Abstract
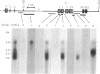
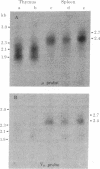
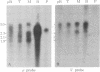
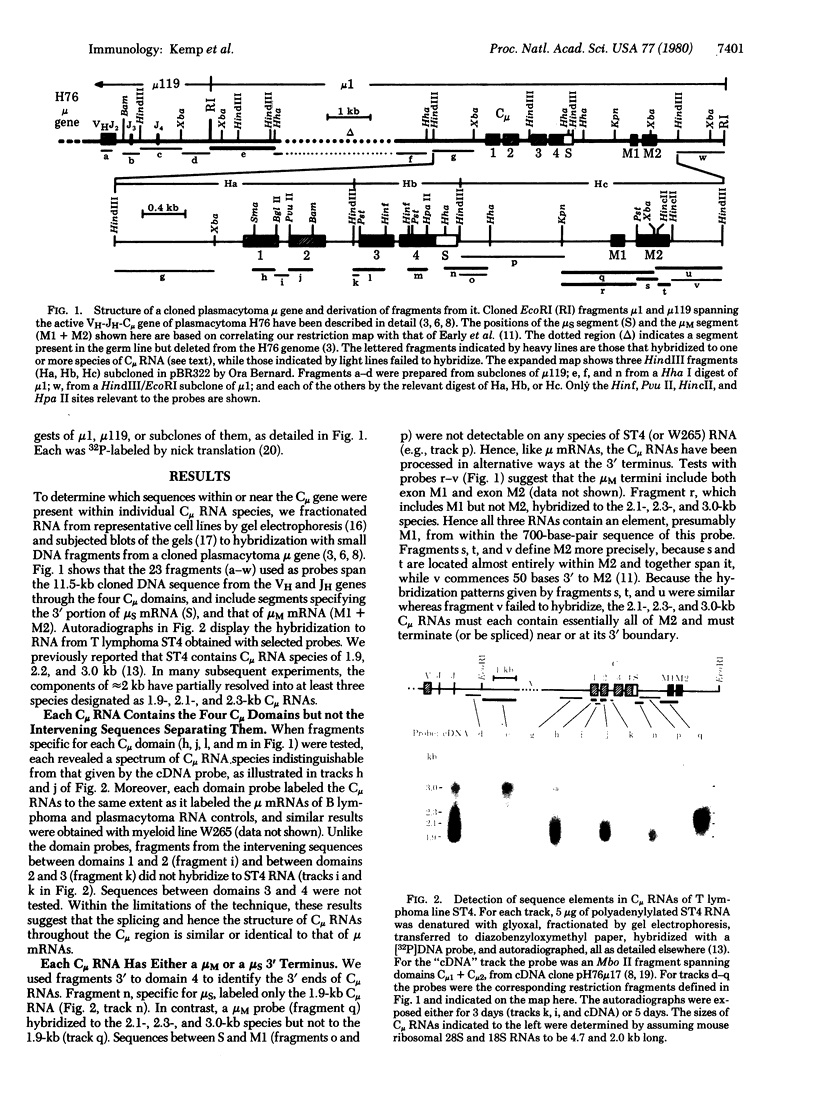
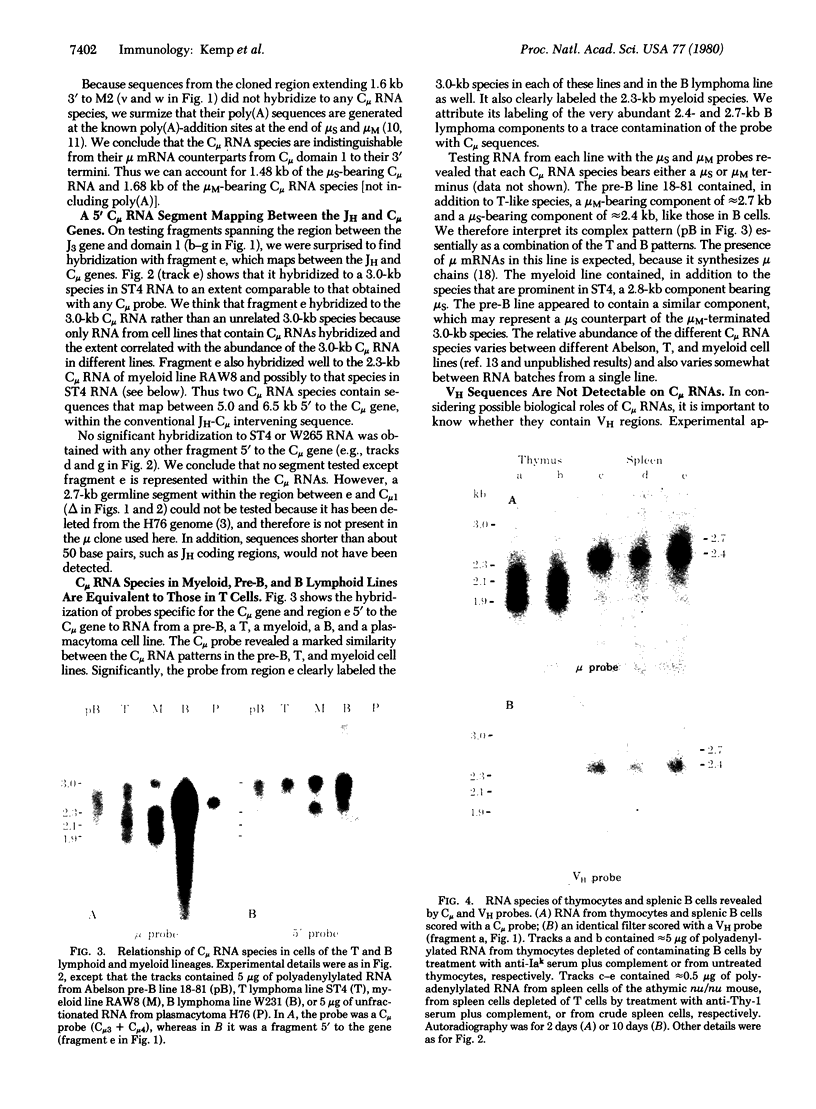
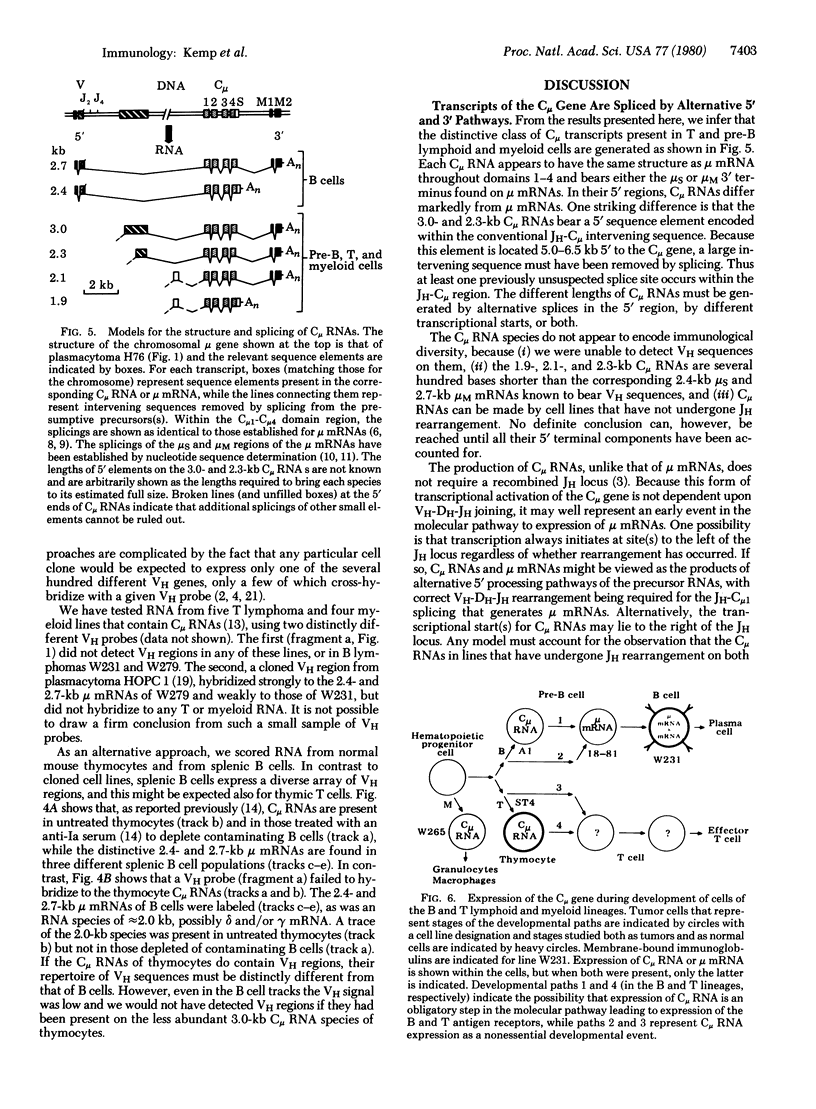
Two classes of transcripts of the mouse immunoglobulin mu constant region (C mu) gene can be distinguished. Whereas B cells contain mu mRNAs of 2.4 and 2.7 kilobases (kb), many T lymphoma, Abelson pre-B lymphoma, and myeloid tumor cell lines contain polyadenylylated RNA species bearing C mu sequences (C mu RNAs) of 1.9, 2.1, 2.3, and 3.0 kb. Production of C mu RNAs, unlike mu mRNAs, does not require recombination with the joining region (JH) locus. To define the structure of C mu RNAs, RNA from representative cell lines was fractionated by gel electrophoresis, transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper, and tested for hybridization with 23 DNA fragments that collectively span a chromosomal mu gene, cloned from a plasmacytoma. All the C mu RNAs bear sequences derived from each of the four C mu domains, but none contain the intervening sequences separating domains; thus each represents a spliced RNA species. The 1.9-kb C mu RNA contains the 3' sequence characteristic of secreted mu chain, whereas the longer species bear that of membrane-bound mu chin. Hence C mu RNAs and mu mRNAs are equivalent throughout the C mu and 3' terminal regions. They differ markedly, however, in their 5' regions, because the 3.0-and 2.3-kb C mu RNAs bear sequences from within the conventional JH-C mu intervening sequence. Because these sequences are several kb from C mu, this region must contain at least one hitherto unsuspected splice site. C mu RNAs may not express immunological diversity, because no evidence was found that they bear variable regions. T and pre-B lymphoid and myeloid cells contain equivalent C mu RNA species, which coexist with mu mRNAs in some pre-B and B lymphoid lines. C mu RNA expression appears to reflect an activated state of the C mu gene common to cells at early stages of T, B, and myeloid development.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Gough N. M., Webb E. A., Tyler B. M., Jackson J., Cory S. Molecular cloning of mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain messenger ribonucleic acids coding for mu, alpha, gamma 1, gamma 2a, and gamma 3 chains. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2711–2719. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Gough N. M. Nucleotide sequence of immunoglobulin heavy chain joining segments between translocated VH and mu constant regions genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3630–3634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calame K., Rogers J., Early P., Davis M., Livant D., Wall R., Hood L. Mouse Cmu heavy chain immunoglobulin gene segment contains three intervening sequences separating domains. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):452–455. doi: 10.1038/284452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Weissman I. Development and function of subpopulations of thymocytes and T lymphocytes. Prog Allergy. 1976;20:1–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Adams J. M. Deletions are associated with somatic rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90386-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Adams J. M., Kemp D. J. Somatic rearrangements forming active immunoglobulin mu genes in B and T lymphoid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4943–4947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Huang H., Davis M., Calame K., Hood L. An immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene is generated from three segments of DNA: VH, D and JH. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):981–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Kemp D. J., Tyler B. M., Adams J. M., Cory S. Intervening sequences divide the gene for the constant region of mouse immunoglobulin mu chains into segments, each encoding a domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):554–558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Cory S., Adams J. M. Cloned pairs of variable region genes for immunoglobulin heavy chains isolated from a clone library of the entire mouse genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4627–4631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Harris A. W., Cory S., Adams J. M. Expression of the immunoglobulin C mu gene in mouse T and B lymphoid and myeloid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2876–2880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Wilson A., Harris A. W., Shortman K. The immunoglobulin mu constant region gene is expressed in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):168–170. doi: 10.1038/286168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Schibler U., Perry R. P. Nuclear transcripts of mouse heavy chain immunoglobulin genes contain only the expressed class of C-region sequences. Science. 1979 Jun 8;204(4397):1087–1088. doi: 10.1126/science.109919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E., Coleclough C., Seidman J. G., Leder P., Tonegawa S., Matthyssens G., Weigert M. Transcription of mouse kappa chain genes: implications for allelic exclusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1937–1941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E. Immunoglobulin messenger RNAs in murine cell lines that have characteristics of immature B lymphocytes. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1333–1339. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Matthyssens G., Hamlyn P. H. Contribution of immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable-region genes to antibody diversity. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):238–243. doi: 10.1038/284238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Early P., Carter C., Calame K., Bond M., Hood L., Wall R. Two mRNAs with different 3' ends encode membrane-bound and secreted forms of immunoglobulin mu chain. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90616-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siden E. J., Baltimore D., Clark D., Rosenberg N. E. Immunoglobulin synthesis by lymphoid cells transformed in vitro by Abelson murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]