Drosophila: comparison of spacers and insertions. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. The structural organization of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):193–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. G., Blattner F. R. Construction and characterization of the hybrid bacteriophage lambda Charon vectors for DNA cloning. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):555–575. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.555-575.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. N., Hollar B. A., Waterson J. R., Schmickel R. D. Molecular analysis of cloned human 18S ribosomal DNA segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5367–5371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer E. A., Martin S. L., Beverley S. M., Kan Y. W., Wilson A. C. Rapid duplication and loss of genes coding for the alpha chains of hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2158–2162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]