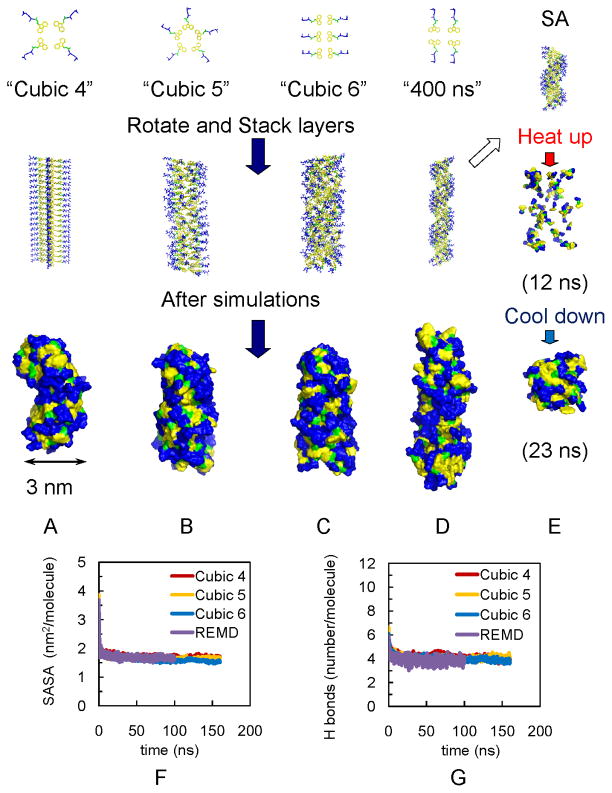
Figure 2.
Models of fibrils in simulations show independence of final assembly of initial structures. (A) Fibril with 4 Fmoc-AA soaked in cubic box (“Cubic 4”). (B) Fibril with 5 Fmoc-AA soaked in cubic box (“Cubic 5”). (C) Fibril with 6 Fmoc-AA soaked in cubic box (“Cubic 6”). (D) Fibril with 4 Fmoc-AA soaked in long rectangular box with 400 ns simulation (“400 ns”). For A–C, all simulations were 160 ns. (E) Simulated annealing of 15 layers from model in (D); also used as initial structures for REMD simulations. Note: yellow indicates fluorenyl group of Fmoc, green is the carbamate linker, and blue is the peptide chain. For A–D, Top: the arrangement of Fmoc-AA molecules (hydrogens are not shown) on each layer. Middle: initial structures for simulations. Bottom: snapshots of the solvent accessible surfaces from the last frames of simulations show self-assembled fibril structures. The convergence of SASA and hydrogen bonding calculations over time indicates structural stability: (F) SASA per molecule for Cubic 4, Cubic 5, Cubic 6 and REMD ensemble at 299 K (“REMD”); all converge to ~1.7 nm2/molecule, and (G) Number of hydrogen bonds per molecule for Cubic 4 to 6 and REMD simulations (~ 4).