Abstract
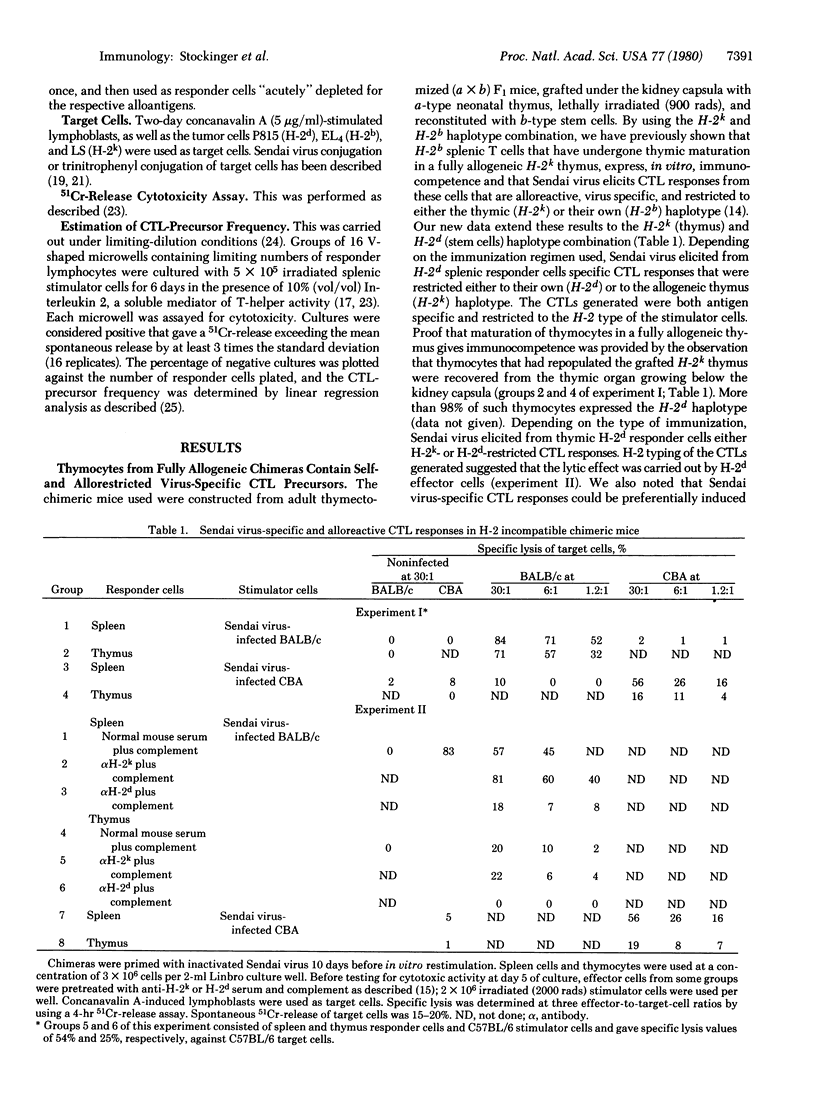
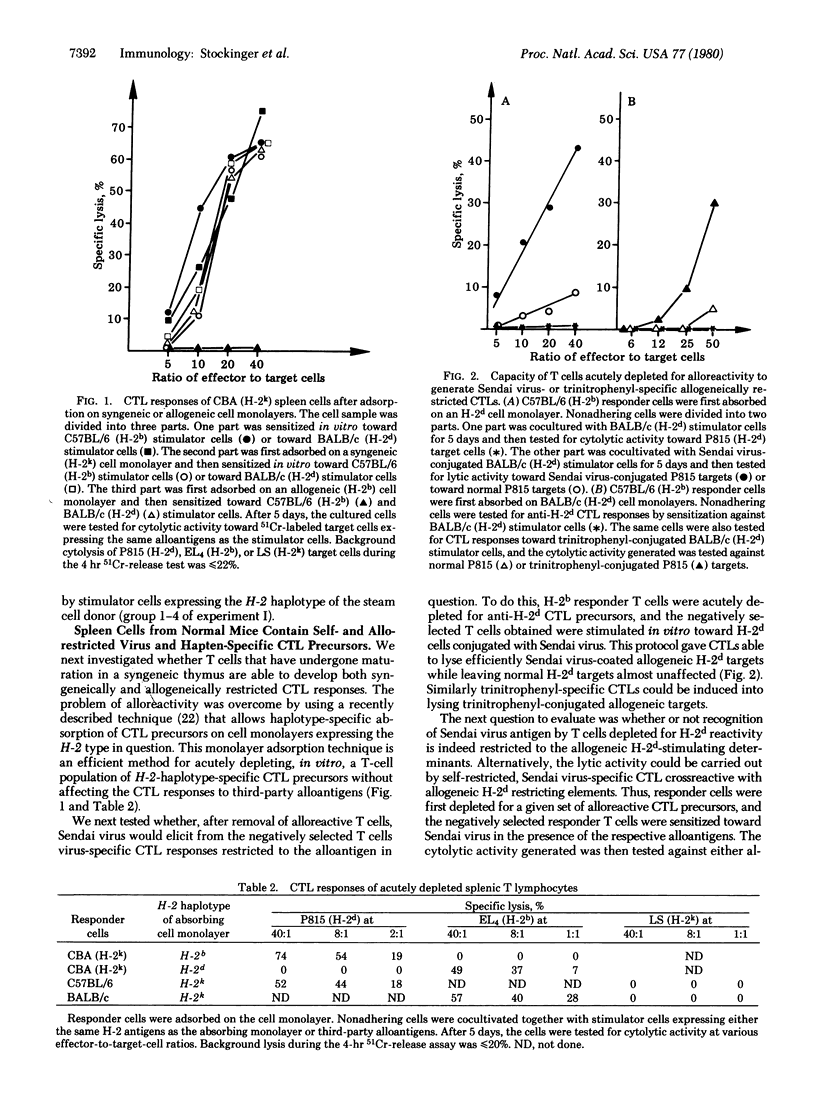
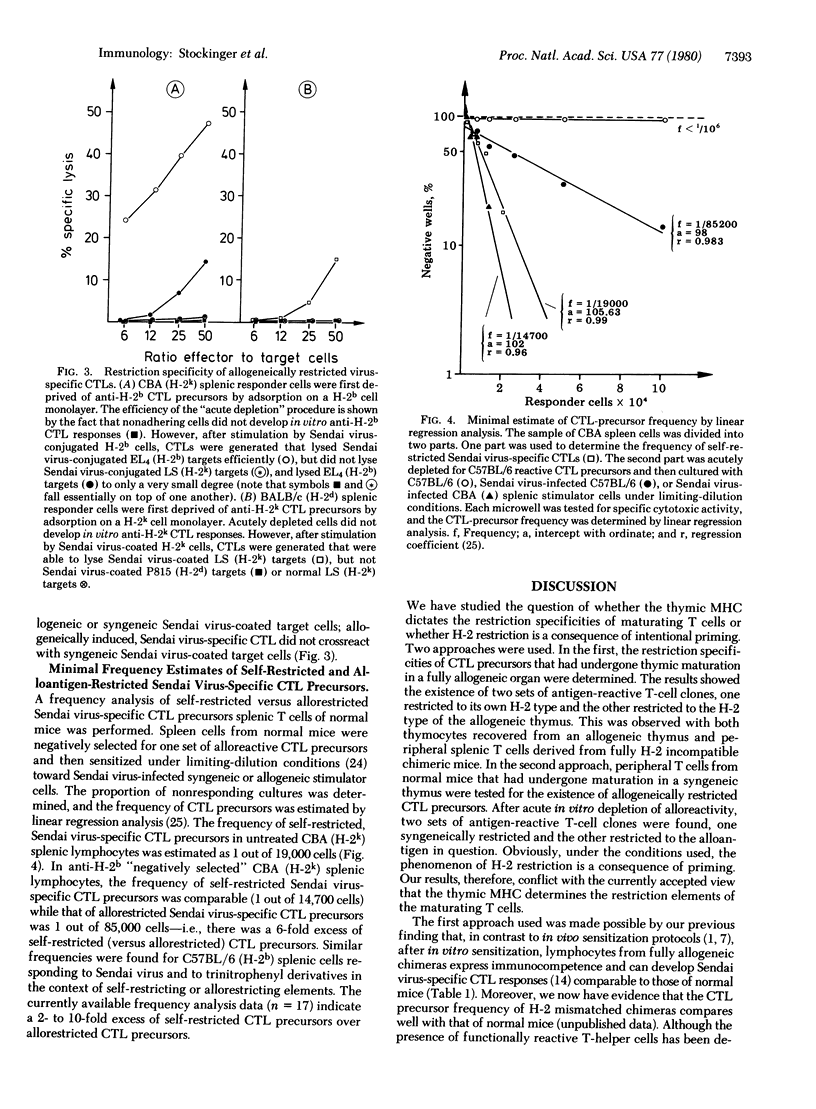
Fully allogeneic chimeras were able to develop in vitro alloantigen-specific, as well as H-2-restricted, Sendai virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) response. Depending on the immunization regimen used, Sendai virus-specific CTL responses were restricted to the H-2 antigens of either the stem cell donor or the thymus. Similarly, unprimed splenic T cells of normal mice were found to contain CTL-precursor cells that specifically reacted against Sendai virus or trinitrophenyl derivatives in the context of allogeneic major histocompatibility complex determinants that had not been encountered during their thymic differentiation. A frequency analysis of allogeneically versus syngeneically restricted virus-specific CTL precursors present in splenic T cells showed a ratio of about 1 to 6. These results provide evidence that H-2 restriction of trinitrophenyl- or Sendai virus-specific T cells is dictated by the complex type of the antigen-presenting cell and thus appears to be independent of the type of thymus in which the T cells have undergone maturation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevan M. J. Cross-priming for a secondary cytotoxic response to minor H antigens with H-2 congenic cells which do not cross-react in the cytotoxic assay. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1283–1288. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. J., Fink P. J. The influence of thymus H-2 antigens on the specificity of maturing killer and helper cells. Immunol Rev. 1978;42:3–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Andrew M. E. Primary anti-viral cytotoxic T-cell responses in semiallogeneic chimeras are not absolutely restricted to host H-2 type. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):535–538. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Bennink J. R. Patterns of virus-immune T-cell responsiveness. Comparison of (H-2k X H-2b) leads to H-2b radiation chimeras and negatively selected H-2b lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1187–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford W. L., Atkins R. C. Specific unresponsiveness of recirculating lymphocytes ater exposure to histocompatibility antigen in F 1 hybrid rats. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 8;234(49):178–180. doi: 10.1038/newbio234178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman J., Streilein J. W. T cells recognize minor histocompatibility antigens on H-2 allogeneic cells. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):1001–1007. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Union N. A., Baker P. E., Smith K. A. The in vitro generation and sustained culture of nude mouse cytolytic T-lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1460–1476. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T., Schimpl A. Studies on the generation and expression of H-2-controlled T helper function in chimeric mice: evidence for two levels of H-2 resitriction. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Sep;9(9):730–736. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Murphy P. D., Kemp J., Wigzell H. T cells specific for hapten-modified self are precommitted for self major histocompatibility complex antigens before encounter with the hapten. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1065–1077. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung H., Pfizenmaier K., Starzinski-Powitz A., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. Primary in vitro sensitization of virus specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1978 Apr;34(4):763–769. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Skidmore B. J., Katz L. R., Bogowitz C. A. Adaptive differentiation of murine lymphocytes. I. Both T and B lymphocytes differentiating in F1 transplanted to parental chimeras manifest preferential cooperative activity for partner lymphocytes derived from the same parental type corresponding to the chimeric host. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):727–745. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindred B. Lymphocytes which differentiate in an allogeneic thymus. III. Parental T cells which differentiate in an allogeneic or semiallogeneic thymus help only B cells of their own genotype. Cell Immunol. 1980 Apr;51(1):64–71. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzinger P., Mirkwood G. In a fully H-2 incompatible chimera, T cells of donor origin can respond to minor histocompatibility antigens in association with either donor or host H-2 type. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):84–92. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F. Influence of the major histocompatibility complex on T-cell activation. Adv Cancer Res. 1979;29:1–44. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60845-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. G., Teh H. S., Harley E., Phillips R. A. Quantitative studies of the activation of cytotoxic lymphocyte precursor cells. Immunol Rev. 1977;35:38–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Delzeit R., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. T-T cell interactions during in vitro cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses. III. Antigen-specific T helper cells release nonspecific mediator(s) able to help induction of H-2-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses across cell-impermeable membranes. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):577–582. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W., Kapp J. A., Benacerraf B. Regulation by the H-2 gene complex of macrophage-lymphoid cell interactions in secondary antibody responses in vitro. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):371–381. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer G. M. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity to trinitrophenyl-modified syngeneic lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Aug;4(8):527–533. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E., Gordon R. D. Responsiveness to HY antigen Ir gene complementation and target cell specificity. Immunol Rev. 1977;35:59–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J. Role of H-2 gene products in the function of T helper cells from normal and chimeric mice in vivo. Immunol Rev. 1978;42:108–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzinski-Powitz A., Pfizenmaier K., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. In vivo sensitization of T cells to hapten-conjugated syngeneic structures of major histocompatibility complex. I. Effect of in vitro culture upon generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Nov;6(11):799–805. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830061109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C., MacDonald H. R., Cerottini J. C. Limiting dilution analysis of alloantigen-reactive T lymphocytes. II. Effect of cortisone and cyclophosphamide on cytolytic T lymphocyte precursor frequencies in the thymus. Thymus. 1979 Sep;1(1-2):119–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. W., Shevach E. M. Nature of the antigenic complex recognized by T lymphocytes: specific sensitization by antigens associated with allogeneic macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2104–2108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Hardt C., Heeg K., Röllinghoff M., Pfizenmaier K. T-cell-derived helper factor allows in vivo induction of cytotoxic T cells in nu/nu mice. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):278–278. doi: 10.1038/284278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Räollinghoff M., Pfizenmaier K., Hardt C., Johnscher G. T-T cell interactions during in vitro cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses. II. Helper factor from activated Lyt 1+ T cells is rate limiting i) in T cell responses to nonimmunogenic alloantigen, ii) in thymocyte responses to allogeneic stimulator cells, and III) recruits allo- or H-2-restricted CTL precursors from the Lyt 123+ T subset. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1058–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Röllinghoff M., Rodt H., Thierfelder S. T cell-mediated cytotoxic immune responsiveness of chimeric mice bearing a thymus graft fully allogeneic to the graft of lymphoid stem cells. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Jul;10(7):521–525. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Lindahl K. F., Wilson D. H., Sprent J. The generation of killer cells to trinitrophenyl-modified allogeneic targets by lymphocyte populations negatively selected to strong alloantigens. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):361–367. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Althage A., Cooper S., Callahan G., Klein J. In irradiation chimeras, K or D regions of the chimeric host, not of the donor lymphocytes, determine immune responsiveness of antiviral cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):805–810. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Althage A., Waterfield E., Kindred B., Welsh R. M., Callahan G., Pincetl P. Restriction specificities, alloreactivity, and allotolerance expressed by T cells from nude mice reconstituted with H-2-compatible or -incompatible thymus grafts. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):376–399. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


