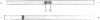Abstract
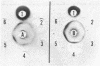
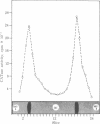
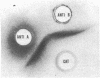
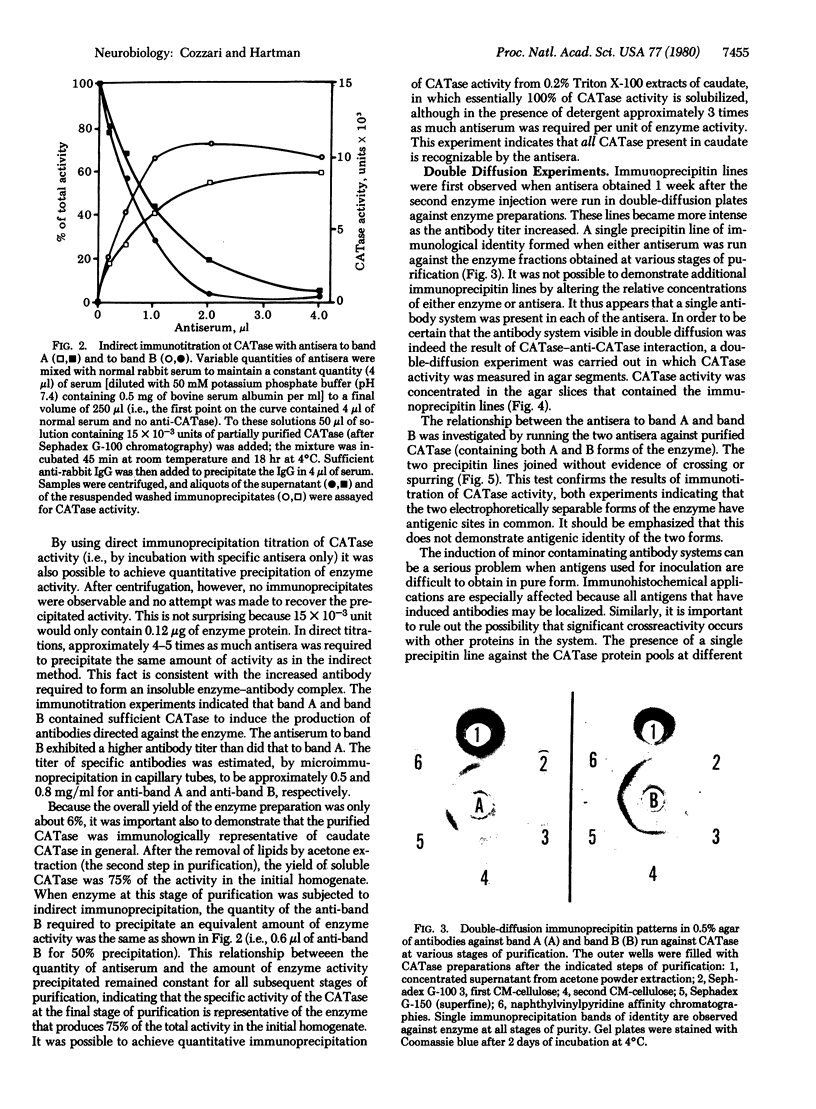
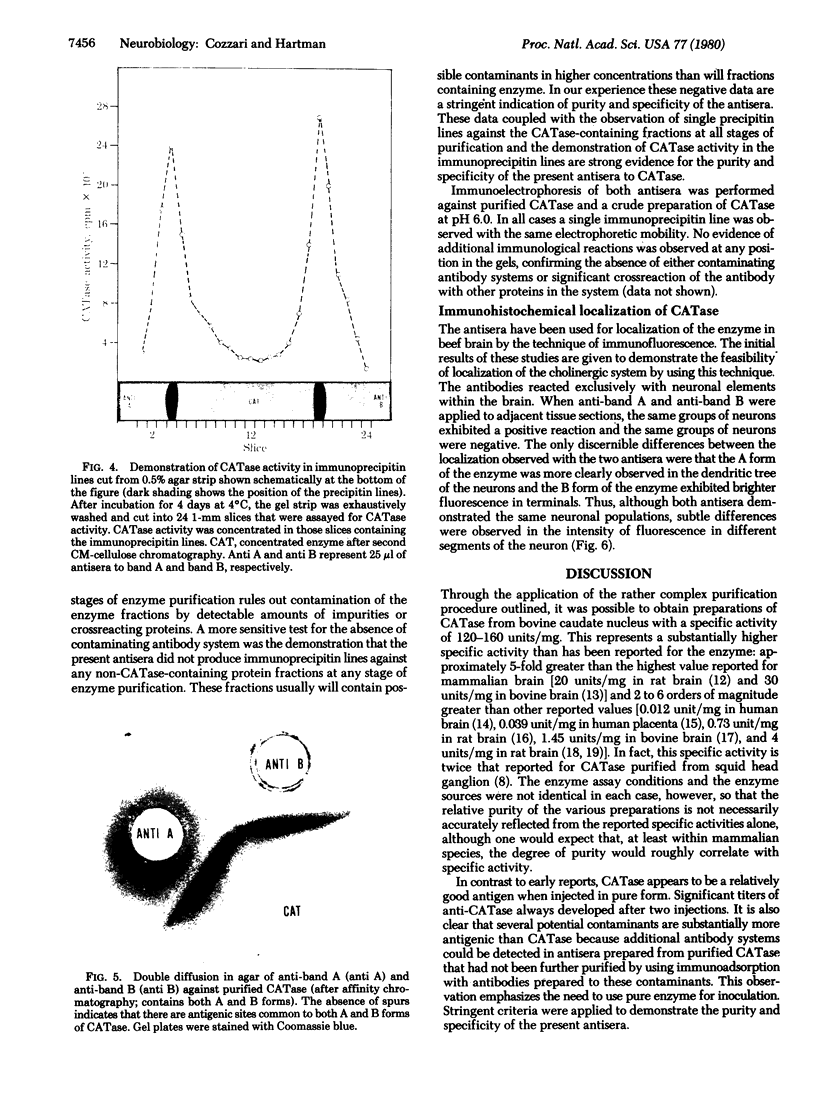
Choline acetyltransferase (CATase; acetyl-CoA:choline O-acetyltransferase, EC 2.3.1.6) has been purified from bovine caudate nucleus. The specific activity of the pure enzyme was 120-160 mumol of acetylcholine formed per mg per min. The purified enzyme separated into two bands (band A and band B) when electrophoresed in a pH 4.3 gradient gel. Both bands exhibited CATase activity. Antisera were prepared in rabbits to each form. Immunotitrations using either antisera resulted in quantitative precipitation of CATase activity from enzyme preparations at all stages of purification. Both antisera produced single immunoprecipitin lines in double-diffusion experiments when run against the enzyme at each stage of purity. Immunoprecipitin lines cut from double-diffusion gels contained CATase activity, demonstrating that the observed reaction was due to antibody interaction with the enzyme. Immunoelectrophoresis also showed a single immunoprecipitin line against the purified enzyme as well as against a crude caudate extract. These results indicated that immunochemically pure and specific antisera have been prepared to bovine CATase and that both the A and B forms of the enzyme have common antigenic sites. The antisera were utilized to localize the enzyme in bovine brain. The localization was exclusively neuronal with both antisera, and both forms of CATase were present in the same population of neurons. Subtle differences in the precise intracellular distribution of enzyme were observed with the two antisera, indicating that although the two molecular forms of CATase have antigenic sites in common they are not antigenically identical.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chao L. P., Wolfgram F. Purification and some properties of choline acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.6) from bovine brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Apr;20(4):1075–1081. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng L. F., Uyeda C. T., Chao L. P., Wolfgram F. Antibody to bovine choline acetyltransferase and immunofluorescent localisation of the enzyme in neurones. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):243–245. doi: 10.1038/250243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger P. J., Bessman S. P. Protein determination by Lowry's method in the presence of sulfhydryl reagents. Anal Biochem. 1972 Oct;49(2):467–473. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90450-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. K. Immunofluorescence of dopamine- -hydroxylase. Application of improved methodology to the localization of the peripheral and central noradrenergic nervous system. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Apr;21(4):312–332. doi: 10.1177/21.4.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. K., Udenfriend S. A method for immediate visualization of proteins in acrylamide gels and its use for preparation of antibodies to enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1969 Sep;30(3):391–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain S. S., Mautner H. G. The purification of choline acetyltransferase of squid-head ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3749–3753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P. Separation of proteins by ammonium sulfate gradient solubilization. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 1;11(3):367–371. doi: 10.1021/bi00753a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malthe-Sorenssen D., Eskeland T., Fonnum F. Purification of rat brain choline acetyltransferase; some immunochemical properties of a highly purified preparation. Brain Res. 1973 Nov 23;62(2):517–522. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90716-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malthe-Sørenssen D., Lea T., Fonnum F., Eskeland T. Molecular characterization of choline acetyltransferase from bovine brain caudate nucleus and some immunological properties of the highly purified enzyme. J Neurochem. 1978 Jan;30(1):35–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter L. T., Glover V. A., Saelens J. K. Choline acetyltransferase from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 25;243(14):3864–3870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskoski R., Jr, Lim C. T., Roskoski L. M. Human brain and placental choline acetyltransferase: purification and properties. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5105–5110. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J. Immunohistochemical localization of choline acetyltransferase: real or artefact? Brain Res. 1975 Nov 21;98(3):619–622. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90381-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J. Purification of rat brain choline acetyltransferase. J Neurochem. 1976 Mar;26(3):543–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb01509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier B. K., Shuster L. A simplified radiochemical assay for choline acetyltransferase. J Neurochem. 1967 Oct;14(10):977–985. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh V. K., McGeer P. L. Antibody production to choline acetyltransferase purified from human brain. Life Sci. 1974 Sep 1;15(5):901–913. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenthold R. J., Mahler H. R. Purification of rat brain choline acetyltransferase and an estimation of its half-life. J Neurochem. 1975 May;24(5):963–967. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb03663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]